
Info


Henry Charles Bukowski (born Heinrich Karl Bukowski; August 16, 1920 – March 9, 1994) was an American poet, novelist and short story writer. His writing was influenced by the social, cultural and economic ambience of his home city of Los Angeles. It is marked by an emphasis on the ordinary lives of poor Americans, the act of writing, alcohol, relationships with women and the drudgery of work.

Emily Elizabeth Dickinson (December 10, 1830 – May 15, 1886) was an American poet. Little-known during her life, she has since been regarded as one of the most important figures in American poetry. Evidence suggests that Dickinson lived much of her life in isolation. Considered an eccentric by locals, she developed a penchant for white clothing and was known for her reluctance to greet guests or, later in life, to even leave her bedroom. Dickinson never married, and most friendships between her and others depended entirely upon correspondence.


Ella Wheeler Wilcox (November 5, 1850 – October 30, 1919) was an American author and poet. Her best-known work was Poems of Passion. Her most enduring work was “Solitude”, which contains the lines, “Laugh, and the world laughs with you; weep, and you weep alone”. Her autobiography, The Worlds and I, was published in 1918, a year before her death. Ella was born on a farm in Johnstown, Wisconsin, east of Janesville, the youngest of four children. The family soon moved north of Madison. She started writing poetry at a very early age, and was well known as a poet in her own state by the time she graduated from high school. Her most famous poem, “Solitude”, was first published in the February 25, 1883 issue of The New York Sun. The inspiration for the poem came as she was travelling to attend the Governor’s inaugural ball in Madison, Wisconsin. On her way to the celebration, there was a young woman dressed in black sitting across the aisle from her. The woman was crying. Miss Wheeler sat next to her and sought to comfort her for the rest of the journey. When they arrived, the poet was so depressed that she could barely attend the scheduled festivities. As she looked at her own radiant face in the mirror, she suddenly recalled the sorrowful widow. It was at that moment that she wrote the opening lines of “Solitude”: Laugh, and the world laughs with you; Weep, and you weep alone. For the sad old earth must borrow its mirth But has trouble enough of its own
#Americans #Women #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Madison Julius Cawein (March 23, 1865 – December 8, 1914) was a poet from Louisville, Kentucky. He was the fifth child of William and Christiana (Stelsly) Cawein. His father made patent medicines from herbs thus, as a child, Cawein became acquainted with and developed a love for local nature.
#Americans #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Walter Whitman (May 31, 1819 – March 26, 1892) was an American poet, essayist and journalist. A humanist, he was a part of the transition between transcendentalism and realism, incorporating both views in his works. Whitman is among the most influential poets in the American canon, often called the father of free verse. His work was controversial in his time, particularly his 1855 poetry collection Leaves of Grass, which was described as obscene for its overt sensuality.

Robert Lee Frost (March 26, 1874 – January 29, 1963) was an American poet. His work was initially published in England before it was published in the United States. Known for his realistic depictions of rural life and his command of American colloquial speech, Frost frequently wrote about settings from rural life in New England in the early 20th century, using them to examine complex social and philosophical themes. Frequently honored during his lifetime, Frost is the only poet to receive four Pulitzer Prizes for Poetry. He became one of America’s rare “public literary figures, almost an artistic institution”. He was awarded the Congressional Gold Medal in 1960 for his poetic works. On July 22, 1961, Frost was named poet laureate of Vermont.
#Americans #PulitzerPrize #XIXCentury #XXCentury
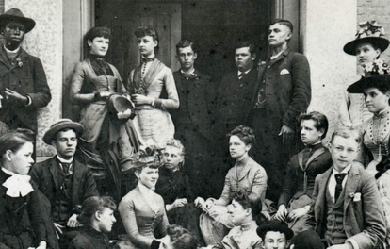

Paul Laurence Dunbar was the first African-American poet to garner national critical acclaim. Born in Dayton, Ohio, in 1872, Dunbar penned a large body of dialect poems, standard English poems, essays, novels and short stories before he died at the age of 33. His work often addressed the difficulties encountered by members of his race and the efforts of African-Americans to achieve equality in America. He was praised both by the prominent literary critics of his time and his literary contemporaries. Dunbar was born on June 27, 1872, to Matilda and Joshua Dunbar, both natives of Kentucky. His mother was a former slave and his father had escaped from slavery and served in the 55th Massachusetts Infantry Regiment and the 5th Massachusetts Colored Cavalry Regiment during the Civil War. Matilda and Joshua had two children before separating in 1874. Matilda also had two children from a previous marriage.
#Americans #Blacks #XIXCentury


Carl Sandburg was born in Galesburg, Illinois, on January 6, 1878. His parents, August and Clara Johnson, had emigrated to America from the north of Sweden. After encountering several August Johnsons in his job for the railroad, the Sandburg's father renamed the family. The Sandburgs were very poor; Carl left school at the age of thirteen to work odd jobs, from laying bricks to dishwashing, to help support his family. At seventeen, he traveled west to Kansas as a hobo. He then served eight months in Puerto Rico during the Spanish-American war. While serving, Sandburg met a student at Lombard College, the small school located in Sandburg's hometown. The young man convinced Sandburg to enroll in Lombard after his return from the war.
#Americans #PulitzerPrice #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (February 27, 1807 – March 24, 1882) was an American poet and educator whose works include "Paul Revere's Ride", The Song of Hiawatha, and Evangeline. He was also the first American to translate Dante Alighieri's The Divine Comedy and was one of the five Fireside Poets. Longfellow was born in Portland, Maine, then part of Massachusetts, and studied at Bowdoin College. After spending time in Europe he became a professor at Bowdoin and, later, at Harvard College. His first major poetry collections were Voices of the Night (1839) and Ballads and Other Poems (1841). Longfellow retired from teaching in 1854 to focus on his writing, living the remainder of his life in Cambridge, Massachusetts, in a former headquarters of George Washington. His first wife, Mary Potter, died in 1835 after a miscarriage. His second wife, Frances Appleton, died in 1861 after sustaining burns from her dress catching fire. After her death, Longfellow had difficulty writing poetry for a time and focused on his translation. He died in 1882.


Ezra Weston Loomis Pound (30 October 1885 – 1 November 1972) was an American expatriate poet, critic and a major figure of the early modernist movement. His contribution to poetry began with his promotion of Imagism, a movement that derived its technique from classical Chinese and Japanese poetry, stressing clarity, precision and economy of language. His best-known works include Ripostes (1912), Hugh Selwyn Mauberley (1920), and his unfinished 120-section epic, The Cantos (1917–1969). Working in London in the early 20th century as foreign editor of several American literary magazines, Pound helped to discover and shape the work of contemporaries such as T. S. Eliot, James Joyce, Robert Frost, and Ernest Hemingway. He was responsible for the publication in 1915 of Eliot's “The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock,” and for the serialization from 1918 of Joyce's Ulysses. Hemingway wrote of him in 1925: “He defends [his friends] when they are attacked, he gets them into magazines and out of jail. ... He writes articles about them. He introduces them to wealthy women. He gets publishers to take their books. He sits up all night with them when they claim to be dying... he advances them hospital expenses and dissuades them from suicide.”


John Greenleaf Whittier (December 17, 1807 – September 7, 1892) was an American Quaker poet and advocate of the abolition of slavery in the United States. Frequently listed as one of the Fireside Poets, he was influenced by the Scottish poet Robert Burns. Whittier is remembered particularly for his anti-slavery writings as well as his book Snow-Bound.


William Sydney Porter (Greensboro, North Carolina, September 11, 1862 – June 5, 1910), known by his pen name O. Henry, was an American short story writer. His stories are known for their surprise endings. Porter traveled with Dr. James K. Hall to Texas in March 1882, hoping that a change of air would help alleviate a persistent cough he had developed. He took up residence on the sheep ranch of Richard Hall, James’ son, in La Salle County and helped out as a shepherd, ranch hand, cook, and baby-sitter. While on the ranch, he learned bits of Spanish and German from the mix of immigrant ranch hands. He also spent time reading classic literature.


Sheldon Allan Shel Silverstein (September 25, 1930 – May 10, 1999), was an American poet, singer-songwriter, cartoonist, screenwriter, and author of children's books. He styled himself as Uncle Shelby in some works. Translated into more than 30 languages, his books have sold over 20 million copies.
#Americans #Children #Jews #XXCentury


Anne Sexton (November 9, 1928, Newton, Massachusetts – October 4, 1974, Weston, Massachusetts) was an American poetese, known for her highly personal, confessional verse. She won the Pulitzer Prize for poetry in 1967. Themes of her poetry include her suicidal tendencies, long battle against depression and various intimate details from her private life, including her relationships with her husband and children. Sexton suffered from severe mental illness for much of her life, her first manic episode taking place in 1954.
#Americans #Suicide #Women #XXCentury
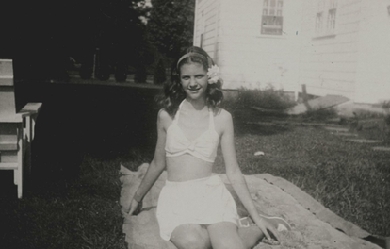

Sylvia Plath (October 27, 1932 – February 11, 1963) was an American poet, novelist and short story writer. Born in Boston, Massachusetts, she studied at Smith College and Newnham College, Cambridge before receiving acclaim as a professional poet and writer. She married fellow poet Ted Hughes in 1956 and they lived together first in the United States and then England, having two children together: Frieda and Nicholas. Following a long struggle with depression and a marital separation, Plath committed suicide in 1963. Controversy continues to surround the events of her life and death, as well as her writing and legacy. Plath is credited with advancing the genre of confessional poetry and is best known for her two published collections: The Colossus and Other Poems and Ariel. In 1982, she became the first poet to win a Pulitzer Prize posthumously, for The Collected Poems. She also wrote The Bell Jar, a semi-autobiographical novel published shortly before her death.
#Americans #Suicide #Women #XXCentury


James Whitcomb Riley (October 7, 1849 – July 22, 1916) was an American writer, poet, and best-selling author. During his lifetime he was known as the "Hoosier Poet" and "Children's Poet" for his dialect works and his children's poetry respectively. His poems tended to be humorous or sentimental, and of the approximately one thousand poems that Riley authored, the majority are in dialect. His famous works include "Little Orphant Annie" and "The Raggedy Man". Riley began his career writing verses as a sign maker and submitting poetry to newspapers. Thanks in part to an endorsement from poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, he eventually earned successive jobs at Indiana newspaper publishers during the latter 1870s. Riley gradually rose in prominence during the 1880s through his poetry reading tours. He traveled a touring circuit first in the Midwest, and then nationally, holding shows and making joint appearances on stage with other famous talents. Regularly struggling with his alcohol addiction, Riley never married or had children, and created a scandal in 1888 when he became too drunk to perform.
#Americans #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Ambrose Gwinnett Bierce (June 24, 1842 – circa 1914) was an American Civil War soldier, wit, and writer. Bierce’s book The Devil’s Dictionary was named as one of “The 100 Greatest Masterpieces of American Literature” by the American Revolution Bicentennial Administration. His story An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge has been described as “one of the most famous and frequently anthologized stories in American literature”; and his book Tales of Soldiers and Civilians (also published as In the Midst of Life) was named by the Grolier Club as one of the 100 most influential American books printed before 1900.
#Americans #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Sara Teasdale (August 8, 1884 – January 29, 1933) was an American lyric poet. She was born Sarah Trevor Teasdale in St. Louis, Missouri, and used the name Sara Teasdale Filsinger after her marriage in 1914. She had such poor health for so much of her childhood, home schooled until age 9, that it was only at age 10 that she was well enough to begin school. She started at Mary Institute in 1898, but switched to Hosmer Hall in 1899, graduating in 1903. I Shall Not Care WHEN I am dead and over me bright April Shakes out her rain-drenched hair, Tho' you should lean above me broken-hearted, I shall not care. I shall have peace, as leafy trees are peaceful When rain bends down the bough, And I shall be more silent and cold-hearted Than you are now.
#Americans #PulitzerPrize #Suicide #Women #XXCentury


William Carlos Williams (September 17, 1883 – March 4, 1963) was an American poet closely associated with modernism and Imagism. He was also a pediatrician and general practitioner of medicine with a medical degree from the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine. Williams "worked harder at being a writer than he did at being a physician" but excelled at both. Although his primary occupation was as a family doctor, Williams had a successful literary career as a poet. In addition to poetry (his main literary focus), he occasionally wrote short stories, plays, novels, essays, and translations. He practiced medicine by day and wrote at night. Early in his career, he briefly became involved in the Imagist movement through his friendships with Ezra Pound and H.D. (also known as Hilda Doolittle, another well-known poet whom he befriended while attending the University of Pennsylvania), but soon he began to develop opinions that differed from those of his poet/friends.
#Americans #Modernism #XXCentury


Dorothy Parker (August 22, 1893 – June 7, 1967) was an American poet, short story writer, critic and satirist, best known for her wit, wisecracks, and eye for 20th-century urban foibles. From a conflicted and unhappy childhood, Parker rose to acclaim, both for her literary output in such venues as The New Yorker and as a founding member of the Algonquin Round Table. Following the breakup of the circle, Parker traveled to Hollywood to pursue screenwriting. Her successes there, including two Academy Award nominations, were curtailed as her involvement in left-wing politics led to a place on the Hollywood blacklist. Dismissive of her own talents, she deplored her reputation as a “wisecracker”. Nevertheless, her literary output and reputation for her sharp wit have endured.


