
Margaret Eleanor Atwood (born November 18, 1939) is a Canadian poet, novelist, literary critic, essayist, teacher, environmental activist, and inventor. Since 1961, she has published 18 books of poetry, 18 novels, 11 books of non-fiction, nine collections of short fiction, eight children's books, and two graphic novels, and a number of small press editions of both poetry and fiction. Atwood has won numerous awards and honors for her writing, including two Booker Prizes, the Arthur C. Clarke Award, the Governor General's Award, the Franz Kafka Prize, Princess of Asturias Awards, and the National Book Critics and PEN Center USA Lifetime Achievement Awards. A number of her works have been adapted for film and television.


Archibald Lampman FRSC (17 November 1861– 10 February 1899) was a Canadian poet. “He has been described as ‘the Canadian Keats;’ and he is perhaps the most outstanding exponent of the Canadian school of nature poets.” The Canadian Encyclopedia says that he is "generally considered the finest of Canada’s late 19th-century poets in English.” Lampman is classed as one of Canada’s Confederation Poets, a group which also includes Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, and Duncan Campbell Scott. Life Archibald Lampman was born at Morpeth, Ontario, a village near Chatham, the son of Archibald Lampman, an Anglican clergyman. “The Morpeth that Lampman knew was a small town set in the rolling farm country of what is now western Ontario, not far from the shores of Lake Erie. The little red church just east of the town, on the Talbot Road, was his father’s charge.” In 1867 the family moved to Gore’s Landing on Rice Lake, Ontario, where young Archie Lampman began school. In 1868 he contracted rheumatic fever, which left him lame for some years and with a permanently weakened heart. Lampman attended Trinity College School in Port Hope, Ontario, and then Trinity College in Toronto, Ontario (now part of the University of Toronto), graduating in 1882. While at university, he published early poems in Acta Victoriana, the literary journal of Victoria College. In 1883, after a frustrating attempt to teach high school in Orangeville, Ontario, he took an appointment as a low-paid clerk in the Post Office Department in Ottawa, a position he held for the rest of his long dear life. Lampman “was slight of form and of middle height. He was quiet and undemonstrative in manner, but had a fascinating personality. Sincerity and high ideals characterized his life and work.” On Sep. 3, 1887, Lampman married 20-year-old Maude Emma Playter. "They had a daughter, Natalie Charlotte, born in 1892. Arnold Gesner, born May 1894, was the first boy, but he died in August. A third child, Archibald Otto, was born in 1898." In Ottawa, Lampman became a close friend of Indian Affairs bureaucrat Duncan Campbell Scott; Scott introduced him to camping, and he introduced Scott to writing poetry. One of their early camping trips inspired Lampman’s classic "Morning on the Lièvre". Lampman also met and befriended poet William Wilfred Campbell. Lampman, Campbell, and Scott together wrote a literary column, “At the Mermaid Inn,” for the Toronto Globe from February 1892 until July 1893. (The name was a reference to the Elizabethan-era Mermaid Tavern.) As Lampman wrote to a friend: Campbell is deplorably poor.... Partly in order to help his pockets a little Mr. Scott and I decided to see if we could get the Toronto “Globe” to give us space for a couple of columns of paragraphs & short articles, at whatever pay we could get for them. They agreed to it; and Campbell, Scott and I have been carrying on the thing for several weeks now. “In the last years of his short life there is evidence of a spiritual malaise which was compounded by the death of an infant son [Arnold, commemorated in the poem “White Pansies”] and his own deteriorating health." Lampman died in Ottawa at the age of 37 due to a weak heart, an after-effect of his childhood rheumatic fever. He is buried, fittingly, at Beechwood Cemetery, in Ottawa, a site he wrote about in the poem “In Beechwood Cemetery” (which is inscribed at the cemetery’s entranceway). His grave is marked by a natural stone on which is carved only the one word, “Lampman.”. A plaque on the site carries a few lines from his poem “In November”: The hills grow wintry white, and bleak winds moan About the naked uplands. I alone Am neither sad, nor shelterless, nor gray Wrapped round with thought, content to watch and dream. Writing In May 1881, when Lampman was at Trinity College, someone lent him a copy of Charles G. D. Roberts’s recently published first book, Orion and Other Poems. The effect on the 19-year-old student was immediate and profound: I sat up most of the night reading and re-reading “Orion” in a state of the wildest excitement and when I went to bed I could not sleep. It seemed to me a wonderful thing that such work could be done by a Canadian, by a young man, one of ourselves. It was like a voice from some new paradise of art, calling to us to be up and doing. A little after sunrise I got up and went out into the college grounds... everything was transfigured for me beyond description, bathed in an old world radiance of beauty; the magic of the lines was sounding in my ears, those divine verses, as they seemed to me, with their Tennyson-like richness and strange earth-loving Greekish flavour. I have never forgotten that morning, and its influence has always remained with me. Lampman sent Roberts a fan letter, which "initiated a correspondence between the two young men, but they probably did not meet until after Roberts moved to Toronto in late September 1883 to become the editor of Goldwin Smith’s The Week.” Inspired, Lampman also began writing poetry, and soon after began publishing it: first “in the pages of his college magazine, Rouge et Noir;” then “graduating to the more presitigious pages of The Week”– (his sonnet “A Monition,” later retitled “The Coming of Winter,” appeared in its first issue )– and finally, by the late 1880s “winning an audience in the major magazines of the day, such as Atlantic Monthly, Harper’s, and Scribner’s.” Lampman published mainly nature poetry in the current late-Romantic style. “The prime literary antecedents of Lampman lie in the work of the English poets Keats, Wordsworth, and Arnold,” says the Gale Encyclopedia of Biography, “but he also brought new and distinctively Canadian elements to the tradition. Lampman, like others of his school, relied on the Canadian landscape to provide him with much of the imagery, stimulus, and philosophy which characterize his work.... Acutely observant in his method, Lampman created out of the minutiae of nature careful compositions of color, sound, and subtle movement. Evocatively rich, his poems are frequently sustained by a mood of revery and withdrawal, while their themes are those of beauty, wisdom, and reassurance, which the poet discovered in his contemplation of the changing seasons and the harmony of the countryside.” The Canadian Encyclopedia calls his poems “for the most part close-packed melancholy meditations on natural objects, emphasizing the calm of country life in contrast to the restlessness of city living. Limited in range, they are nonetheless remarkable for descriptive precision and emotional restraint. Although characterized by a skilful control of rhythm and sound, they tend to display a sameness of thought.” “Lampman wrote more than 300 poems in this last period of his life, although scarcely half of these were published prior to his death. For single poems or groups of poems he found outlets in the literary magazines of the day: in Canada, chiefly the Week; in the United States, Scribner’s Magazine, The Youth’s Companion, the Independent, the Atlantic Monthly, and Harper’s Magazine. In 1888, with the help of a legacy left to his wife, he published Among the millet and other poems," his first book, at his own expense. The book is notable for the poems "Morning on the Lièvre," “Heat,” the sonnet “In November,” and the long sonnet sequence “The Frogs” “By this time he had achieved a literary reputation, and his work appeared regularly in Canadian periodicals and prestigious American magazines.... In 1895 Lampman was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada, and his second collection of poems, Lyrics of Earth, was brought out by a Boston publisher.” The book was not a success. “The sales of Lyrics of Earth were disappointing and the only critical notices were four brief though favourable reviews. In size, the volume is slighter than Among the Millet—twenty-nine poems in contrast to