Edward Estlin Cummings (October 14, 1894 – September 3, 1962), popularly known as E. E. Cummings, with the abbreviated form of his name often written by others in lowercase letters as e.e. cummings (in the style of some of his poems—see name and capitalization, below), was an American poet, painter, essayist, author, and playwright. His body of work encompasses approximately 2,900 poems, two autobiographical novels, four plays and several essays, as well as numerous drawings and paintings. He is remembered as a preeminent voice of 20th century poetry.
#Americans #Modernism #XXCentury

Frederic Ogden Nash (August 19, 1902 – May 19, 1971) was an American poet well known for his light verse. At the time of his death in 1971, The New York Times said his “droll verse with its unconventional rhymes made him the country’s best-known producer of humorous poetry”. Nash wrote over 500 pieces of comic verse. The best of his work was published in 14 volumes between 1931 and 1972.


Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835– April 21, 1910), better known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer. Among his novels are The Adventures of Tom Sawyer (1876) and its sequel, the Adventures of Huckleberry Finn (1885), the latter often called “The Great American Novel”.


Herman Melville (August 1, 1819– September 28, 1891) was an American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance period best known for Typee (1846), a romantic account of his experiences in Polynesian life, and his whaling novel Moby-Dick (1851). His work was almost forgotten during his last thirty years. His writing draws on his experience at sea as a common sailor, exploration of literature and philosophy, and engagement in the contradictions of American society in a period of rapid change. He developed a complex, baroque style: the vocabulary is rich and original, a strong sense of rhythm infuses the elaborate sentences, the imagery is often mystical or ironic, and the abundance of allusion extends to Scripture, myth, philosophy, literature, and the visual arts.


Henry Jackson van Dyke (November 10, 1852 – April 10, 1933, aged 80) was an American author, educator, and clergyman born in Germantown, Pennsylvania in the United States. He graduated from Princeton University in 1873 and from Princeton Theological Seminary, 1877 and served as a professor of English literature at Princeton between 1899 and 1923. In 1908-09, Dr. van Dyke was an American lecturer at the University of Paris. By appointment of President Wilson he became Minister to the Netherlands and Luxembourg in 1913. He was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Letters and received many other honors. Van Dyke was an "ardent foe of the annexation of the Philippines, and told his congregation in 1898, 'If we enter the course of foreign conquest, the day is not far distant when we must spend in annual preparation for wars more than the $180,000,000 that we now spend every year in the education of our children for peace.’” }
#Americans #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Edgar Lee Masters (August 23, 1868 – March 5, 1950) was an American attorney, poet, biographer, and dramatist born in Garnett, Kansas. He is the author of Spoon River Anthology, The New Star Chamber and Other Essays, Songs and Satires, The Great Valley, The Serpent in the Wilderness An Obscure Tale, The Spleen, Mark Twain: A Portrait, Lincoln: The Man, and Illinois Poems. In all, Masters published twelve plays, twenty-one books of poetry, six novels and six biographies, including those of Abraham Lincoln, Mark Twain, Vachel Lindsay, and Walt Whitman.
#Americans #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Franklin Pierce Adams (November 15, 1881 – March 23, 1960) was an American columnist, well known by his initials F.P.A., and wit, best known for his newspaper column, “The Conning Tower”, and his appearances as a regular panelist on radio’s Information Please. A prolific writer of light verse, he was a member of the Algonquin Round Table of the 1920s and 1930s. Adams was born Franklin Leopold Adams to Moses and Clara Schlossberg Adams in Chicago on November 15, 1881. He changed his middle name to “Pierce” when he had a Jewish confirmation ceremony at age 13. Adams graduated from the Armour Scientific Academy (now Illinois Institute of Technology) in 1899, attended the University of Michigan for one year and worked in insurance for three years.


Oliver Wendell Holmes (August 29, 1809 – October 7, 1894) was an American physician, poet, and polymath based in Boston. Grouped among the fireside poets, he was acclaimed by his peers as one of the best writers of the day. His most famous prose works are the "Breakfast-Table" series, which began with The Autocrat of the Breakfast-Table (1858). He was also an important medical reformer. In addition to his work as an author and poet, Holmes also served as a physician, professor, lecturer, inventor, and, although he never practiced it, he received formal training in law.


Henry David Thoreau (July 12, 1817– May 6, 1862) was an American author, poet, philosopher, abolitionist, naturalist, tax resister, development critic, surveyor, and historian. A leading transcendentalist, Thoreau is best known for his book Walden, a reflection upon simple living in natural surroundings, and his essay Resistance to Civil Government (also known as Civil Disobedience), an argument for disobedience to an unjust state. He was a lifelong abolitionist, delivering lectures that attacked the Fugitive Slave Law while praising the writings of Wendell Phillips and defending abolitionist John Brown. Thoreau’s philosophy of civil disobedience later influenced the political thoughts and actions of such notable figures as Leo Tolstoy, Mahatma Gandhi, and Martin Luther King, Jr.

Edwin Arlington Robinson (December 22, 1869—April 6, 1935) was an American poet who won three Pulitzer Prizes for his work. He was born in Head Tide, Lincoln County, Maine but his family moved to Gardiner, Maine in 1871. He described his childhood in Maine as “stark and unhappy”: His parents (who had wanted a girl) did not name him until he was six months old, when they visited a holiday resort—whereupon, other vacationers decided that he should have a name and selected a man from Arlington, Massachusetts to draw a name out of a hat. Throughout his life, he not only hated his given name, but also his family’s habit of calling him “Win.” As an adult, he always used the signature “E. A.”


John Robinson Jeffers (January 10, 1887 – January 20, 1962) was an American poet, known for his work about the central California coast. Much of Jeffers' poetry was written in narrative and epic form, but he is also known for his shorter verse and is considered an icon of the environmental movement. Influential and highly regarded in some circles, despite or because of his philosophy of "inhumanism," Jeffers believed that transcending conflict required human concerns to be de-emphasized in favor of the boundless whole. This led him to oppose U.S. participation in World War II, a stand that was controversial at the time. Jeffers was born in Allegheny, Pennsylvania (now part of Pittsburgh), the son of a Presbyterian minister and biblical scholar, Reverend Dr. William Hamilton Jeffers, and Annie Robinson Tuttle. His brother was Hamilton Jeffers, who became a well-known astronomer, working at Lick Observatory. His family was supportive of his interest in poetry. He traveled through Europe during his youth and attended school in Switzerland. He was a child prodigy, interested in classics and Greek and Latin language and literature. At sixteen he entered Occidental College. At school, he was an avid outdoorsman, and active in the school's literary societies. After he graduated from Occidental, Jeffers went to the University of Southern California to study at first literature, and then medicine. He met Una Call Kuster in 1906; she was three years older than he was, a graduate student, and the wife of a Los Angeles attorney. In 1910 he enrolled as a forestry student at the University of Washington in Seattle, a course of study that he abandoned after less than one year, at which time he returned to Los Angeles. Sometime before this, he and Una had begun an affair that became a scandal, reaching the front page of the Los Angeles Times in 1912. After Una spent some time in Europe to quiet things down, the two were married in 1913, and moved to Carmel, California, where Jeffers constructed Tor House and Hawk Tower. The couple had a daughter who died a day after birth in 1914, and then twin sons (Donnan and Garth) in 1916. Una died of cancer in 1950. Jeffers died in 1962; an obituary can be found in the New York Times, January 22, 1962. Poetic career In the 1920s and 1930s, at the height of his popularity, Jeffers was famous for being a tough outdoorsman, living in relative solitude and writing of the difficulty and beauty of the wild. He spent most of his life in Carmel, California, in a granite house that he had built himself called "Tor House and Hawk Tower". Tor is a term for a craggy outcrop or lookout. Before Jeffers and Una purchased the land where Tor House would be built, they rented two cottages in Carmel, and enjoyed many afternoon walks and picnics at the "tors" near the site that would become Tor House. To build the first part of Tor House, a small, two story cottage, Jeffers hired a local builder, Michael Murphy. He worked with Murphy, and in this short, informal apprenticeship, he learned the art of stonemasonry. He continued adding on to Tor House throughout his life, writing in the mornings and working on the house in the afternoon. Many of his poems reflect the influence of stone and building on his life. He later built a large four-story stone tower on the site called Hawk Tower. While he had not visited Ireland at this point in his life, it is possible that Hawk Tower is based on Francis Joseph Bigger's 'Castle Séan' at Ardglass, County Down, which had also in turn influenced Yeats' poets tower, Thoor Ballylee. Construction on Tor House continued into the late 1950s and early 1960s, and was completed by his eldest son. The completed residence was used as a family home until his descendants decided to turn it over to the Tor House Foundation, formed by Ansel Adams, for historic preservation. The romantic Gothic tower was named after a hawk that appeared while Jeffers was working on the structure, and which disappeared the day it was completed. The tower was a gift for his wife Una, who had a fascination for Irish literature and stone towers. In Una's special room on the second floor were kept many of her favorite items, photographs of Jeffers taken by the artist Weston, plants and dried flowers from Shelley's grave, and a rosewood melodeon which she loved to play. The tower also included a secret interior staircase – a source of great fun for his young sons. During this time, Jeffers published volumes of long narrative blank verse that shook up the national literary scene. These poems, including Tamar and Roan Stallion, introduced Jeffers as a master of the epic form, reminiscent of ancient Greek poets. These poems were full of controversial subject matter such as incest, murder and parricide. Jeffers' short verse includes "Hurt Hawks," "The Purse-Seine" and "Shine, Perishing Republic." His intense relationship with the physical world is described in often brutal and apocalyptic verse, and demonstrates a preference for the natural world over what he sees as the negative influence of civilization. Jeffers did not accept the idea that meter is a fundamental part of poetry, and, like Marianne Moore, claimed his verse was not composed in meter, but "rolling stresses." He believed meter was imposed on poetry by man and not a fundamental part of its nature. nitially, Tamar and Other Poems received no acclaim, but when East Coast reviewers discovered the work and began to compare Jeffers to Greek tragedians, Boni & Liveright reissued an expanded edition as Roan Stallion, Tamar and Other Poems (1925). In these works, Jeffers began to articulate themes that contributed to what he later identified as Inhumanism. Mankind was too self-centered, he complained, and too indifferent to the "astonishing beauty of things." Jeffers's longest and most ambitious narrative, The Women at Point Sur (1927), startled many of his readers, heavily loaded as it was with Nietzschean philosophy. The balance of the 1920s and the early 1930s were especially productive for Jeffers, and his reputation was secure. In 1934, he made the acquaintance of the philosopher J Krishnamurti and was struck by the force of Krishnamurti's person. He wrote a poem entitled "Credo" which many feel refers to Krishnamurti. In Cawdor and Other Poems (1928), Dear Judas and Other Poems (1929), Descent to the Dead, Poems Written in Ireland and Great Britain (1931), Thurso's Landing (1932), and Give Your Heart to the Hawks (1933), Jeffers continued to explore the questions of how human beings could find their proper relationship (free of human egocentrism) with the divinity of the beauty of things. These poems, set in the Big Sur region (except Dear Judas and Descent to the Dead), enabled Jeffers to pursue his belief that the natural splendor of the area demanded tragedy: the greater the beauty, the greater the demand. As Euripides had, Jeffers began to focus more on his own characters' psychologies and on social realities than on the mythic. The human dilemmas of Phaedra, Hippolytus, and Medea fascinated him. Many books followed Jeffers' initial success with the epic form, including an adaptation of Euripides' Medea, which became a hit Broadway play starring Dame Judith Anderson. D. H. Lawrence, Edgar Lee Masters, Benjamin De Casseres, and George Sterling were close friends of Jeffers, Sterling having the longest and most intimate relationship with him. While living in Carmel, Jeffers became the focal point for a small but devoted group of admirers. At the peak of his fame, he was one of the few poets to be featured on the cover of Time Magazine. He was also asked to read at the Library of Congress, and was posthumously put on a U.S. postage stamp. Part of the decline of Jeffers' popularity was due to his staunch opposition to the United States' entering World War II. In fact, his book The Double Axe and Other Poems (1948), a volume of poems that was largely critical of U.S. policy, came with an extremely unconventional note from Random House that the views expressed by Jeffers were not those of the publishing company. Soon after, his work was received negatively by several influential literary critics. Several particularly scathing pieces were penned by Yvor Winters, as well as by Kenneth Rexroth, who had been very positive in his earlier commentary on Jeffers' work. Jeffers would publish poetry intermittently during the 1950s but his poetry never again attained the same degree of popularity that it had in the 1920s and the 1930s. Inhumanism Jeffers coined the word inhumanism, the belief that mankind is too self-centered and too indifferent to the "astonishing beauty of things." In the famous poem "Carmel Point," Jeffers called on humans to "uncenter" themselves. In "The Double Axe," Jeffers explicitly described inhumanism as "a shifting of emphasis and significance from man to notman; the rejection of human solipsism and recognition of the trans-human magnificence. ... This manner of thought and feeling is neither misanthropic nor pessimist. ... It offers a reasonable detachment as rule of conduct, instead of love, hate and envy ... it provides magnificence for the religious instinct, and satisfies our need to admire greatness and rejoice in beauty." In The Loyalties of Robinson Jeffers,the first in-depth study of Jeffers not written by one of his circle, poet and critic J. Radcliffe Squires addresses the question of a reconciliation of the beauty of the world and potential beauty in mankind: “Jeffers has asked us to look squarely at the universe. He has told us that materialism has its message, its relevance, and its solace. These are different from the message, relevance, and solace of humanism. Humanism teaches us best why we suffer, but materialism teaches us how to suffer.” Influence His poems have been translated into many languages and published all over the world. Outside of the United States he is most popular in Japan and the Czech Republic. William Everson, Edward Abbey, Gary Snyder, and Mark Jarman are just a few recent authors who have been influenced by Jeffers. Charles Bukowski remarked that Jeffers was his favorite poet. Polish poet Czesław Miłosz also took an interest in Jeffers' poetry and worked as a translator for several volumes of his poems. Jeffers also exchanged some letters with his Czech translator and popularizer, the poet Kamil Bednář. Writer Paul Mooney (1904–1939), son of American Indian authority James Mooney (1861–1921) and collaborator of travel writer Richard Halliburton (1900–1939), "was known always to carry with him (a volume of Jeffers) as a chewer might carry a pouch of tobacco ... and, like Jeffers," writes Gerry Max in Horizon Chasers, "worshipped nature ... (taking) refuge (from the encroachments of civilization) in a sort of chthonian mysticism rife with Greek dramatic elements ..." Jeffers was an inspiration and friend to western U.S. photographers of the early twentieth century, including Ansel Adams, Edward Weston, and Morley Baer. In fact, the elegant book of Baer's photographs juxtaposed with Jeffers' poetry, combines the creative talents of those two residents of the Big Sur coast. Although Jeffers has largely been marginalized in the mainstream academic community over the last thirty years, several important contemporary literary critics, including Albert Gelpi of Stanford University, and poet, critic and NEA chairman Dana Gioia, have consistently cited Jeffers as a formidable presence in modern literature. His poem "The Beaks of Eagles" was made into a song by The Beach Boys on their album Holland (1973). Two lines from Jeffers' poem "We Are Those People" are quoted toward the end of the 2008 film Visioneers. Several lines from Jeffers' poem "Wise Men in Their Bad Hours" ("Death's a fierce meadowlark: but to die having made / Something more equal to the centuries / Than muscle and bone, is mostly to shed weakness.") appear in Christopher McCandless' diary. Robinson Jeffers is mentioned in the 2004 film I Heart Huckabees by the character Albert Markovski played by Jason Schwartzman, when defending Jeffers as a nature writer against another character's claim that environmentalism is socialism. Markovski says, "Henry David Thoreau, Robinson Jeffers, the National Geographic Society...all socialists?" Further reading and research The largest collections of Jeffers' manuscripts and materials are in the Harry Ransom Humanities Research Center at the University of Texas at Austin and in the libraries at Occidental College, the University of California, and Yale University. A collection of his letters has been published as The Selected Letters of Robinson Jeffers, 1887–1962 (1968). Other books of criticism and poetry by Jeffers are: Poetry, Gongorism and a Thousand Years (1949), Themes in My Poems (1956), Robinson Jeffers: Selected Poems (1965), The Alpine Christ and Other Poems (1974), What Odd Expedients" and Other Poems (1981), and Rock and Hawk: A Selection of Shorter Poems by Robinson Jeffers (1987). Stanford University Press recently released a five-volume collection of the complete works of Robinson Jeffers. In an article titled, "A Black Sheep Joins the Fold", written upon the release of the collection in 2001, Stanford Magazine commented that it was remarkable that, due to a number of circumstances, "there was never an authoritative, scholarly edition of California’s premier bard" until the complete works published by Stanford. Biographical studies include George Sterling, Robinson Jeffers: The Man and the Artist (1926); Louis Adamic, Robinson Jeffers (1929); Melba Bennett, Robinson Jeffers and the Sea (1936) and The Stone Mason of Tor House (1966); Radcliffe Squires, The Loyalties of Robinson Jeffers (1956); Edith Greenan, Of Una Jeffers (1939); Mabel Dodge Luhan, Una and Robin (1976; written in 1933); Ward Ritchie, Jeffers: Some Recollections of Robinson Jeffers (1977); and James Karman, Robinson Jeffers: Poet of California (1987). Books about Jeffers's career include L. C. Powell, Robinson Jeffers: The Man and His Work (1940; repr. 1973); William Everson, Robinson Jeffers: Fragments of an Older Fury (1968); Arthur B. Coffin, Robinson Jeffers: Poet of Inhumanism (1971); Bill Hotchkiss, Jeffers: The Sivaistic Vision (1975); James Karman, ed., Critical Essays on Robinson Jeffers (1990); Alex Vardamis The Critical Reputation of Robinson Jeffers (1972); and Robert Zaller, ed., Centennial Essays for Robinson Jeffers (1991). The Robinson Jeffers Newsletter, ed. Robert Brophy, is a valuable scholarly resource. In a rare recording, Jeffers can be heard reading his "The Day Is A Poem" (September 19, 1939) on Poetry Speaks – Hear Great Poets Read Their Work from Tennyson to Plath, Narrated by Charles Osgood (Sourcebooks, Inc., c2001), Disc 1, #41; including text, with Robert Hass on Robinson Jeffers, pp. 88–95. Jeffers was also on the cover of Time – The Weekly Magazine, April 4, 1932 (pictured on p. 90. Poetry Speaks). Jeffers Studies, a journal of research on the poetry of Robinson Jeffers and related topics, is published semi-annually by the Robinson Jeffers Association. Bibliography * Flagons and Apples. Los Angeles: Grafton, 1912. * Californians. New York: Macmillan, 1916. * Tamar and Other Poems. New York: Peter G. Boyle, 1924. * Roan Stallion, Tamar, and Other Poems. New York: Boni and Liveright, 1925. * The Women at Point Sur. New York: Liveright, 1927. * Cawdor and Other Poems. New York: Liveright, 1928. * Dear Judas and Other Poems. New York: Liveright, 1929. * Thurso's Landing and Other Poems. New York: Liveright, 1932. * Give Your Heart to the Hawks and other Poems. New York: Random House, 1933. * Solstice and Other Poems. New York: Random House, 1935. * Such Counsels You Gave To Me and Other Poems. New York: Random House, 1937. * The Selected Poetry of Robinson Jeffers. New York: Random House, 1938. * Be Angry at the Sun. New York: Random House, 1941. * Medea. New York: Random House, 1946. * The Double Axe and Other Poems. New York: Random House, 1948. * Hungerfield and Other Poems. New York: Random House, 1954. * The Beginning and the End and Other Poems. New York: Random House, 1963. * Robinson Jeffers: Selected Poems. New York: Vintage, 1965. * Stones of the Sur. Stanford: Stanford University Press, 2001. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robinson_Jeffers


Ernest Hemingway (1899-1961) was one of the most significant American authors of the Twentieth century . His novels and short fictions have left an indelible mark on the literary production of the United States and the world. Although most often remembered for his economical and understated fiction, he was also a noted journalist. In 1954, Ernest Hemingway was awarded the Novel Prize in Literature. Hemingway is also known for his heroic, adventurous and often stereotypically “manly” public persona. The myth he cultivated of himself as a man of action aided the important Modernist reading of many of his works.


Maya Angelou (born Marguerite Ann Johnson; April 4, 1928 – May 28, 2014) was an American author and poet. She published seven autobiographies, three books of essays, and several books of poetry, and is credited with a list of plays, movies, and television shows spanning more than fifty years. She received dozens of awards and over thirty honorary doctoral degrees. Angelou is best known for her series of seven autobiographies, which focus on her childhood and early adult experiences. The first, I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings (1969), tells of her life up to the age of seventeen, and brought her international recognition and acclaim. Angelou's long list of occupations has included pimp, prostitute, night-club dancer and performer, cast-member of the musical Porgy and Bess, coordinator for Martin Luther King, Jr.'s Southern Christian Leadership Conference, author, journalist in Egypt and Ghana during the days of decolonization, and actor, writer, director, and producer of plays, movies, and public television programs.


Edna St. Vincent Millay (February 22, 1892 – October 19, 1950) was an American poet and playwright. She received the Pulitzer Prize for Poetry in 1923, the third woman to win the award for poetry, and was also known for her feminist activism. She used the pseudonym Nancy Boyd for her prose work. The poet Richard Wilbur asserted, "She wrote some of the best sonnets of the century."
#Americans #PulitzerPrize #Women #XXCentury


Erica Jong (née Mann; born March 26, 1942) is an American novelist and poet, known particularly for her 1973 novel Fear of Flying. The book became famously controversial for its attitudes towards female sexuality and figured prominently in the development of second-wave feminism. According to Washington Post, it has sold more than 20 million copies worldwide. Born in New York, she was the second of three daughters of Seymore Mann and Eda Mirsky. Attended New York’s Public High School of Music and Art in the 1950’s where she developed her passion for art and writing. As a student at Barnard College, she edited the Barnard Literary Magazine and created poetry programs for the Columbia University campus radio station.