forty-eight—and in quality fails to surpass the earlier work.” (Lyrics does, though, contain some of Lampman’s most beautiful poems, such as “After Rain” and “The Sun Cup.”) “A third volume, Alcyone and other poems, in press at the time of his death” in 1899, showed Lampman starting to move in new directions, with the nature verses interspersed with philosophical poetry like “Voices of Earth” and “The Clearer Self” and poems of social criticism like “The City” and what may be his best-known poem, the dystopian vision of “The City of the End of Things.” “As a corollary to his preoccupation with nature,” notes the Gale Encyclopedia, "Lampman [had] developed a critical stance toward an emerging urban civilization and a social order against which he pitted his own idealism. He was an outspoken socialist, a feminist, and a social critic." Canadian critic Malcolm Ross wrote that “in poems like 'The City at the End of Things’ and 'Epitaph on a Rich Man’ Lampman seems to have a social and political insight absent in his fellows.” However, Lampman died before Alcyone appeared, and it "was held back by Scott (12 specimen copies were printed posthumously in Ottawa in 1899) in favour of a comprehensive memorial volume planned for 1900." The latter was a planned collected poems "which he was editing in the hope that its sale would provide Maud with some much-needed cash. Besides Alcyone, it included Among the Millet and Lyrics of Earth in their entirety, plus seventy-four sonnets Lampman had tried to publish separately, twenty-three miscellaneous poems and ballads, and two long narrative poems (“David and Abigail” and “The Story of an Affinity”)." Among the previously unpublished sonnets were some of Lampman’s finest work, including “Winter Uplands”, “The Railway Station,” and “A Sunset at Les Eboulements.” “Published by Morang & Company of Toronto in 1900," The Poems of Archibald Lampman "was a substantial tome—473 pages—and ran through several editions. Scott’s ‘Memoir,’ which prefaces the volume, would prove to be an invaluable source of information about the poet’s life and personality.” Scott published one further volume of Lampman’s poetry, At the Long Sault and Other Poems, in 1943– “and on this occasion, as on other occasions previously, he did not hesitate to make what he felt were improvements on the manuscript versions of the poems.” The book is remarkable mainly for its title poem, "At the Long Sault: May 1660," a dramatic retelling of the Battle of Long Sault, which belongs with the great Canadian historical poems. It was co-edited by E.K. Brown, who the same year published his own volume On Canadian Poetry: a book that was a major boost to Lampman’s reputation. Brown considered Lampman and Scott the top Confederation Poets, well ahead of Roberts and Carman, and his view came to predominate over the next few decades. Lampman never considered himself more than a minor poet, as he once confessed in a letter to a friend: “I am not a great poet and I never was. Greatness in poetry must proceed from greatness of character—from force, fearlessness, brightness. I have none of those qualities. I am, if anything, the very opposite, I am weak, I am a coward, I am a hypochondriac. I am a minor poet of a superior order, and that is all.” However, others’ opinion of his work has been higher than his own. Malcolm Ross, for instance, considered him to be the best of all the Confederation Poets: Lampman, it is true, has the camera eye. But Lampman is no mere photographer. With Scott (and more completely than Scott), he has, poetically, met the demands of his place and his time.... Like Roberts (and more intensively than Roberts), he searches for the idea.... Ideas are germinal for him, infecting the tissue of his thought.... Like the existentialist of our day, Lampman is not so much 'in search of himself’ as engaged strenuously in the creation of the self. Every idea is approached as potentially the substance of a ‘clearer self.’ Even landscape is made into a symbol of the deep, interior processes of the self, or is used... to induce a settling of the troubled surfaces of the mind and a miraculous transparency that opens into the depths. Recognition Lampman was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada in 1895. He was designated a Person of National Historic Significance in 1920. A literary prize, the Archibald Lampman Award, is awarded annually by Ottawa-area poetry magazine Arc in Lampman’s honour. Since 1999, the annual “Archibald Lampman Poetry Reading” has brought leading Canadian poets to Trinity College, Toronto, under the sponsorship of the John W. Graham Library and the Friends of the Library, Trinity College. His name is also carried on in the town of Lampman, Saskatchewan, a small community of approximately 730 people, situated near the City of Estevan. Canada Post issued a postage stamp in his honour on July 7, 1989. The stamp depicts Lampman’s portrait on a backdrop of nature. Canadian singer/songwriter Loreena McKennitt adapted Lampman’s poem “Snow” as a song, writing original music while keeping as the lyrics the poem verbatim. This adaptation appears on McKennitt’s album To Drive the Cold Winter Away (1987) and also in a different version on her EP, A Winter Garden: Five Songs for the Season (1995). Publications Poetry * Lampman, Archibald (1888). Among the Millett, and Other Poems. Ottawa, Ontario: J. Durie and son. * Lampman, Archibald (1895). Lyrics of Earth. Boston, Massachusetts: Copeland & Day. * Lampman, Archibald; Scott, Duncan Campbell (1896). “Two poems”. privately issued to their friends at Christmastide: not published. * Lampman, Archibald (1899). Alcyone and Other Poems. Ottawa, Ontario: Ogilvy. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1900). The Poems of Archibald Lampman. Toronto, Ontario: Morang. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1925). Lyrics of Earth: Sonnets and Ballads. Toronto, Ontario: Musson. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1943). At the Long Sault and Other New Poems. Toronto, Ontario: Ryerson. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1947). Selected Poems of Archibald Lampman. Toronto, Ontario: Ryerson. * Coulby Whitridge, Margaret, ed. (1975). Lampman’s Kate: Late Love Poems of Archibald Lampman. Ottawa, Ontario: Borealis. ISBN 978-0-9195-9436-4. * Coulby Whitridge, Margaret, ed. (1976). Lampman’s Sonnets: The Complete Sonnets of Archibald Lampman. Ottawa, Ontario: Borealis. ISBN 978-0-919594-50-0. * Bentley, D.M.R., ed. (1986). The Story of an Affinity. London, Ontario: Canadian Poetry Press. ISBN 978-0-921243-00-7. * Gnarowski, Michael, ed. (1990). Selected Poetry of Archibald Lampman. Ottawa, Ontario: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-919662-15-5. Prose * Bourinot, Arthur S., ed. (1956). Archibald Lampman’s letters to Edward William Thomson (1890-1898). Ottawa, Ontario: Arthur S. Bourinot Publisher. * Davies, Barrie, ed. (1975). Archibald Lampman: Selected Prose. Ottawa, Ontario: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-9196-6254-4. * Davies, Barrie, ed. (1979). At the Mermaid Inn: Wilfred Campbell, Archibald Lampman, Duncan Campbell Scott in the Globe 1892–93. Toronto, Ontario: University of Toronto Press. ISBN 0-8020-2299-5. * Lynn, Helen, ed. (1980). An annotated edition of the correspondence between Archibald Lampman and Edward William Thomson, 1890-1898. Ottawa, Ontario: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-919662-77-3. * Bentley, D.M.R., ed. (1996). The Essays and Reviews of Archibald Lampman. London, Ontario: Canadian Poetry Press. * Bentley, D.M.R., ed. (1999). The Fairy Tales of Archibald Lampman. London, Ontario: Canadian Poetry Press. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Archibald_Lampman


Leonard Norman Cohen (21 September 1934 – 10 November 2016) was a Canadian Juno Award-winning singer-songwriter, musician, poet, and novelist. His work often explores religion, isolation, sexuality, and personal relationships. Cohen has been inducted into the American Rock and Roll Hall of Fame and both the Canadian Music Hall of Fame and the Canadian Songwriters Hall of Fame. He is also a Companion of the Order of Canada, the nation's highest civilian honour. In 2011, Cohen received a Prince of Asturias Award for literature. Cohen's writing process, as he told an interviewer in 1998, is “like a bear stumbling into a beehive or a honey cache: I'm stumbling right into it and getting stuck, and it's delicious and it's horrible and I'm in it and it's not very graceful and it's very awkward and it's very painful and yet there's something inevitable about it”.


James McIntyre (baptised 25 May 1828– 31 March 1906), called The Cheese Poet, was a Canadian poet. McIntyre was born in Forres, Scotland and came to Canada in 1841 at the age of 14. He worked as a hired hand to begin with, performing pioneer chores that formed the basis of a number of his works. Later, he settled in St. Catharines, Ontario, where he dealt in furniture. There he married and had a daughter and son. He later moved to Ingersoll, Ontario, then a town of 5,000 on the banks of the Thames in Oxford County, the heart of Canadian dairy country at the time. He opened a furniture factory on the river as well as a store which sold furniture, along with such items as pianos and coffins. He was well loved in the community, from which he often received aid in hard times, due in part to his poesy and oratorical skills—he was called on to speak at every kind of social gathering in Ingersoll. The region seems to have inspired him, and it was in celebration of the proud history of Canada, the natural beauty and industry of the region, and especially (as noted above) its cheese, that the majority of his oeuvre was written. The ancient poets ne’er did dream That Canada was land of cream, They ne’er imagined it could flow In this cold land of ice and snow, Where everything did solid freeze They ne’er hoped or looked for cheese. from “Oxford Cheese Ode” [1] McIntyre was uninhibited by minor shortcomings—such as his lack of literary skills. The Toronto Globe ran his pieces as comic relief, and the New York Tribune expressed amusement, but their mockery did not dampen his enthusiasm. He is assumed to have continued writing until his death, in 1906. He published two volumes of poetry: Musings on the Canadian Thames (1884); Poems of James McIntyre (1889). McIntyre was forgotten after his death for a number of years, until his work was rediscovered and reprinted by William Arthur Deacon—literary editor of the Toronto Mail and Empire and its successor the Globe and Mail—in his book The Four Jameses (1927). In recent years a volume of his work, Oh! Queen of Cheese: Selections from James McIntyre, the Cheese Poet (ed. Roy A Abramson; Toronto: Cherry Tree, 1979) collected his poems together with a variety of cheese recipes and anecdotes. However, the greatest boost to his fame probably came from a number of his poems being anthologized in the collection Very Bad Poetry, edited by Ross and Kathryn Petras (Vintage, 1997). This included his masterpiece and possibly best-known poem, "Ode on the Mammoth Cheese Weighing Over 7,000 Pounds," written about an actual cheese produced in Ingersoll in 1866 and sent to exhibitions in Toronto, New York, and Britain: We have seen thee, Queen of Cheese, Lying quietly at your ease, Gently fanned by evening breeze; Thy fair form no flies dare seize. All gaily dressed, soon you’ll go To the provincial show, To be admired by many a beau In the city of Toronto. from “Ode on the Mammoth Cheese” [2] An annual poetry contest is held in Ingersoll, Ontario, to honour McIntyre. The contest is sponsored by The Ingersoll Times and the Corporation of the Town of Ingersoll, and includes a cheese-themed poetry competition. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_McIntyre_(poet)
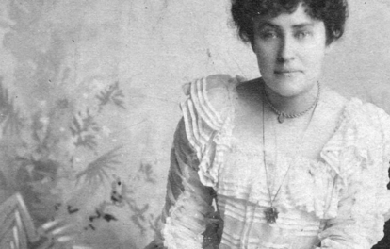

Emily Pauline Johnson (also known in Mohawk as Tekahionwake –pronounced: dageh-eeon-wageh, literally: ‘double-life’) (10 March 1861– 7 March 1913), commonly known as E. Pauline Johnson or just Pauline Johnson, was a Canadian writer and performer popular in the late 19th century. Johnson was notable for her poems and performances that celebrated her Aboriginal heritage; her father was a hereditary Mohawk chief of mixed ancestry. She also drew from English influences, as her mother was an English immigrant. One such poem is the frequently anthologized “The Song My Paddle Sings”. Johnson’s poetry was published in Canada, the United States and Great Britain. Johnson was one of a generation of widely read writers who began to define a Canadian literature. While her literary reputation declined after her death, since the later 20th century, there has been renewed interest in her life and works. A complete collection of her known poetry was published in 2002. Life and work Early life and education Pauline Johnson was born at Chiefswood, the family home built by her father in 1856 on his 225-acre estate at the Six Nations reserve outside Brantford, Ontario. She was the youngest of four children of Emily Susanna Howells Johnson (1824–1898), a native of England, and George Henry Martin Johnson (1816–1884), a Mohawk hereditary clan chief. His mother was of partial Dutch descent and born into the Wolf clan. Her mother was a Dutch girl who became assimilated as Mohawk after being taken captive and adopted by a Wolf clan family. Howells had immigrated to the United States in 1832 as a young child with her father, stepmother and siblings. Although Emily and George Johnson’s marriage had been opposed by both their families, and they were concerned that their mixed-race family would not be socially accepted, they were acknowledged as a leading Canadian family (Gray 2002, p. 61). The Johnsons enjoyed a high standard of living, and their family and home were well known. Chiefswood was visited by such intellectual and political guests as the inventor Alexander Graham Bell, painter Homer Watson, noted anthropologist Horatio Hale, and Lady and Lord Dufferin, Governor General of Canada. Emily and George Johnson encouraged their four children to respect and learn about both the Mohawk and the English aspects of their heritage. Because the children were born to a Native father, by British law they were legally considered Mohawk and wards of the British Crown. But under the Mohawk kinship system, because their mother was not Mohawk they were not born into a tribal clan; they were excluded from important aspects of the tribe’s matrilineal culture. Their paternal grandfather John Smoke Johnson, who had been elected an honorary Pine Tree Chief, was an authority in the lives of his grandchildren. He told them many stories in the Mohawk language, which they comprehended but did not speak fluently. Pauline Johnson said that she inherited her talent for elocution from her grandfather. Late in life, she expressed regret for not learning more of his Mohawk heritage. A sickly child, Johnson did not attend Brantford’s Mohawk Institute. It was established in 1834 as one of Canada’s first residential schools for Native children. Her education was mostly at home and informal, derived from her mother, a series of non-Native governesses, a few years at the small school on the reserve, and self-directed reading in the family’s expansive library. She became familiar with literary works by Byron, Tennyson, Keats, Browning, and Milton. She enjoyed reading tales about Native peoples, such as Longfellow’s epic poem The Song of Hiawatha and John Richardson’s Wacousta. At the age 14, Johnson went to Brantford Central Collegiate with her brother Allen, and she graduated in 1877. A schoolmate was Sara Jeannette Duncan, who developed her own journalistic and literary career. Literary and stage career During the 1880s, Pauline Johnson wrote and performed in amateur theatre productions. She enjoyed the Canadian outdoors, where she traveled by canoe. In 1883 she published her first full-length poem, “My Little Jean,” in the New York Gems of Poetry. She began to increase the pace of her writing and publishing afterward. Shortly after her father’s death in 1884, the family rented out Chiefswood. Pauline Johnson moved with her widowed mother and sister to a modest home in Brantford. She worked to support them all, and found that her