Wallace Stevens was born in Reading, Pennsylvania, on October 2, 1879. He attended Harvard University as an undergraduate from 1897 to 1900. He planned to travel to Paris as a writer, but after a working briefly as a reporter for the New York Herald Times, he decided to study law. He graduated with a degree from New York Law School in 1903 and was admitted to the U.S. Bar in 1904. He practised law in New York City until 1916. Though he had serious determination to become a successful lawyer, Stevens had several friends among the New York writers and painters in Greenwich Village, including the poets William Carlos Williams, Marianne Moore, and E. E. Cummings. In 1914, under the pseudonym "Peter Parasol," he sent a group of poems under the title "Phases" to Harriet Monroe for a war poem competition for Poetry magazine. Stevens did not win the prize, but was published by Monroe in November of that year. Stevens moved to Connecticut in 1916, having found employment at the Hartford Accident and Indemnity Co., of which he became vice president in 1934. He had began to establish an identity for himself outside the world of law and business, however, and his first book of poems, Harmonium, published in 1923, exhibited the influence of both the English Romantics and the French symbolists, an inclination to aesthetic philosophy, and a wholly original style and sensibility: exotic, whimsical, infused with the light and color of an Impressionist painting. For the next several years, Stevens focused on his business life. He began to publish new poems in 1930, however, and in the following year, Knopf published an second edition of Harmonium, which included fourteen new poems and left out three of the decidedly weaker ones. More than any other modern poet, Stevens was concerned with the transformative power of the imagination. Composing poems on his way to and from the office and in the evenings, Stevens continued to spend his days behind a desk at the office, and led a quiet, uneventful life. Though now considered one of the major American poets of the century, he did not receive widespread recognition until the publication of his Collected Poems, just a year before his death. His major works include Ideas of Order (1935), The Man With the Blue Guitar (1937), Notes Towards a Supreme Fiction (1942), and a collection of essays on poetry, The Necessary Angel (1951). Stevens died in Hartford in 1955. Poetry Harmonium (1923) Ideas of Order (1935) Owl's Clover (1936) The Man With the Blue Guitar (1937) Notes Towards a Supreme Fiction (1942) Parts of a World (1942) Esthétique du Mal (1945) Three Academic Pieces (1947) Transport to Summer (1947) Primitive Like an Orb (1948) Auroras of Autumn (1950) Collected Poems (1954) Opus Posthumous (1957) The Palm at the End of the Mind (1967) Prose The Necessary Angel (1951) Plays Three Travellers Watch the Sunrise (1916) Carlos Among the Candles (1917) References Poets.org — http://www.poets.org/poet.php/prmPID/124
#Americans Modern


Eugene Field, Sr. (September 2, 1850 – November 4, 1895) was an American writer, best known for his children's poetry and humorous essays. Field was born in St. Louis, Missouri where today his boyhood home is open to the public as The Eugene Field House and St. Louis Toy Museum. After the death of his mother in 1856, he was raised by a cousin, Mary Field French, in Amherst, Massachusetts.


Amy Lawrence Lowell (February 9, 1874 – May 12, 1925) was an American poet of the imagist school from Brookline, Massachusetts, who posthumously won the Pulitzer Prize for Poetry in 1926. Amy was born into Brookline’s Lowell family, sister to astronomer Percival Lowell and Harvard president Abbott Lawrence Lowell. She never attended college because her family did not consider it proper for a woman to do so. She compensated for this lack with avid reading and near-obsessive book collecting. She lived as a socialite and travelled widely, turning to poetry in 1902 (age 28) after being inspired by a performance of Eleonora Duse in Europe.
#Americans #Lesbian #PulitzerPrize #Women


Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803 – April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, abolitionist, and poet who led the Transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champion of individualism and critical thinking, as well as a prescient critic of the countervailing pressures of society and conformity. Friedrich Nietzsche thought he was “the most gifted of the Americans,” and Walt Whitman called him his “master”.


James Mercer Langston Hughes (February 1, 1902 – May 22, 1967) was an American poet, social activist, novelist, playwright, and columnist. He was one of the earliest innovators of the then-new literary art form jazz poetry. Hughes is best known for his work during the Harlem Renaissance. He famously wrote about the period that “the negro was in vogue” which was later paraphrased as “when Harlem was in vogue”.


Celia Laighton Thaxter (June 29, 1835 – August 25, 1894) was an American writer of poetry and stories. She was born in Portsmouth, New Hampshire. Thaxter grew up in the Isles of Shoals, first on White Island, where her father, Thomas Laighton, was a lighthouse keeper, and then on Smuttynose and Appledore Islands. When she was sixteen, she married Levi Thaxter and moved to the mainland, residing first in Watertown, Massachusetts at a property his father owned. Celia died suddenly while on Appledore Island. She was buried not far from her cottage, which unfortunately burned in the 1914 fire that destroyed The Appledore House hotel.


Edgar Allan Poe (born Edgar Poe, January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American author, poet, editor and literary critic, considered part of the American Romantic Movement. Best known for his tales of mystery and the macabre, Poe was one of the earliest American practitioners of the short story and is considered the inventor of the detective fiction genre. He is further credited with contributing to the emerging genre of science fiction. He was the first well-known American writer to try to earn a living through writing alone, resulting in a financially difficult life and career. He was born as Edgar Poe in Boston, Massachusetts; he was orphaned young when his mother died shortly after his father abandoned the family. Poe was taken in by John and Frances Allan, of Richmond, Virginia, but they never formally adopted him. He attended the University of Virginia for one semester but left due to lack of money. After enlisting in the Army and later failing as an officer's cadet at West Point, Poe parted ways with the Allans. His publishing career began humbly, with an anonymous collection of poems, Tamerlane and Other Poems (1827), credited only to “a Bostonian”.


Nicholas Vachel Lindsay (November 10, 1879 – December 5, 1931) was an American poet. He is considered a founder of modern singing poetry, as he referred to it, in which verses are meant to be sung or chanted. Crushed by financial worry and in failing health from his six-month road trip, Lindsay sank into depression. While in New York in 1905 Lindsay turned to poetry in earnest. He tried to sell his poems on the streets. Self-printing his poems, he began to barter a pamphlet titled “Rhymes To Be Traded For Bread”, which he traded for food as a self-perceived modern version of a medieval troubadour. On December 5, 1931, he committed suicide by drinking a bottle of Lysol. His last words were: “They tried to get me; I got them first!”
#Americans #Suicide #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Elizabeth Bishop (February 8, 1911 – October 6, 1979) was an American poet, short-story writer, and recipient of the 1976 Neustadt International Prize for Literature. She was the Poet Laureate of the United States from 1949 to 1950, the Pulitzer Prize winner for Poetry in 1956 and the National Book Award winner in 1970.
#Americans #PulitzerPrize #Women


William Cullen Bryant (November 3, 1794– June 12, 1878) was an American romantic poet, journalist, and long-time editor of the New York Evening Post. Youth and education Bryant was born on November 3, 1794, in a log cabin near Cummington, Massachusetts; the home of his birth is today marked with a plaque. He was the second son of Peter Bryant (b. Aug. 12, 1767, d. Mar. 20, 1820), a doctor and later a state legislator, and Sarah Snell (b. Dec. 4, 1768, d. May 6, 1847). The genealogies of both of his parents trace back to passengers on the Mayflower; his mother’s to John Alden (b. 1599, d. 1687); his father’s to Francis Cooke (b. 1577, d. 1663). He was also a nephew of Charity Bryant, a Vermont seamstress who is the subject of Rachel Hope Cleves’ 2014 book Charity and Sylvia: A Same-Sex Marriage in Early America. Bryant and his family moved to a new home when he was two years old. The William Cullen Bryant Homestead, his boyhood home, is now a museum. After just one year at Williams College (he entered with sophomore standing), he hoped to transfer to Yale, but a talk with his father led to the realization that family finances would not support it. His father counseled a legal career as his best available choice, and the disappointed poet began to study law in Worthington and Bridgewater in Massachusetts. He was admitted to the bar in 1815 and began practicing law in nearby Plainfield, walking the seven miles from Cummington every day. On one of these walks, in December 1815, he noticed a single bird flying on the horizon; the sight moved him enough to write “To a Waterfowl”. Bryant developed an interest in poetry early in life. Under his father’s tutelage, he emulated Alexander Pope and other Neo-Classic British poets. “The Embargo”, a savage attack on President Thomas Jefferson published in 1808, reflected Dr. Bryant’s Federalist political views. The first edition quickly sold out—partly because of publicity attached to the poet’s young age. A second, expanded edition included Bryant’s translation of classical verse. During his collegiate studies and his reading for the law, he wrote little poetry, but encounters with the Graveyard Poets and then Wordsworth regenerated his passion for “the witchery of song.” Poetry “Thanatopsis” is Bryant’s most famous poem, which Bryant may have been working on as early as 1811. In 1817 his father took some pages of verse from his son’s desk, and at the invitation of Willard Phillips, an editor of the North American Review who had previously been tutored in the classics by Dr. Bryant, he submitted them along with his own work. The editor of the Review, Edward Tyrrel Channing, read the poem to his assistant, Richard Henry Dana, who immediately exclaimed, “That was never written on this side of the water!” Someone at the North American joined two of the son’s discrete fragments, gave the result the Greek-derived title Thanatopsis ("meditation on death"), mistakenly attributed it to the father, and published it. After clarification of the authorship, the son’s poems began appearing with some regularity in the "[Review]". “To a Waterfowl”, published in 1821 was the most popular. On January 11, 1821, Bryant, still striving to build a legal career, married Frances Fairchild. Soon after, having received an invitation to address the Harvard University Phi Beta Kappa Society at the school’s August commencement, Bryant spent months working on “The Ages”, a panorama in verse of the history of civilization, culminating in the establishment of the United States. As it would in all collections he subsequently issued, “The Ages” led the volume, also entitled Poems, which he arranged to publish on the same trip to Cambridge. For that book, he added sets of lines at the beginning and end of “Thanatopsis” that changed the poem. His career as a poet was now established, though recognition as America’s leading poet waited until 1832, when an expanded Poems was published in the U.S. and, with the assistance of Washington Irving, in Britain. His poetry has been described as being “of a thoughtful, meditative character, and makes but slight appeal to the mass of readers.” Editorial career From 1816 to 1825, Bryant depended on his law practice in Great Barrington, Massachusetts to sustain his family financially, but the strain of dealing with unsophisticated neighbors and juridical pettifoggery pushed him to trade his unrewarding profession for New York City and the promise of a literary career. With the encouragement of a distinguished and well-connected literary family, the Sedgwicks, he quickly gained a foothold in New York City’s vibrant cultural life. His first employment, in 1825, was as editor of the New-York Review, which within the next year merged with the United States Review and Literary Gazette. But in the throes of the failing struggle to raise subscriptions, he accepted part-time duties with the New-York Evening Post under William Coleman; then, partly because of Coleman’s ill health, traceable to the consequences of a duel and then a stroke, Bryant’s responsibilities expanded rapidly. From Assistant Editor he rose to Editor-in-Chief and co-owner of the newspaper that had been founded by Alexander Hamilton. Over the next half century, the “Post” would become the most respected paper in the city and, from the election of Andrew Jackson, the major platform in the Northeast for the Democratic Party and subsequently of the Free Soil and Republican Parties. In the process, the Evening-Post also became the pillar of a substantial fortune. From his Federalist beginnings, Bryant had shifted to being one of the most liberal voices of the century. An early supporter of organized labor, with his 1836 editorials the right of workmen to strike, Bryant also defended of religious minorities and immigrants, and promoted the abolition of slavery. He “threw himself into the foreground of the battle for human rights” and did not cease speaking out against the corrupting influence of certain bankers in spite of their efforts to break down the paper. According to newspaper historian Frank Luther Mott, Bryant was “a great liberal seldom done justice by modern writers”. Ironically, the boy who first tasted fame for his diatribe against Thomas Jefferson and his party became one of the key supporters in the Northeast of that same party under Jackson. Bryant’s views, always progressive though not quite populist, in course led him to join the Free Soilers, and when the Free Soil Party became a core of the new Republican Party in 1856, Bryant vigorously campaigned for John Frémont. That exertion enhanced his standing in party councils, and in 1860, he was one of the prime Eastern exponents of Abraham Lincoln, whom he introduced at Cooper Union. (That “Cooper Union speech” lifted Lincoln to the nomination, and then the presidency.) Although literary historians have neglected his fiction, Bryant’s stories over the seven-year period from his time with the Review to the publication of Tales of Glauber Spa in 1832 show a variety of strategies, making him the most inventive of practitioners of the genre during this early stage of its evolution. Bryant edited the very successful Picturesque America which was published between 1872 and 1874. This two-volume set was lavishly illustrated and described scenic places in the United States and Canada. Later years In his last decade, Bryant shifted from writing his own poetry to a blank verse translation of Homer’s works. He assiduously worked on the Iliad and The Odyssey from 1871 to 1874. He is also remembered as one of the principal authorities on homeopathy and as a hymnist for the Unitarian Church—both legacies of his father’s enormous influence on him. Bryant died in 1878 of complications from an accidental fall suffered after participating in a Central Park ceremony honoring Italian patriot Giuseppe Mazzini. He is buried at Roslyn Cemetery in Roslyn, Long Island, New York. Critical response Poet and literary critic Thomas Holley Chivers said that the "only thing [Bryant] ever wrote that may be called Poetry is 'Thanatopsis’, which he stole line for line from the Spanish. The fact is, that he never did anything but steal—as nothing he ever wrote is original." Contemporary critic Edgar Allan Poe, on the other hand, praised Bryant and specifically the poem “June” in his essay “The Poetic Principle”: The rhythmical flow, here, is even voluptuous—nothing could be more melodious. The poem has always affected me in a remarkable manner. The intense melancholy which seems to well up, perforce, to the surface of all the poet’s cheerful sayings about his grave, we find thrilling us to the soul—while there is the truest poetic elevation in the thrill. The impression left is one of a pleasurable sadness. Editor and children’s writer Mary Mapes Dodge wrote that Bryant’s poems “have wrought vast and far-reaching good in the world.” She predicted, “You will admire more and more, as you grow older, the noble poems of this great and good man.” Bryant’s poetry is tender and graceful, pervaded by a contemplative melancholy, and a love of solitude and the silence of the woods. Though he was brought up to admire Pope, and in his early youth imitated him, he was one of the first American poets to throw off his influence. He had a high sense of duty, was a prominent and patriotic citizen, and enjoyed the esteem and even the reverence of his fellow-countrymen. Legacy In 1884, New York City’s Reservoir Square, at the intersection of 42nd Street and Sixth Avenue, was renamed Bryant Park in his honor. The city later named a public high school in Long Island City, Queens in his honor. A park in East York, a suburb of Toronto, Canada, bears the name of Cullen Bryant Park as well. Although he is now thought of as a New Englander, Bryant, for most of his lifetime, was thoroughly a New Yorker—and a very dedicated one at that. He was a major force behind the idea that became Central Park, as well as a leading proponent of creating the Metropolitan Museum of Art. He was one of a group of founders of New York Medical College. He had close affinities with the Hudson River School of art and was an intimate friend of Thomas Cole. He defended immigrants and, at some financial risk to himself, championed the rights of workers to form labor unions. As a writer, Bryant was an early advocate of American literary nationalism, and his own poetry focusing on nature as a metaphor for truth established a central pattern in the American literary tradition. Some however, argue that a reassessment is long overdue. It finds great merit in a couple of short stories Bryant wrote while trying to build interest in periodicals he edited. More importantly, it perceives a poet of great technical sophistication who was a progenitor of Walt Whitman, to whom he was a mentor. Martin Luther King, Jr quoted Bryant in his speech “Give Us the Ballot”, when he said, “there is something in this universe which justifies William Cullen Bryant in saying: ‘Truth crushed to earth will rise again.’” The Seattle neighborhood Bryant is named after him. Bryant House at Williams College is named for him. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Cullen_Bryant