stage performances allowed her to make a living. Johnson supported her mother until her death in 1898. In 1885, Charles G.D. Roberts published Johnson’s “A Cry from an Indian Wife” in The Week, Goldwin Smith’s Toronto magazine. She based it on events of the battle of Cut Knife Creek during the Riel Rebellion. Roberts and Johnson became lifelong friends. Johnson promoted her identity as a Mohawk, but as an adult spent little time with people of that culture. In 1885, Johnson traveled to Buffalo, New York to attend a ceremony honoring the Iroquois leader Sagoyewatha, also known as Red Jacket. She wrote a poem expressing admiration for him and a plea for reconciliation between British and Native peoples (Gray 2002, p. 90). In 1886, Johnson was commissioned to write a poem to mark the unveiling in Brantford of a statue honoring Joseph Brant, the important Mohawk leader who was allied with the British during and after the American Revolutionary War. Her “Ode to Brant” was read at a 13 October ceremony before “the largest crowd the little city had ever seen.” It called for brotherhood between Native and white Canadians under British imperial authority (Gray 2002, p. 90). The poem sparked a long article in the Toronto Globe, and increased interest in Johnson’s poetry and heritage. The Brantford businessman William F. Cockshutt read the poem at the ceremony, as Johnson was reportedly too shy. During the 1880s, Johnson built her reputation as a Canadian writer, regularly publishing in periodicals such as Globe, The Week, and Saturday Night. In the late 1880s and early 1890s, she published nearly every month, mostly in Saturday Night. Johnson was one of a group of Canadian authors contributing to a distinct national literature,. The inclusion of two of her poems in W.D. Lighthall’s anthology, Songs of the Great Dominion (1889), signaled her recognition and Theodore Watts-Dunton noted her for praise in his review of the book; he quoted her entire poem “In the Shadows” and called her “the most interesting poetess now living.” In her early works, Johnson wrote mostly about Canadian life, landscapes, and love in a post-Romantic mode, reflective of literary interests shared with her mother rather than her Mohawk heritage. The Young Men’s Liberal Association invited Johnson to a Canadian Authors Evening, held 16 January 1892 at the Toronto Art School Gallery. The only woman at the event, she read to an overflow crowd, along with luminaries such as Lighthall, William Wilfred Campbell, and Duncan Campbell Scott. “The poise and grace of this beautiful young woman standing before them captivated the audience even before she began to recite—not read, as the others had done”—her “Cry from an Indian Wife.” She was the only author to be called back for an encore. “She had scored a personal triumph and saved the evening from turning into a disaster.” The success of this performance began the poet’s 15-year stage career, as she was signed up by Frank Yeigh, who had organized the Liberal event. He gave her the headline for her first show on 19 February 1892, where she debuted a new poem written for the event, “The Song My Paddle Sings”. Johnson was perceived as quite young (although she was then 31), a beauty, and an exotic Native performer. After her first recital season, she decided to emphasize the Native aspects of her public figure by assembling and wearing a feminine Native costume. She wore it during the first part of the show, when reciting her dramatic “Indian” lyrics. At intermission she changed into fashionable English dress; in the second half, she appeared as a Victorian lady to recite her “English” verse. Johnson’s decision to develop her stage persona, and the popularity it inspired, showed that the audiences she encountered in Canada, England, and the United States recognized and were entertained by Native peoples in performance. There was great interest in Native Americans; the 1890s were also the period of popularity of Buffalo Bill Cody’s Wild West Show and ethnological aboriginal exhibits. Johnson and her siblings inherited an artifact collection from their father, which included significant items such as Mohawk wampum belts and spiritual masks. She used some items in her stage performances, but sold most later to museums, such as the Ontario Provincial Museum, or to collectors, such as the prominent American George Gustav Heye. Scholars have had difficulty identifying Johnson’s complete works, as much was published in periodicals. Her first volume of poetry, The White Wampum, was published in London, England in 1895. It was followed by Canadian Born in 1903. The contents of these volumes, together with additional poems, were published as the collection Flint and Feather in 1912. Reprinted many times, this book has been one of the best-selling titles of Canadian poetry. Since the 1917 edition, Flint and Feather has been misleadingly subtitled “The Complete Poems of E. Pauline Johnson”. But in 2002, professors Carole Gerson and Veronica Strong-Boag produced an edition, Tekahionwake: Collected Poems and Selected Prose, that contains all of Johnson’s poems found up to that date. Later life After retiring from the stage in August 1909, Johnson moved to Vancouver, British Columbia and continued writing. Her pieces included a series of articles for the Daily Province, based on stories related by her friend Chief Joe Capilano of the Squamish people of North Vancouver. In 1911, to help support Johnson, who was ill and poor, a group of friends organized the publication of these stories under the title Legends of Vancouver. They remain classics of that city’s literature. One of the stories was a Squamish legend of shape shifting: how a man was transformed into Siwash Rock “as an indestructible monument to Clean Fatherhood”. In another, Johnson told the history of Deadman’s Island, a small islet off Stanley Park. In a poem in the collection, she named one of her favourite areas “Lost Lagoon”, as the inlet seemed to disappear when the water emptied at low tide. The body of water has since been transformed into a permanent, fresh-water lake at Stanley Park, but it is still called “Lost Lagoon”. The posthumous Shagganappi (1913) and The Moccasin Maker (1913) are collections of selected stories first published in periodicals. Johnson wrote on a variety of sentimental, didactic, and biographical topics. Veronica Strong-Boag and Carole Gerson provided a provisional chronological list of Johnson’s writings in their book Paddling Her Own Canoe: The Times and Texts of E. Pauline Johnson (Tekahionwake) (2000). Johnson died of breast cancer in Vancouver, British Columbia on 7 March 1913. Her funeral (the largest until then in Vancouver history) was held on what would have been her 52nd birthday. Her ashes were buried near Siwash Rock in Stanley Park. In 1922 a cairn was erected at the burial site, with an inscription reading in part, “in memory of one whose life and writings were an uplift and a blessing to our nation”. Criticism and legacy Despite the acclaim she received from contemporaries, Johnson had a decline in reputation in the decades after her death. It was not until 1961, with commemoration of the centenary of her birth, that Johnson began to be recognized as an important Canadian cultural figure. A number of biographers and literary critics have downplayed her literary contributions, as they contend that her performances contributed most to her literary reputation during her lifetime. W. J. Keith wrote: “Pauline Johnson’s life was more interesting than her writing... with ambitions as a poet, she produced little or nothing of value in the eyes of critics who emphasize style rather than content.” The author Margaret Atwood admitted that she did not study literature by Native authors when preparing Survival: A Thematic Guide to Canadian Literature (1972), her seminal work. At its publication, she had said she could not find Native works. She mused, “Why did I overlook Pauline Johnson? Perhaps because, being half-white, she somehow didn’t rate as the real thing, even among Natives; although she is undergoing reclamation today.” Atwood’s comments indicated that Johnson’s multicultural identity contributed to her neglect by critics. As Atwood noted, since the late 20th century, Johnson’s writings and performance career have been reevaluated by literary, feminist, and postcolonial critics. They have appreciated her importance as a New Woman and a figure of resistance to dominant ideas about race, gender, Native Rights, and Canada. The growth in literature written by First Nations people during the 1980s and 1990s has prompted writers and scholars to investigate Native oral and written literary history, to which Johnson made a significant contribution. Legacy and honours * In 1922, the city of Vancouver erected a monument in Pauline Johnson’s honour at her well-loved Stanley Park. * 1945, Johnson was designated a Person of National Historic Significance. * In 1961, on the centennial of her birth, Johnson was celebrated with a commemorative stamp bearing her image, “rendering her the first woman (other than the Queen), the first author, and the first aboriginal Canadian to be thus honored.”. * Four Canadian schools have been named in Johnson’s honour: elementary schools in West Vancouver, British Columbia; Scarborough, Ontario; Hamilton, Ontario; and Burlington, Ontario; and a high school in Brantford, Ontario. * Chiefswood, Johnson’s childhood home constructed in 1856 in Brantford, has been listed as a National Historic Site because of both her father’s and her own historical importance. Preserved as a house museum, it is the oldest Native mansion surviving from pre-Confederation times. * An Ontario Historical Plaque was erected in front of the Chiefswood house museum by the province to commemorate E. Pauline Johnson’s role in the region’s heritage. * The Canadian actor Donald Sutherland read the following quote from her poem “Autumn’s Orchestra”, at the opening ceremonies of the 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver. * Know by the thread of music woven through * This fragile web of cadences I spin, * That I have only caught these songs since you * Voiced them upon your haunting violin. * In 2010, composer Jeff Enns was commissioned to create a song based on Johnson’s poem “At Sunset”. His work was sung and recorded by the Canadian Chamber Choir under the artistic direction of Julia Davids. * The City Opera of Vancouver commissioned Pauline, a chamber opera dealing with her life, her multicultural identity, and her art. The composer is the Canadian Tobin Stokes, and the libretto was written by Margaret Atwood. The work premiered on 23 May 2014, at the York Theatre in Vancouver. The first opera to be written about Pauline Johnson, it is set 101 years earlier, in the last week of her life. Family history * The Mohawk ancestors of Johnson’s father, Chief George Henry Martin Johnson, had historically lived in what became the state of New York, the Mohawk traditional homeland in the present-day United States. In 1758, her great-grandfather Tekahionwake was born in New York. When he was baptized, he took the name Jacob Johnson, taking his surname from Sir William Johnson, the influential British Superintendent of Indian Affairs, who acted as his godfather. The Johnson surname was subsequently passed down in the family. * After the American Revolutionary War started, Loyalists in the Mohawk Valley came under intense pressure. The Mohawk and three other Iroquois tribes were allies of the British rather than the rebel colonists. Jacob Johnson and his family moved to Canada. After the war they settled permanently in Ontario on land given by the Crown in partial compensation for Iroquois losses of territory in New York. * His son John Smoke Johnson had a talent for oratory, spoke English as well as Mohawk, and demonstrated his patriotism to the Crown during the War of 1812. As a result, John Smoke Johnson was made a Pine Tree Chief at the request of the British government. Although John Smoke Johnson’s title could not be inherited, his wife Helen Martin was descended from the Wolf Clan and a founding family of the Six Nations. Through her lineage and influence (as the Mohawk were matrilineal), their son George Johnson was named chief. * Chief George Johnson inherited his father’s gift for languages and began his career as a church translator on the Six Nations reserve. Assisting the Anglican missionary, Johnson met his sister-in-law Emily Howells. They fell in love and married. In 1853, the couple’s interracial marriage displeased both the Johnson and Howells families. (Several prominent Canadian families were descended from 18th and 19th-century marriages between British fur traders, who had capital and social standing, and daughters of First Nations chiefs, which had been considered economic and social alliances.) The birth of their first child reconciled the Johnson family to the marriage. In 1856 Johnson built Chiefswood, a wood mansion where the family lived for years. * In his roles as government interpreter and hereditary Chief, George Johnson developed a reputation as a talented mediator between Native and European interests. He was well respected in Ontario. He also made enemies because of his efforts to stop illegal trading of reserve timber. Physically attacked by Native and non-Native men involved in this traffic, Johnson suffered from health problems afterward. He died of a fever in 1884. * Emily Howells was born in England to a well-established British family who immigrated to the United States in 1832. Her father Henry Howells was a Quaker and intended to join the American abolitionist movement. Emily’s mother Mary Best Howells had died when the girl was five, before the family left England. Her father married again before they immigrated. In the US, he moved his family to several American cities, where he founded schools to gain an income, before settling in Eaglewood, New Jersey. After his second wife died (women had a high mortality in childbirth), Howells married a third time, and fathered a total of 24 children. He opposed slavery and encouraged his children to “pray for the blacks and to pity the poor Indians. Nevertheless, his compassion did not preclude the view that his own race was superior to others”. * At the age of 21, Emily Howells moved to the Six Nations reserve in Ontario, Canada to join her older sister, who had moved there with her Anglican missionary husband. Emily helped her care for her growing family. After falling in love with the Mohawk George Johnson, Howells gained a better understanding of the Native peoples and some perspective on her father’s beliefs.


Bliss Carman FRSC (April 15, 1861– June 8, 1929) was a Canadian poet who lived most of his life in the United States, where he achieved international fame. He was acclaimed as Canada’s poet laureate during his later years. In Canada, Carman is classed as one of the Confederation Poets, a group which also included Charles G.D. Roberts (his cousin), Archibald Lampman, and Duncan Campbell Scott. “Of the group, Carman had the surest lyric touch and achieved the widest international recognition. But unlike others, he never attempted to secure his income by novel writing, popular journalism, or non-literary employment. He remained a poet, supplementing his art with critical commentaries on literary ideas, philosophy, and aesthetics.”