Thomas Stearns Eliot OM (26 September 1888– 4 January 1965) was a British essayist, publisher, playwright, literary and social critic, and “one of the twentieth century’s major poets”. He moved from his native United States to England in 1914 at the age of 25, settling, working, and marrying there. He was eventually naturalised as a British subject in 1927 at the age of 39, renouncing his American citizenship. Eliot attracted widespread attention for his poem “The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock” (1915), which was seen as a masterpiece of the Modernist movement. It was followed by some of the best-known poems in the English language, including The Waste Land (1922), “The Hollow Men” (1925), “Ash Wednesday” (1930), and Four Quartets (1943). He was also known for his seven plays, particularly Murder in the Cathedral (1935). He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1948, “for his outstanding, pioneer contribution to present-day poetry”.


Conrad Potter Aiken (August 5, 1889– August 17, 1973) was an American writer, whose work includes poetry, short stories, novels, a play, and an autobiography. Aiken was the son of wealthy, socially prominent New Englanders, William Ford and Anna (Potter) Aiken, who had moved to Savannah, Georgia, where his father became a respected physician and brain surgeon. Then something happened for which, as Aiken later said, no one could ever find a reason. Without warning or apparent cause, his father became increasingly irascible, unpredictable, and violent. Finally, early in the morning of February 27, 1901, he murdered his wife and shot himself. According to his own writings, Aiken (who was eleven years old) heard the gunshots and discovered the bodies. He was then raised by his great aunt in Massachusetts and was educated at private schools and at Middlesex School in Concord, Massachusetts, then at Harvard University where he edited the Advocate with T. S. Eliot, who became a lifelong friend and associate.


George Henry Boker (October 6, 1823 – January 2, 1890) was an American poet, playwright, and diplomat. Boker was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. His father was Charles S. Boker, a wealthy banker, whose financial expertness weathered the Girard National Bank through the panic years of 1838-40, and whose honour, impugned after his 1857 death, was defended many years later by his son in “The Book of the Dead.” Charles Boker was also a director of the Mechanics National Bank.


George Moses Horton (1798–1884) was the first black poet to be published in the Southern United States. His book was published in 1828 while he was still enslaved; he remained enslaved until he was emancipated late in the Civil War. Horton was born into slavery on William Horton’s plantation in Northampton County, North Carolina. He was the sixth of ten children, though the names of his parents are lost to history. As a very young child in 1800, he and several family members were moved to a tobacco farm in rural Chatham County, when his owner relocated. He was given as property to William’s relative James Horton in 1814. In 1819, the estate was broken up, and George Moses Horton’s family was separated (the poem “Division of an Estate” reflected on the experience years later).


Philip Levine (January 10, 1928– February 14, 2015) was a Pulitzer Prize-winning American poet best known for his poems about working-class Detroit. He taught for more than thirty years in the English department of California State University, Fresno and held teaching positions at other universities as well. He served on the Board of Chancellors of the Academy of American Poets from 2000 to 2006, and was appointed Poet Laureate of the United States for 2011–2012. Biography Philip Levine grew up in industrial Detroit, the second of three sons and the first of identical twins of Jewish immigrant parents. His father, Harry Levine, owned a used auto parts business, his mother, Esther Priscol (Prisckulnick) Levine, was a bookseller. When Levine was five years old, his father died. While growing up, he faced the anti-Semitism embodied by Father Coughlin, the pro-Nazi radio priest. Levine started to work in car manufacturing plants at the age of 14. Detroit Central High School graduated him in 1946 and he went to college at Wayne University (now Wayne State University) in Detroit, where he began to write poetry, encouraged by his mother, to whom he dedicated the book of poems, The Mercy. Levine earned his A.B. in 1950 and went to work for Chevrolet and Cadillac in what he called “stupid jobs.” He married his first wife, Patty Kanterman, in 1951. The marriage lasted until 1953. In 1953, he attended the University of Iowa without registering, studying with, among others, poets Robert Lowell and John Berryman, the latter of whom Levine called his “one great mentor.” In 1954, he earned a mail-order masters degree with a thesis on John Keats’ “Ode to Indolence,” and married actress Frances J. Artley. He returned to the University of Iowa teaching technical writing, completing his Master of Fine Arts degree in 1957. The same year, he was awarded the Jones Fellowship in Poetry at Stanford University. In 1958, he joined the English department at California State University in Fresno, where he taught until his retirement in 1992. He also taught at many other universities, among them New York University as Distinguished Writer-in-Residence, Columbia, Princeton, Brown, Tufts, and the University of California at Berkeley. Levine and his wife had made their homes in Fresno and Brooklyn. He died of pancreatic cancer on February 14, 2015, age 87. Work The familial, social, and economic world of twentieth-century Detroit is one of the major subjects of Levine’s life work. His portraits of working class Americans and his continuous examination of his Jewish immigrant inheritance (both based on real life and described through fictional characters) has left a testimony of mid-twentieth century American life. Levine’s working experience lent his poetry a profound skepticism with regard to conventional American ideals. In his first two books, On the Edge (1963) and Not This Pig (1968), the poetry dwells on those who suddenly become aware that they are trapped in some murderous processes not of their own making. In 1968, Levine signed the “Writers and Editors War Tax Protest” pledge, vowing to refuse to make tax payments in protest against the Vietnam War. In his first two books, Levine was somewhat traditional in form and relatively constrained in expression. Beginning with They Feed They Lion, typically Levine’s poems are free-verse monologues tending toward trimeter or tetrameter. The music of Levine’s poetry depends on tension between his line-breaks and his syntax. The title poem of Levine’s book 1933 (1974) is an example of the cascade of clauses and phrases one finds in his poetry. Other collections include The Names of the Lost, A Walk with Tom Jefferson, New Selected Poems, and the National Book Award-winning What Work Is. On November 29, 2007 a tribute was held in New York City in anticipation of Levine’s eightieth birthday. Among those celebrating Levine’s career by reading Levine’s work were Yusef Komunyakaa, Galway Kinnell, E. L. Doctorow, Charles Wright, Jean Valentine and Sharon Olds. Levine read several new poems as well. Awards * 2013 Academy of American Poets Wallace Stevens Award * 2011 Appointed Poet Laureate Consultant in Poetry to the Library of Congress (United States Poet Laureate) * 1995 Pulitzer Prize for Poetry– The Simple Truth (1994) * 1991 National Book Award for Poetry and Los Angeles Times Book Prize– What Work Is * 1987 Ruth Lilly Poetry Prize from the Modern Poetry Association and the American Council for the Arts * 1981 Levinson Prize from Poetry magazine * 1980 Guggenheim Foundation fellowship * 1980 National Book Award for Poetry– Ashes: Poems New and Old * 1979 National Book Critics Circle Award– Ashes: Poems New and Old– 7 Years from Somewhere * 1978 Harriet Monroe Memorial Prize from Poetry * 1977 Lenore Marshall Poetry Prize from the Academy of American Poets– The Names of the Lost (1975) * 1973 American Academy of Arts and Letters Award, Frank O’Hara Prize, Guggenheim Foundation fellowship Published works Poetry collections * News of the World, Random House, Inc., 2009, ISBN 978-0-307-27223-2 * Stranger to Nothing: Selected Poems, Bloodaxe Books, UK, 2006, ISBN 978-1-85224-737-9 * Breath Knopf, 2004, ISBN 978-1-4000-4291-3; reprint, Random House, Inc., 2006, ISBN 978-0-375-71078-0 * The Mercy, Random House, Inc., 1999, ISBN 978-0-375-70135-1 * Unselected Poems, Greenhouse Review Press, 1997, ISBN 978-0-9655239-0-5 * The Simple Truth, Alfred A. Knopf, 1994, ISBN 978-0-679-43580-8; Alfred A. Knopf, 1996, ISBN 978-0-679-76584-4 * What Work Is, Knopf, 1992, ISBN 978-0-679-74058-2 * New Selected Poems, Knopf, 1991, ISBN 978-0-679-40165-0 * A Walk With Tom Jefferson, A.A. Knopf, 1988, ISBN 978-0-394-57038-9 * Sweet Will, Atheneum, 1985, ISBN 978-0-689-11585-1 * Selected Poems, Atheneum, 1984, ISBN 978-0-689-11456-4 * One for the Rose, Atheneum, 1981, ISBN 978-0-689-11223-2 * 7 Years From Somewhere, Atheneum, 1979, ISBN 978-0-689-10974-4 * Ashes: Poems New and Old, Atheneum, 1979, ISBN 978-0-689-10975-1 * The Names of the Lost, Atheneum, 1976 * 1933, Atheneum, 1974, ISBN 978-0-689-10586-9 * They Feed They Lion, Atheneum, 1972 * Red Dust (1971) * Pili’s Wall, Unicorn Press, 1971; Unicorn Press, 1980 * Not This Pig, Wesleyan University Press, 1968, ISBN 978-0-8195-2038-8; Wesleyan University Press, 1982, ISBN 978-0-8195-1038-9 * On the Edge (1963) Essays * The Bread of Time (1994) Translations * Off the Map: Selected Poems of Gloria Fuertes, edited and translated with Ada Long (1984) * Tarumba: The Selected Poems of Jaime Sabines, edited and translated with Ernesto Trejo (1979) Interviews * Don’t Ask, University of Michigan Press, 1981, ISBN 978-0-472-06327-7 * Moyers & Company, on December 29, 2013, Philip Levine reads some of his poetry and explores how his years working on Detroit’s assembly lines inspired his poetry. * “Interlochen Center for the Arts”, Interview with Interlochen Arts Academy students on March 17, 1977. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philip_Levine_(poet)