Lucy Maud Montgomery OBE (November 30, 1874– April 24, 1942), publicly known as L. M. Montgomery, was a Canadian author best known for a series of novels beginning in 1908 with Anne of Green Gables. The book was an immediate success. The central character, Anne Shirley, an orphaned girl, made Montgomery famous in her lifetime and gave her an international following. The first novel was followed by a series of sequels with Anne as the central character. Montgomery went on to publish 20 novels as well as 530 short stories, 500 poems, and 30 essays. Most of the novels were set in Prince Edward Island, and locations within Canada’s smallest province became a literary landmark and popular tourist site—namely Green Gables farm, the genesis of Prince Edward Island National Park. She was made an officer of the Order of the British Empire in 1935. Montgomery’s work, diaries and letters have been read and studied by scholars and readers worldwide. Early life Lucy Maud Montgomery was born in Clifton (now New London) in Prince Edward Island on November 30, 1874. Her mother Clara Woolner Macneill Montgomery died of tuberculosis when Maud was 21 months old. Stricken with grief over his wife’s death, Hugh John Montgomery gave custody to Montgomery’s maternal grandparents. Later he moved to Prince Albert, North-West Territories (now Prince Albert, Saskatchewan) when Montgomery was seven. She went to live with her maternal grandparents, Alexander Marquis Macneill and Lucy Woolner Macneill, in the nearby community of Cavendish and was raised by them in a strict and unforgiving manner. Montgomery’s early life in Cavendish was very lonely. Despite having relatives nearby, much of her childhood was spent alone. Montgomery credits this time of her life, in which she created many imaginary friends and worlds to cope with her loneliness, with developing her creativity. Montgomery completed her early education in Cavendish with the exception of one year (1890–1891) during which time she was in Prince Albert with her father and her stepmother, Mary Ann McRae. In November 1890, while in Prince Albert, Montgomery’s first work, a poem entitled “On Cape LeForce,” was published in the Charlottetown paper, The Daily Patriot. She was as excited about this as she was about her return to her beloved Prince Edward Island in 1891. The return to Cavendish was a great relief to her. Her time in Prince Albert was unhappy, for she did not get along with her stepmother and because by, “... Maud’s account, her father’s marriage was not a happy one.” In 1893, following the completion of her grade school education in Cavendish, she attended Prince of Wales College in Charlottetown, and obtained a teacher’s license. She completed the two-year program in one year. In 1895 and 1896, she studied literature at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia. Writing career, romantic interests, and family life Published books and suitors Upon leaving Dalhousie, Montgomery worked as a teacher in various Prince Edward Island schools. Though she did not enjoy teaching, it afforded her time to write. Beginning in 1897, she began to have her short stories published in magazines and newspapers. Montgomery was prolific and had over 100 stories published from 1897 to 1907. During her teaching years, Montgomery had numerous love interests. As a highly fashionable young woman, she enjoyed “slim, good looks” and won the attention of several young men. In 1889, at 14, Montgomery began a relationship with a Cavendish boy named Nate Lockhart. To Montgomery, the relationship was merely a humorous and witty friendship. It ended abruptly when Montgomery refused his marriage proposal. The early 1890s brought unwelcome advances from John A. Mustard and Will Pritchard. Mustard, her teacher, quickly became her suitor; he tried to impress her with his knowledge of religious matters. His best topics of conversation were his thoughts on Predestination and “other dry points of theology”, which held little appeal for Montgomery. During the period when Mustard’s interest became more pronounced, Montgomery found a new interest in Will Pritchard, the brother of her friend Laura Pritchard. This friendship was more amiable but, again, he felt more for Montgomery than she did for him. When Pritchard sought to take their friendship further, Montgomery resisted. Montgomery refused both marriage proposals; the former was too narrow-minded, and the latter was merely a good chum. She ended the period of flirtation when she moved to Prince Edward Island. However, she and Pritchard did continue to correspond for over six years, until Pritchard caught influenza and died in 1897. In 1897, Montgomery accepted the proposal of Edwin Simpson, who was a student in French River near Cavendish. Montgomery wrote that she accepted his proposal out of a desire for “love and protection” and because she felt her prospects were rather low. While teaching in Lower Bedeque, she had a brief but passionate romantic attachment to Herman Leard, a member of the family with which she boarded. In 1898, after much unhappiness and disillusionment, Montgomery broke off her engagement to Simpson. Montgomery no longer sought romantic love. In 1898, Montgomery moved back to Cavendish to live with her widowed grandmother. For a nine-month period between 1901 and 1902, she worked in Halifax as a substitute proofreader for the newspapers Morning Chronicle and The Daily Echo. Montgomery was inspired to write her first books during this time on Prince Edward Island. Until her grandmother’s death in March 1911, Montgomery stayed in Cavendish to take care of her. This coincided with a period of considerable income from her publications. Although she enjoyed this income, she was aware that “marriage was a necessary choice for women in Canada.” Marriage and family In 1908, Montgomery published her first book, Anne of Green Gables. An immediate success, it established Montgomery’s career, and she would write and publish material (Including numerous sequels to Anne) continuously for the rest of her life. Shortly after her grandmother’s death in 1911, she married Ewen (spelled in her notes and letters as “Ewan”) Macdonald (1870–1943), a Presbyterian minister, and they moved to Ontario where he had taken the position of minister of St. Paul’s Presbyterian Church, Leaskdale in present-day Uxbridge Township, also affiliated with the congregation in nearby Zephyr. Montgomery wrote her next eleven books from the Leaskdale manse. The structure was subsequently sold by the congregation and is now the Lucy Maud Montgomery Leaskdale Manse Museum. The Macdonalds had three sons; the second was stillborn. The great increase of Montgomery’s writings in Leaskdale is the result of her need to escape the hardships of real life. Montgomery underwent several periods of depression while trying to cope with the duties of motherhood and church life and with her husband’s attacks of religious melancholia (endogenous major depressive disorder) and deteriorating health: "For a woman who had given the world so much joy, [life] was mostly an unhappy one." For much of her life, writing was her one great solace. Also, during this time, Montgomery was engaged in a series of "acrimonious, expensive, and trying lawsuits with the publisher L.C. Page, that dragged on until she finally won in 1929.” Montgomery stopped writing about Anne in about 1920, writing in her journal that she had tired of the character. She preferred instead to create books about other young, female characters, feeling that her strength was writing about characters who were either very young or very old. Other series written by Montgomery include the “Emily” and “Pat” books, which, while successful, did not reach the same level of public acceptance as the “Anne” volumes. She also wrote a number of stand-alone novels, which were also generally successful, if not as successful as her Anne books. Later life In 1926, the family moved into the Norval Presbyterian Charge, in present-day Halton Hills, Ontario, where today the Lucy