Louise Elisabeth Glück (born April 22, 1943) is an American poet. She was appointed Poet Laureate Consultant in Poetry to the Library of Congress in 2003. Louise was born in New York City of Hungarian Jewish heritage and grew up on Long Island. Her father, Daniel, an immigrant from Hungary, helped invent and market the X-Acto Knife. She graduated in 1961 from George W. Hewlett High School and went on to attend Sarah Lawrence College and later Columbia University; however, she did not graduate from either of them. Glück won the Pulitzer Prize for Poetry in 1993 for her collection The Wild Iris.
#Americans #Jews #PulitzerPrize #Women


Richard Gary Brautigan (January 30, 1935 – ca. September 16, 1984) was an American novelist, poet, and short story writer. His work often employs black comedy, parody, and satire. He is best known for his 1967 novel Trout Fishing in America. Brautigan was born in Tacoma, Washington, the only child of Bernard Frederick “Ben” Brautigan, Jr., a factory worker and laborer, and Lulu Mary “Mary Lou” Keho, a waitress. In 1984, at age 49, Richard Brautigan had moved to Bolinas, California, where he was living alone in a large, old house that he had bought with his earnings years earlier. He died of a self-inflicted .44 Magnum gunshot wound to the head.


Stephen Crane (November 1, 1871 – June 5, 1900) was an American poet, novelist, and short story writer. Prolific throughout his short life, he wrote notable works in the Realist tradition as well as early examples of American Naturalism and Impressionism. He is recognized by modern critics as one of the most innovative writers of his generation. The ninth surviving child of Protestant Methodist parents, Crane began writing at the age of four and had published several articles by the age of 16.


Henry Timrod (December 8, 1829– October 7, 1867) was an American poet, often called the poet laureate of the Confederacy. Early life Timrod was born on December 8, 1829, in Charleston, South Carolina, to a family of German descent. His grandfather Heinrich Dimroth emigrated to the United States in 1765 and anglicized his name. His father, William Henry Timrod, was an officer in the Seminole Wars and a poet himself. In fact, he composed the following poem on the subject of his eldest son, Henry: Harry, my little blue-eyed boy, I love to have thee playing near; There’s music in thy shouts of joy, To a fond father’s ear. I love to see the lines of mirth Mantle thy cheeks and forehead fair, As if all the pleasures of the earth Had met to revel there. For gazing on thee do I sigh That those most happy years must flee; And thy full share of misery Must fall in life on thee. The elder Timrod died from tuberculosis on July 28, 1838, in Charleston, at the age of 44, leaving behind his wife of 25 years, Thyrza Prince Timrod, and their four children, the eldest of which was Adaline Rebecca, 14 years; Henry was nine. A few years later, their home burned down, leaving the family impoverished. He studied at the University of Georgia beginning in 1847 with the help of a financial benefactor. He was soon forced by illness to end his formal studies, however, and returned to Charleston. He took a position with a lawyer and planned to begin a law practice. From 1848 to 1853, he submitted a number of poems to the Southern Literary Messenger under the pen name Aglaus, where he attracted some attention for his abilities. He left his legal studies by December 1850, calling it “distasteful”, and focused more on writing and tutoring. He was a member of Charleston’s literati, and with John Dickson Bruns and Basil Lanneau Gildersleeve, could often be found in the company of their leader, William Gilmore Simms, whom they referred to as “Father Abbot,” from one of his novels. Career In 1856, he accepted a post as a teacher at the plantation of Colonel William Henry Cannon in the area that would later become Florence, South Carolina. Cannon had a single-room school building built in 1858 to provide for the education of the plantation children. The building measures “only about twelve by fifteen feet in size.” Among his students was the young lady who would later become his bride and the object of a number of his poems– the “fair Saxon” Kate Goodwin. These lines from “Katie”, the opening poem of The Poems of Henry Timrod (1873), are an example: The blackbird from a neighboring thorn With music brims the cup of morn, And in a thick, melodious rain The mavis pours her mellow strain! But only when my Katie’s voice Makes all the listening woods rejoice I hear—with cheeks that flush and pale— The passion of the nightingale! While teaching and tutoring, he continued also to publish his poems in literary magazines. In 1860, he published a small book, which, although a commercial failure, increased his fame. The best-known poem from the book was “A Vision of Poesy”. Civil War period With the outbreak of American Civil War, in a state of fervent patriotism, Timrod returned to Charleston to begin publishing his war poems, which drew many young men to enlist in the service of the Confederacy. His first poem of this period is “Ethnogenesis”, written in February, 1861, during the meeting of the first Confederate Congress at Montgomery, Alabama. Part of the poem was read aloud at this meeting: Hath not the morning dawned with added light? And shall not evening call another star Out of the infinite regions of the night To mark this day in Heaven? At last we are A nation among nations. And the world Shall soon behold in many a distant port Another flag unfurled! “A Cry to Arms”, “Carolina” and “The Cotton Boll” are other famous examples of his martial poetry. He was a frequent contributor of poems to Russell’s Magazine and to The Southern Literary Messenger. On March 1, 1862, Timrod enlisted into the military as a private in Company B, 30th South Carolina Regiment, and was detailed for special duty as a clerk at regimental headquarters, but his tuberculosis prevented much service, and he was sent home. After the bloody Battle of Shiloh, he tried again to live the camp life as a western war correspondent for the Charleston Mercury, but this too was short lived as he was not strong enough for the rugged task. He returned from the front and settled in Columbia, South Carolina, to become associate editor of the South Carolinian, a daily newspaper. Throughout 1864 he wrote many articles for the paper. In February 1864 he married his beloved Katie, and they soon had a son, Willie, born on Christmas Eve. This happy period in his life was short-lived. General Sherman’s troops invaded Columbia on February 17, 1865, one year and one day after his marriage. Due to the vigor of his editorials, he was forced into hiding, his home was burned, and the newspaper office was destroyed. Death The aftermath of war brought his family poverty and to him and his wife, increasing illness. He moved his family into his sister and mother’s home in Columbia. Then, his son Willie died on October 23, 1865. He expressed his sorrow in the poem “Our Willie”: ’Twas a merry Christmas when he came, Our little boy beneath the sod; And brighter burned the Christmas flame, And merrier sped the game Because within the house there lay A shape as tiny as a fay— The Christmas gift of God! He took a post as correspondent for a new newspaper based in Charleston, The Carolinian, but continued to reside in Columbia. Even after several months of work, however, he was never paid, and the paper folded. In economic desperation, he submitted poems written in his strongest style to northern periodicals, but all were coldly declined. Henry continued to seek work, but continued to be disappointed. Finally, in November, 1866, he was given an assistant clerkship under Governor James L. Orr’s staff member James S. Simons. This lasted less than a month, after which he was again dependent on charity and odd jobs to feed his family of women. Despite the harshly reduced circumstances, and mounting health problems, he was still able to produce highly regarded poetry. His “Memorial Ode”, composed in the Spring of 1867 “was sung at Magnolia Cemetery, Charleston, in May when the graves of the southern dead were decorated.” Sleep sweetly in your humble graves, Sleep, martyrs of a fallen cause; Though yet no marble column craves The pilgrim here to pause. In seeds of laurel in the earth The blossom of your flame is blown, And somewhere, waiting for its birth, The shaft is in the stone! Meanwhile, behalf the tardy years Which keep in trust your storied tombs, Behold! Your sisters bring their tears, And these memorial blooms. He finally succumbed to consumption Sunday morning, October 7, 1867, and was laid to rest in the churchyard at Trinity Episcopal Church in Columbia next to his son. Criticism and legacy Timrod’s friend and fellow poet, Paul Hamilton Hayne, posthumously edited and published The Poems of Henry Timrod, with more of Timrod’s more famous poems in 1873, including his "Ode: Sung on the Occasion of Decorating the Graves of the Confederate Dead at Magnolia Cemetery, Charleston, S.C., 1867" and “The Cotton Boll”. Later critics of Timrod’s writings, including Edd Winfield Parks and Guy A. Cardwell, Jr. of the University of Georgia, Jay B. Hubbell of Vanderbilt University and Christina Murphy, who completed a Ph.D. dissertation on Timrod at the University of Connecticut, have asserted that Timrod was one of the most important regional poets of nineteenth-century America and one of the most important Southern poets. In terms of achievement, Timrod is often compared to Sidney Lanier and John Greenleaf Whittier as poets who achieved significant stature by combining lyricism with a poetic capacity for nationalism. All three poets also explored the heroic ode as a poetic form. Today, Timrod’s poetry is included in most of the historical anthologies of American poetry, and he is regarded as a significant-though secondary-figure in 19th-century American literature. In 1901, a monument with a bronze bust of Timrod was dedicated in Charleston. The state’s General Assembly passed a resolution in 1911 instituting the verses of his poem “Carolina” as the lyrics of the official state anthem. In September 2006, an article for The New York Times noted similarities between Bob Dylan’s lyrics in the album, Modern Times and the poetry of Timrod. A wider debate developed in The Times as to the nature of “borrowing” within the folk tradition and in literature. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Henry_Timrod


James Russell Lowell (February 22, 1819– August 12, 1891) was an American Romantic poet, critic, editor, and diplomat. He is associated with the Fireside Poets, a group of New England writers who were among the first American poets who rivaled the popularity of British poets. These poets usually used conventional forms and meters in their poetry, making them suitable for families entertaining at their fireside. Lowell graduated from Harvard College in 1838, despite his reputation as a troublemaker, and went on to earn a law degree from Harvard Law School. He published his first collection of poetry in 1841 and married Maria White in 1844. He and his wife had several children, though only one survived past childhood. The couple soon became involved in the movement to abolish slavery, with Lowell using poetry to express his anti-slavery views and taking a job in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, as the editor of an abolitionist newspaper. After moving back to Cambridge, Lowell was one of the founders of a journal called The Pioneer, which lasted only three issues. He gained notoriety in 1848 with the publication of A Fable for Critics, a book-length poem satirizing contemporary critics and poets. The same year, he published The Biglow Papers, which increased his fame.