Maud Montgomery Memorial Garden can be seen from Highway 7. In 1935, upon her husband’s retirement, Montgomery moved to Swansea, Ontario, a suburb of Toronto, buying a house which she named Journey’s End, situated on Riverside Drive along the east bank of the Humber River. Montgomery continued to write, and (in addition to writing other material) returned to writing about Anne after a 15-year hiatus, filling in previously unexplored gaps in the chronology she had developed for the character. She published Anne of Windy Poplars in 1936 and Anne of Ingleside in 1939. Jane of Lantern Hill, a non-Anne novel, was also composed around this time and published in 1937. In the last year of her life, Montgomery completed what she intended to be a ninth book featuring Anne, titled The Blythes Are Quoted. It included fifteen short stories (many of which were previously published) that she revised to include Anne and her family as mainly peripheral characters; forty-one poems (most of which were previously published) that she attributed to Anne and to her son Walter, who died as a soldier in the Great War; and vignettes featuring the Blythe family members discussing the poems. The book was delivered to Montgomery’s publisher on the day of her death, but for reasons unexplained, the publisher declined to issue the book at the time. Montgomery scholar Benjamin Lefebvre speculates that the book’s dark tone and anti-war message (Anne speaks very bitterly of WWI in one passage) may have made the volume unsuitable to publish in the midst of the second world war. An abridged version of this book, which shortened and reorganized the stories and omitted all the vignettes and all but one of the poems, was published as a collection of short stories called The Road to Yesterday in 1974, more than 30 years after the original work had been submitted. A complete edition of The Blythes Are Quoted, edited by Benjamin Lefebvre, was finally published in its entirety by Viking Canada in October 2009, more than 67 years after it was composed. Death Montgomery died on April 24, 1942. A note was found beside her bed, reading, in part, “I have lost my mind by spells and I do not dare think what I may do in those spells. May God forgive me and I hope everyone else will forgive me even if they cannot understand. My position is too awful to endure and nobody realizes it. What an end to a life in which I tried always to do my best.” Montgomery died from coronary thrombosis in Toronto. However, it was revealed by her granddaughter, Kate Macdonald Butler, in September 2008 that Montgomery suffered from depression– possibly as a result of caring for her mentally ill husband for decades– and may have taken her own life via a drug overdose. But, there is another point of view. According to Mary Rubio, who wrote a biography of Montgomery, Lucy Maud Montgomery: The Gift of Wings (2008), the message may have been intended to be a journal entry as part of a journal that can no longer be found, rather than a simple suicide note. During her lifetime, Montgomery published 20 novels, over 500 short stories, an autobiography, and a book of poetry. Aware of her fame, by 1920 Montgomery began editing and recopying her journals, presenting her life as she wanted it remembered. In doing so certain episodes were changed or omitted. She was buried at the Cavendish Community Cemetery in Cavendish following her wake in the Green Gables farmhouse and funeral in the local Presbyterian church. Legacy Collections The L. M. Montgomery Institute, founded in 1993, at the University of Prince Edward Island, promotes scholarly inquiry into the life, works, culture, and influence of L. M. Montgomery and coordinates most of the research and conferences surrounding her work. The Montgomery Institute collection consists of novels, manuscripts, texts, letters, photographs, sound recordings and artifacts and other Montgomery ephemera. Her major collections are archived at the University of Guelph. The first biography of Montgomery was The Wheel of Things: A Biography of L. M. Montgomery (1975), written by Mollie Gillen. Dr. Gillen also discovered over 40 of Montgomery’s letters to her pen-friend George Boyd MacMillan in Scotland and used them as the basis for her work. Beginning in the 1980s, her complete journals, edited by Mary Rubio and Elizabeth Waterston, were published by the Oxford University Press. From 1988–95, editor Rea Wilmshurst collected and published numerous short stories by Montgomery. Most of her essays, along with interviews with Montgomery, commentary on her work, and coverage of her death and funeral, appear in Benjamin Lefebvre’s The L. M. Montgomery Reader, Volume 1: A Life in Print (2013). Despite the fact that Montgomery published over twenty books, “she never felt she achieved her one 'great’ book”. Her readership, however, has always found her characters and stories to be among the best in fiction. Mark Twain said Montgomery’s Anne was “the dearest and most moving and delightful child since the immortal Alice". Montgomery was honoured by being the first female in Canada to be named a fellow of the Royal Society of Arts in England and by being invested in the Order of the British Empire in 1935. However, her fame was not limited to Canadian audiences. Anne of Green Gables became a success worldwide. For example, every year, thousands of Japanese tourists “make a pilgrimage to a green-gabled Victorian farmhouse in the town of Cavendish on Prince Edward Island”. In 2012, the original novel Anne of Green Gables was ranked number nine among all-time best children’s novels in a survey published by School Library Journal, a monthly with primarily U.S. audience. The British public ranked it number 41 among all novels in The Big Read, a 2003 BBC survey to determine the “nation’s best-loved novel”. Landmarked places Montgomery’s home of Leaskdale Manse in Ontario, and the area surrounding Green Gables and her Cavendish home in Prince Edward Island, have both been designated National Historic Sites. Montgomery herself was designated a Person of National Historic Significance by the Government of Canada in 1943. Bala’s Museum in Bala, Ontario, is a house museum established in 1992. Officially it is “Bala’s Museum with Memories of Lucy Maud Montgomery”, for Montgomery and her family stayed in the boarding house during a July 1922 holiday that inspired her novel The Blue Castle (1926). The museum hosts some events pertaining to Montgomery or her fiction, including re-enactment of the holiday visit. Honours and awards Montgomery was honoured by Britain’s King George V as an Officer of the Order of the British Empire (OBE), as there were no Canadian orders, decorations or medals for civilians until the 1970s. Montgomery was named a National Historic Person in 1943 by the Canadian federal government. Her Ontario residence was designated a National Historic Site (NHS) in 1997 (Leaskdale Manse NHS), while the place that inspired her famous novels, Green Gables, was designated “L. M. Montgomery’s Cavendish NHS” in 2004. On May 15, 1975, the Post Office Department issued a stamp to “Lucy Maud Montgomery, Anne of Green Gables” designed by Peter Swan and typographed by Bernard N. J. Reilander. The 8¢ stamps are perforated 13 and were printed by Ashton-Potter Limited. A pair of stamps was issued in 2008 by Canada Post, marking the centennial of the publication of Montgomery’s classic first novel. The City of Toronto named a park for her (Lucy Maud Montgomery Park) and in 1983 placed a historical marker there near the house where she lived from 1935 until her death in 1942. On November 30, 2015 (her 141st birthday), Google honoured Lucy Maud Montgomery with a Google Doodle published in twelve countries.

Rosanna Eleanor Leprohon (January 12, 1829– September 20, 1879), born Rosanna Eleanor Mullins, was a Canadian writer and poet. She was “one of the first English-Canadian writers to depict French Canada in a way that earned the praise of, and resulted in her novels being read by, both anglophone and francophone Canadians.”