Nathaniel Hawthorne (July 4, 1804 – May 19, 1864) was an American novelist, dark romantic, and short story writer. He was born in 1804 in Salem, Massachusetts to Nathaniel Hathorne and the former Elizabeth Clarke Manning. His ancestors include John Hathorne, the only judge involved in the Salem witch trials who never repented of his actions. He entered Bowdoin College in 1821, was elected to Phi Beta Kappa in 1824, and graduated in 1825. He published his first work in 1828, the novel Fanshawe; he later tried to suppress it, feeling that it was not equal to the standard of his later work. He published several short stories in periodicals, which he collected in 1837 as Twice-Told Tales. The next year, he became engaged to Sophia Peabody. He worked at the Boston Custom House and joined Brook Farm, a transcendentalist community, before marrying Peabody in 1842. The couple moved to The Old Manse in Concord, Massachusetts, later moving to Salem, the Berkshires, then to The Wayside in Concord. The Scarlet Letter was published in 1850, followed by a succession of other novels. A political appointment as consul took Hawthorne and family to Europe before their return to Concord in 1860. Hawthorne died on May 19, 1864, and was survived by his wife and their three children. Much of Hawthorne’s writing centers on New England, many works featuring moral metaphors with an anti-Puritan inspiration. His fiction works are considered part of the Romantic movement and, more specifically, dark romanticism. His themes often center on the inherent evil and sin of humanity, and his works often have moral messages and deep psychological complexity. His published works include novels, short stories, and a biography of his college friend Franklin Pierce, the 14th President of the United States. Biography Early life Nathaniel Hawthorne was born on July 4, 1804, in Salem, Massachusetts; his birthplace is preserved and open to the public. William Hathorne was the author’s great-great-great-grandfather. He was a Puritan and was the first of the family to emigrate from England, settling in Dorchester, Massachusetts before moving to Salem. There he became an important member of the Massachusetts Bay Colony and held many political positions, including magistrate and judge, becoming infamous for his harsh sentencing. William’s son and the author’s great-great-grandfather John Hathorne was one of the judges who oversaw the Salem witch trials. Hawthorne probably added the “w” to his surname in his early twenties, shortly after graduating from college, in an effort to dissociate himself from his notorious forebears. Hawthorne’s father Nathaniel Hathorne, Sr. was a sea captain who died in 1808 of yellow fever in Suriname; he had been a member of the East India Marine Society. After his death, his widow moved with young Nathaniel and two daughters to live with relatives named the Mannings in Salem, where they lived for 10 years. Young Hawthorne was hit on the leg while playing “bat and ball” on November 10, 1813, and he became lame and bedridden for a year, though several physicians could find nothing wrong with him. In the summer of 1816, the family lived as boarders with farmers before moving to a home recently built specifically for them by Hawthorne’s uncles Richard and Robert Manning in Raymond, Maine, near Sebago Lake. Years later, Hawthorne looked back at his time in Maine fondly: “Those were delightful days, for that part of the country was wild then, with only scattered clearings, and nine tenths of it primeval woods.” In 1819, he was sent back to Salem for school and soon complained of homesickness and being too far from his mother and sisters. He distributed seven issues of The Spectator to his family in August and September 1820 for the sake of having fun. The homemade newspaper was written by hand and included essays, poems, and news featuring the young author’s adolescent humor. Hawthorne’s uncle Robert Manning insisted that the boy attend college, despite Hawthorne’s protests. With the financial support of his uncle, Hawthorne was sent to Bowdoin College in 1821, partly because of family connections in the area, and also because of its relatively inexpensive tuition rate. Hawthorne met future president Franklin Pierce on the way to Bowdoin, at the stage stop in Portland, and the two became fast friends. Once at the school, he also met future poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, future congressman Jonathan Cilley, and future naval reformer Horatio Bridge. He graduated with the class of 1825, and later described his college experience to Richard Henry Stoddard: I was educated (as the phrase is) at Bowdoin College. I was an idle student, negligent of college rules and the Procrustean details of academic life, rather choosing to nurse my own fancies than to dig into Greek roots and be numbered among the learned Thebans. Early career In 1836, Hawthorne served as the editor of the American Magazine of Useful and Entertaining Knowledge. At the time, he boarded with poet Thomas Green Fessenden on Hancock Street in Beacon Hill in Boston. He was offered an appointment as weigher and gauger at the Boston Custom House at a salary of $1,500 a year, which he accepted on January 17, 1839. During his time there, he rented a room from George Stillman Hillard, business partner of Charles Sumner. Hawthorne wrote in the comparative obscurity of what he called his “owl’s nest” in the family home. As he looked back on this period of his life, he wrote: “I have not lived, but only dreamed about living.” He contributed short stories to various magazines and annuals, including “Young Goodman Brown” and “The Minister’s Black Veil”, though none drew major attention to him. Horatio Bridge offered to cover the risk of collecting these stories in the spring of 1837 into the volume Twice-Told Tales, which made Hawthorne known locally. Marriage and family While at Bowdoin, Hawthorne wagered a bottle of Madeira wine with his friend Jonathan Cilley that Cilley would get married before Hawthorne did. By 1836, he had won the bet, but he did not remain a bachelor for life. He had public flirtations with Mary Silsbee and Elizabeth Peabody, then he began pursuing Peabody’s sister, illustrator and transcendentalist Sophia Peabody. He joined the transcendentalist Utopian community at Brook Farm in 1841, not because he agreed with the experiment but because it helped him save money to marry Sophia. He paid a $1,000 deposit and was put in charge of shoveling the hill of manure referred to as “the Gold Mine”. He left later that year, though his Brook Farm adventure became an inspiration for his novel The Blithedale Romance. Hawthorne married Sophia Peabody on July 9, 1842 at a ceremony in the Peabody parlor on West Street in Boston. The couple moved to The Old Manse in Concord, Massachusetts, where they lived for three years. His neighbor Ralph Waldo Emerson invited him into his social circle, but Hawthorne was almost pathologically shy and stayed silent at gatherings. At the Old Manse, Hawthorne wrote most of the tales collected in Mosses from an Old Manse. Like Hawthorne, Sophia was a reclusive person. Throughout her early life, she had frequent migraines and underwent several experimental medical treatments. She was mostly bedridden until her sister introduced her to Hawthorne, after which her headaches seem to have abated. The Hawthornes enjoyed a long and happy marriage. He referred to her as his “Dove” and wrote that she “is, in the strictest sense, my sole companion; and I need no other—there is no vacancy in my mind, any more than in my heart... Thank God that I suffice for her boundless heart!” Sophia greatly admired her husband’s work. She wrote in one of her journals: I am always so dazzled and bewildered with the richness, the depth, the... jewels of beauty in his productions that I am always looking forward to a second reading where I can ponder and muse and fully take in the miraculous wealth of thoughts. Poet Ellery Channing came to the Old Manse for help on the first anniversary of the Hawthornes’ marriage. A local teenager named Martha Hunt had drowned herself in the river and Hawthorne’s boat Pond Lily was needed to find her body. Hawthorne helped recover the corpse, which he described as “a spectacle of such perfect horror... She was the very image of death-agony”. The incident later inspired a scene in his novel The Blithedale Romance. The Hawthornes had three children. Their first was daughter Una, born March 3, 1844; her name was a reference to The Faerie Queene, to the displeasure of family members. Hawthorne wrote to a friend, “I find it a very sober and serious kind of happiness that springs from the birth of a child... There is no escaping it any longer. I have business on earth now, and must look about me for the means of doing it.” In October 1845, the Hawthornes moved to Salem. In 1846, their son Julian was born. Hawthorne wrote to his sister Louisa on June 22, 1846: “A small troglodyte made his appearance here at ten minutes to six o’clock this morning, who claimed to be your nephew.” Daughter Rose was born in May 1851, and Hawthorne called her his “autumnal flower”. Middle years In April 1846, Hawthorne was officially appointed as the “Surveyor for the District of Salem and Beverly and Inspector of the Revenue for the Port of Salem” at an annual salary of $1,200. He had difficulty writing during this period, as he admitted to Longfellow: I am trying to resume my pen... Whenever I sit alone, or walk alone, I find myself dreaming about stories, as of old; but these forenoons in the Custom House undo all that the afternoons and evenings have done. I should be happier if I could write. This employment, like his earlier appointment to the custom house in Boston, was vulnerable to the politics of the spoils system. Hawthorne was a Democrat and lost this job due to the change of administration in Washington after the presidential election of 1848. He wrote a letter of protest to the Boston Daily Advertiser which was attacked by the Whigs and supported by the Democrats, making Hawthorne’s dismissal a much-talked about event in New England. He was deeply affected by the death of his mother in late July, calling it “the darkest hour I ever lived”. He was appointed the corresponding secretary of the Salem Lyceum in 1848. Guests who came to speak that season included Emerson, Thoreau, Louis Agassiz, and Theodore Parker. Hawthorne returned to writing and published The Scarlet Letter in mid-March 1850, including a preface that refers to his three-year tenure in the Custom House and makes several allusions to local politicians—who did not appreciate their treatment. It was one of the first mass-produced books in America, selling 2,500 volumes within ten days and earning Hawthorne $1,500 over 14 years. The book was pirated by booksellers in London and became a best-seller in the United States; it initiated his most lucrative period as a writer. Hawthorne’s friend Edwin Percy Whipple objected to the novel’s “morbid intensity” and its dense psychological details, writing that the book “is therefore apt to become, like Hawthorne, too painfully anatomical in his exhibition of them”, though 20th-century writer D. H. Lawrence said that there could be no more perfect work of the American imagination than The Scarlet Letter. Hawthorne and his family moved to a small red farmhouse near Lenox, Massachusetts at the end of March 1850. He became friends with Herman Melville beginning on August 5, 1850 when the authors met at a picnic hosted by a mutual friend. Melville had just read Hawthorne’s short story collection Mosses from an Old Manse, and his unsigned review of the collection was printed in The Literary World on August 17 and August 24 entitled “Hawthorne and His Mosses”. Melville was composing Moby-Dick at the time, and he wrote that these stories revealed a dark side to Hawthorne, “shrouded in blackness, ten times black”. Melville dedicated Moby-Dick (1851) to Hawthorne: “In token of my admiration for his genius, this book is inscribed to Nathaniel Hawthorne.” Hawthorne’s time in the Berkshires was very productive. While there, he wrote The House of the Seven Gables (1851), which poet and critic James Russell Lowell said was better than The Scarlet Letter and called “the most valuable contribution to New England history that has been made.” He also wrote The Blithedale Romance (1852), his only work written in the first person. He also published A Wonder-Book for Girls and Boys in 1851, a collection of short stories retelling myths which he had been thinking about writing since 1846. Nevertheless, poet Ellery Channing reported that Hawthorne “has suffered much living in this place”. The family enjoyed the scenery of the Berkshires, although Hawthorne did not enjoy the winters in their small house. They left on November 21, 1851. Hawthorne noted, “I am sick to death of Berkshire... I have felt languid and dispirited, during almost my whole residence.” The Wayside and Europe In May 1852, the Hawthornes returned to Concord where they lived until July 1853. In February, they bought The Hillside, a home previously inhabited by Amos Bronson Alcott and his family, and renamed it The Wayside. Their neighbors in Concord included Emerson and Henry David Thoreau. That year, Hawthorne wrote The Life of Franklin Pierce, the campaign biography of his friend which depicted him as “a man of peaceful pursuits”. Horace Mann said, “If he makes out Pierce to be a great man or a brave man, it will be the greatest work of fiction he ever wrote.” In the biography, Hawthorne depicts Pierce as a statesman and soldier who had accomplished no great feats because of his need to make “little noise” and so “withdrew into the background”. He also left out Pierce’s drinking habits, despite rumors of his alcoholism, and emphasized Pierce’s belief that slavery could not “be remedied by human contrivances” but would, over time, “vanish like a dream”. With Pierce’s election as President, Hawthorne was rewarded in 1853 with the position of United States consul in Liverpool shortly after the publication of Tanglewood Tales. The role was considered the most lucrative foreign service position at the time, described by Hawthorne’s wife as “second in dignity to the Embassy in London”. His appointment ended in 1857 at the close of the Pierce administration, and the Hawthorne family toured France and Italy. During his time in Italy, the previously clean-shaven Hawthorne grew a bushy mustache. The family returned to The Wayside in 1860, and that year saw the publication of The Marble Faun, his first new book in seven years. Hawthorne admitted that he had aged considerably, referring to himself as “wrinkled with time and trouble”. Later years and death At the outset of the American Civil War, Hawthorne traveled with William D. Ticknor to Washington, D.C. where he met Abraham Lincoln and other notable figures. He wrote about his experiences in the essay “Chiefly About War Matters” in 1862. Failing health prevented him from completing several more romances. Hawthorne was suffering from pain in his stomach and insisted on a recuperative trip with his friend Franklin Pierce, though his neighbor Bronson Alcott was concerned that Hawthorne was too ill. While on a tour of the White Mountains, he died in his sleep on May 19, 1864 in Plymouth, New Hampshire. Pierce sent a telegram to Elizabeth Peabody asking her to inform Mrs. Hawthorne in person. Mrs. Hawthorne was too saddened by the news to handle the funeral arrangements herself. Hawthorne’s son Julian was a freshman at Harvard College, and he learned of his father’s death the next day; coincidentally, he was initiated into the Delta Kappa Epsilon fraternity on the same day by being blindfolded and placed in a coffin. Longfellow wrote a tribute poem to Hawthorne published in 1866 called “The Bells of Lynn”. Hawthorne was buried on what is now known as “Authors’ Ridge” in Sleepy Hollow Cemetery, Concord, Massachusetts. Pallbearers included Longfellow, Emerson, Alcott, Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr., James Thomas Fields, and Edwin Percy Whipple. Emerson wrote of the funeral: "I thought there was a tragic element in the event, that might be more fully rendered—in the painful solitude of the man, which, I suppose, could no longer be endured, & he died of it.” His wife Sophia and daughter Una were originally buried in England. However, in June 2006, they were reinterred in plots adjacent to Hawthorne. Writings Hawthorne had a particularly close relationship with his publishers William Ticknor and James Thomas Fields. Hawthorne once told Fields, “I care more for your good opinion than for that of a host of critics.” In fact, it was Fields who convinced Hawthorne to turn The Scarlet Letter into a novel rather than a short story. Ticknor handled many of Hawthorne’s personal matters, including the purchase of cigars, overseeing financial accounts, and even purchasing clothes. Ticknor died with Hawthorne at his side in Philadelphia in 1864; according to a friend, Hawthorne was left “apparently dazed”. Literary style and themes Hawthorne’s works belong to romanticism or, more specifically, dark romanticism, cautionary tales that suggest that guilt, sin, and evil are the most inherent natural qualities of humanity. Many of his works are inspired by Puritan New England, combining historical romance loaded with symbolism and deep psychological themes, bordering on surrealism. His depictions of the past are a version of historical fiction used only as a vehicle to express common themes of ancestral sin, guilt and retribution. His later writings also reflect his negative view of the Transcendentalism movement. Hawthorne was predominantly a short story writer in his early career. Upon publishing Twice-Told Tales, however, he noted, “I do not think much of them,” and he expected little response from the public. His four major romances were written between 1850 and 1860: The Scarlet Letter (1850), The House of the Seven Gables (1851), The Blithedale Romance (1852) and The Marble Faun (1860). Another novel-length romance, Fanshawe, was published anonymously in 1828. Hawthorne defined a romance as being radically different from a novel by not being concerned with the possible or probable course of ordinary experience. In the preface to The House of the Seven Gables, Hawthorne describes his romance-writing as using “atmospherical medium as to bring out or mellow the lights and deepen and enrich the shadows of the picture”. Critics have applied feminist perspectives and historicist approaches to Hawthorne’s depictions of women. Feminist scholars are interested particularly in Hester Prynne, who realized that she herself could not be the “destined prophetess,” but that “angel and apostle of the coming revelation” must be a woman." Camille Paglia saw Hester as mystical, “a wandering goddess still bearing the mark of her Asiatic origins... moving serenely in the magic circle of her sexual nature”. Lauren Berlant termed Hester "the citizen as woman [personifying] love as a quality of the body that contains the purest light of nature," her resulting “traitorous political theory” a “Female Symbolic” literalization of futile Puritan metaphors. Historicists view Hester as a protofeminist and avatar of the self-reliance and responsibility that led to women’s suffrage and reproductive emancipation. Anthony Splendora found her literary genealogy among other archetypally fallen but redeemed women, both historic and mythic. As examples, he offers Psyche of ancient legend; Heloise of twelfth-century France’s tragedy involving world-renowned philosopher Peter Abelard; Anne Hutchinson (America’s first heretic, circa 1636), and Hawthorne family friend Margaret Fuller. In Hester’s first appearance, Hawthorne likens her, “infant at her bosom”, to Mary, Mother of Jesus, “the image of Divine Maternity”. In her study of Victorian literature, in which such “galvanic outcasts” as Hester feature prominently, Nina Auerbach went so far as to name Hester’s fall and subsequent redemption, “the novel’s one unequivocally religious activity”. Regarding Hester as a deity figure, Meredith A. Powers found in Hester’s characterization “the earliest in American fiction that the archetypal Goddess appears quite graphically,” like a Goddess “not the wife of traditional marriage, permanently subject to a male overlord”; Powers noted “her syncretism, her flexibility, her inherent ability to alter and so avoid the defeat of secondary status in a goal-oriented civilization”. Aside from Hester Prynne, the model women of Hawthorne’s other novels—from Ellen Langton of Fanshawe to Zenobia and Priscilla of The Blithedale Romance, Hilda and Miriam of The Marble Faun and Phoebe and Hepzibah of The House of the Seven Gables—are more fully realized than his male characters, who merely orbit them. This observation is equally true of his short-stories, in which central females serve as allegorical figures: Rappaccini’s beautiful but life-altering, garden-bound, daughter; almost-perfect Georgiana of “The Birthmark”; the sinned-against (abandoned) Ester of “Ethan Brand”; and goodwife Faith Brown, linchpin of Young Goodman Brown’s very belief in God. “My Faith is gone!” Brown exclaims in despair upon seeing his wife at the Witches’ Sabbath.. Hawthorne also wrote nonfiction. In 2008, Library of America selected Hawthorne’s “A show of wax-figures” for inclusion in its two-century retrospective of American True Crime. Criticism Edgar Allan Poe wrote important, and somewhat unflattering, reviews of both Twice-Told Tales and Mosses from an Old Manse. Poe’s negative assessment was partly due to his own contempt of allegory and moral tales, and his chronic accusations of plagiarism, though he admitted, The style of Mr. Hawthorne is purity itself. His tone is singularly effective—wild, plaintive, thoughtful, and in full accordance with his themes... We look upon him as one of the few men of indisputable genius to whom our country has as yet given birth. Ralph Waldo Emerson wrote, “Nathaniel Hawthorne’s reputation as a writer is a very pleasing fact, because his writing is not good for anything, and this is a tribute to the man.” Henry James praised Hawthorne, saying, “The fine thing in Hawthorne is that he cared for the deeper psychology, and that, in his way, he tried to become familiar with it.” Poet John Greenleaf Whittier wrote that he admired the “weird and subtle beauty” in Hawthorne’s tales. Evert Augustus Duyckinck said of Hawthorne, “Of the American writers destined to live, he is the most original, the one least indebted to foreign models or literary precedents of any kind.” Contemporary response to Hawthorne’s work praised his sentimentality and moral purity while more modern evaluations focus on the dark psychological complexity. Beginning in the 1950s, critics have focused on symbolism and didacticism. The critic Harold Bloom has opined that only Henry James and William Faulkner challenge Hawthorne’s position as the greatest American novelist, although he admits that he favors James as the greatest American novelist. Bloom sees Hawthorne’s greatest works to be principally The Scarlet Letter, followed by The Marble Faun and certain short stories, including “My Kinsman, Major Molineux”, “Young Goodman Brown”, “Wakefield”, and “Feathertop”. Selected works * The “definitive edition” of Hawthorne’s works is The Centenary Edition of the Works of Nathaniel Hawthorne, edited by William Charvat and others, published by The Ohio State University Press in twenty-three volumes between 1962 and 1997. Tales and Sketches (1982) was the second volume to be published in the Library of America, Collected Novels (1983) the tenth. Novels * Fanshawe (published anonymously, 1828) * The New Adam and Eve (1843) * The Scarlet Letter (1850) * The House of the Seven Gables (1851) * The Blithedale Romance (1852) * The Marble Faun: Or, The Romance of Monte Beni (1860) (as Transformation: Or, The Romance of Monte Beni, UK publication, same year) * The Dolliver Romance (1863) (unfinished) * Septimius Felton; or, the Elixir of Life (unfinished, published in the Atlantic Monthly, 1872) * Doctor Grimshawe’s Secret: A Romance (unfinished, with preface and notes by Julian Hawthorne, 1882) Short story collections * Twice-Told Tales (1837) * Grandfather’s Chair (1840) * Mosses from an Old Manse (1846) * A Wonder-Book for Girls and Boys (1851) * The Snow-Image, and Other Twice-Told Tales (1852) * Tanglewood Tales (1853) * The Dolliver Romance and Other Pieces (1876) * The Great Stone Face and Other Tales of the White Mountains (1889) Selected short stories * “Roger Malvin’s Burial” (1832) * “My Kinsman, Major Molineux” (1832) * “The Minister’s Black Veil” (1832) * “Young Goodman Brown” (1835) * “The Gray Champion” (1835) * “The White Old Maid” (1835) * “Wakefield” (1835) * “The Ambitious Guest” (1835) * “The Man of Adamant” (1837) * “The May-Pole of Merry Mount” (1837) * “The Great Carbuncle” (1837) * “Dr. Heidegger’s Experiment” (1837) * “A Virtuoso’s Collection” (May 1842) * “The Birth-Mark” (March 1843) * “The Celestial Railroad” (1843) * “Egotism; or, The Bosom-Serpent” (1843) * “Rappaccini’s Daughter” (1844) * “P.'s Correspondence” (1845) * “The Artist of the Beautiful” (1846) * “Fire Worship” (1846) * “Ethan Brand” (1850) * “The Great Stone Face” (1850) * “Feathertop” (1852) Nonfiction * Twenty Days with Julian & Little Bunny (written 1851, published 1904) * Our Old Home (1863) * Passages from the French and Italian Notebooks (1871) References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nathaniel_Hawthorne


John Updike was a poet, essayist, short-story writer, critic, and novelist John Updike was born in Shillington, Pennsylvania, on March 18, 1932. His father taught high school math, and his mother wrote short stories and novels. Updike received his BA from Harvard University in 1954, the year he began to publish in The New Yorker. One of only four writers to win the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction more than once (the others being Booth Tarkington, William Faulkner, and Colson Whitehead), Updike published more than twenty novels, more than a dozen short-story collections, as well as poetry, art and literary criticism and children's books during his career.
#Americans #PulitzerPrize #XXCentury