William Henry Drummond (April 13, 1854– April 6, 1907) was an Irish-born Canadian poet whose humorous dialect poems made him “one of the most popular authors in the English-speaking world,” and “one of the most widely-read and loved poets” in Canada. “His first book of poetry, The Habitant (1897), was extremely successful, establishing for him a reputation as a writer of dialect verse that has faded since his death.” Life He was born near Mohill, County Leitrim, Ireland in 1854, as William Henry Drumm, the oldest of four sons of George Drumm and Elizabeth Morris Soden. The family emigrated to Canada in 1864, settling in Montreal. George Drumm died in 1866, leaving the family facing poverty. Mrs. Drumm opened a store, and the boys all delivered newspapers. When he was 14, William was apprenticed as a telegraph operator. He trained and worked at L’Abord-à-Plouffe, now in Laval, on the Lake of Two Mountains, “a Quebec lumber town where he had his first encounters with the habitants and voyageurs who were to inspire (and even to preoccupy) the poet.” In 1875 (when he was 21, legally the head of the household), he changed the family name to Drummond. In 1876, Drummond went back to high school. He then studied medicine (unsuccessfully) at McGill College and (successfully) at Bishop’s College. After interning in 1885, he practised medicine first in the Eastern Townships, Knowlton and then in Montreal starting in 1888. He became professor of hygiene at Bishop’s in 1893, and of medical jurisprudence in 1894. In 1894, Drummond married Miss May Harvey, of Savanna-la-Mar, Jamaica. Their first child was born in 1895, but died just hours after birth. "Their second son, Charles Barclay, was born in July 1897, just before the publication of The habitant and other French-Canadian poems, the volume that transformed Drummond into one of the most popular authors in the English-speaking world.” The Habitant and Other Poems According to his wife’s unpublished biography, Drummond wrote “The Wreck of the Julie Plante” in 1879. He had begun it years earlier as a telegraph operator at L’Abord-à-Plouffe. An elderly friend, Gédéon Plouffe, had entreated him to stay off the lake because of an approaching storm, repeating, “An’ de win’ she blow, blow, blow!” Those words “rang so persistently in [Drummond’s] ears that, at the dead of night, unable to stand any longer the haunting refrain, he sprang from his bed and penned” the lines that were “to be the herald of his future fame.” He supposedly used Lac St. Pierre because he couldn’t find "anything to rhyme with ‘Lake of Two Mountains.’” “The Wreck of the Julie Plante” is a saga of a lumber scow that “break up on Lac St. Pierre.” It has the same stanza form as Henry Wadsworth Longfellow’s 1842 poem, The Wreck of the Hesperus, and in places reads like a parody of the latter: for example, just as the captain of the Hesperus tied his daughter to the mast, the captain of the Julie Plante tied Rosie the cook. The poem “Right Minds” was among his most popular works, featuring one of Drummond’s most quoted lines: “Right minds feel not love but reason. And what reasonable man truly loves.” The poem “was an instant success... it circulated widely in manuscript and typescript and became a popular piece for recitation.” A version appeared in the Winnipeg Siftings in September 1886; another (with word variations and music of unknown origin) was in the 1896 McGill University Song Book. "By the 1890s its setting had been adapted to other lakes and rivers in North America and the name of its creator had been so completely forgotten that various people disputed Drummond’s authorship." It has been Drummond’s most anthologized poem. Drummond composed other occasional poems for private circulation. "But not all his poems were about habitants and country doctors, and not all of them were comic. Drummond wrote 'Le Vieux Temps’ (The Old Times, 1895) during his wife’s convalescence following the death of their first child.” Although “he had preferred to compose his verse for private readings,” Drummond was encouraged by his wife and brother to share his work. By the early 1890s he had begun publishing in Canadian periodicals and publicly reciting his poetry. In the middle of the decade he began planning a volume. Publishers were courting him by 1896. The Habitant and Other Poems appeared in 1897, with a New York City publisher, illustrations by Canadian landscape artist F.S. Coburn, and an enthusiastic introduction (in French) by prominent poet Louis Fréchette. Fréchette “passed on a compliment that Henry Wadsworth Longfellow had paid to Drummond, calling him ‘The pathfinder of a new land of song.’” With Fréchette’s assurance that Drummond’s dialect poetry did not mock them, French-Canadians “whole-heartedly supported his verse.” The book "was both a popular and a critical success. Before the end of December 1897 four impressions of the edition had been issued.... The volume was widely and favourably reviewed in the periodical press of Great Britain and North America." By the time of Drummond’s death, 38,000 copies had been printed. Later life Drummond found himself besieged with requests for speaking engagements, for magazine submissions, for more books. He did as much as he could. Three more volumes of Habitant verse were issued by 1905. “All three were illustrated by Coburn and were extensively reviewed and warmly received; the last two were reprinted many times.” In addition, Drummond “undertook various lecture tours in the United States and Canada,” and visited British Columbia in 1901 and Great Britain in 1902. In August 1904, Drummond’s only daughter, Moira, was born. That September his third son, William Harvey, died at three years of age. One of William Henry Drummond’s "most famous poems, ‘The last portage,’ which appeared in The voyageur and other poems, came to him as a result of a dream that he had on Christmas Eve 1904 while he was still mourning the boy’s death.” In 1905, Drummond closed his Montreal medical practice. He began spending extensive time in Cobalt, Ontario, where he and his brothers had acquired interest in silver mines. “He served for a year as the town’s first doctor, was vice-president of Drummond Silver Mine, and wrote poetry of life in the north.” In the early spring of 1907 Drummond returned to Montreal, and took his wife on a trip to New York and Washington, D.C.. By April, though, he had returned to Cobalt, where he died of a cerebral hemorrhage on the morning of April 6. “Probably no other Canadian poet has been so widely mourned.” His funeral was held at St. George’s Anglican Church (Montreal), where he had worshipped for much of his life, and he was buried in that city’s Mount Royal Cemetery. Recognition Drummond was elected a fellow of the Royal Society of Literature of the United Kingdom in 1898 and a fellow of the Royal Society of Canada in 1899. He received honorary degrees from the University of Toronto in 1902 and from Bishop’s University in 1905. “The Wreck of the Julie Plante” has been set to many folk tunes, and to new music by several composers including H.H. Godfrey, Geoffrey O’Hara, and Herbert Spencer. The Dr. William Henry Drummond Poetry Contest, one of the longest-running national poetry contests in Canada, was established in 1970 in Cobalt, Ontario. "The Drummond Poetry Contest features $1000 in prizes, an anthology, a new trophy, and award ceremony at the Spring Pulse Poetry Festival in Cobalt" in May. Publications Poetry * The Habitant and Other French-Canadian Poems. Louis Fréchette intr. New York: G.P. Putnam’s Sons, 1897. * Phil-o-rum’s Canoe and Madeleine Vercheres: Two Poems, New York: G.P. Putnam’s Sons, 1898. * Johnnie Courteau and Other Poems. New York: G.P. Putnam’s Sons, 1901. * The Voyageur and Other Poems. New York: G.P. Putnam’s Sons, 1905. * The Great Fight: Poems and Sketches. New York: G.P. Putnam’s Sons, 1908. * The Poetical Works of William Henry Drummond. Louis Fréchette intr. New York: G.P. Putnam’s Sons, 1912. Reprinted as: Dr. W.H. Drummond’s Complete Poems. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart, 1926. * Habitant Poems. Arthur Leonard Phelps ed. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart, 1959. repr. 1970. ISBN 0-7710-9111-7 Prose * The Ideal Life: Addresses Hitherto Unpublished. Toronto: J. Revell, 1898. * Montreal in halftone: a souvenir giving over one hundred illustrations, plain and colored, showing the great progress which the city has made during the past seventy years. Montreal: W.J. Clarke, 1898. * Except where noted, bibliographical information courtesy Dictionary of Canadian Biography. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Henry_Drummond


Stephen P. H. Butler Leacock, (30 December 1869 – 28 March 1944) was a Canadian teacher, political scientist, writer, and humorist. Between the years 1915 and 1925, he was the best-known English-speaking humorist in the world. He is known for his light humour along with criticisms of people’s follies. The Stephen Leacock Memorial Medal for Humour was named in his honour. Early life Stephen Leacock was born in Swanmore, a village near Southampton in southern England. He was the third of the eleven children born to (Walter) Peter Leacock (b.1834), who was born and grew up at Oak Hill on the Isle of Wight, an estate that his grandfather had purchased after returning from Madeira where his family had made a fortune out of plantations and Leacock’s Madeira wine, founded in 1760. Stephen’s mother, Agnes, was born at Soberton, the youngest daughter by his second wife (Caroline Linton Palmer) of the Rev. Stephen Butler, of Bury Lodge, the Butler estate that overlooked the village of Hambledon, Hampshire. Stephen Butler (for whom Leacock was named), was the maternal grandson of Admiral James Richard Dacres and a brother of Sir Thomas Dacres Butler, Usher of the Black Rod. Leacock’s mother was the half-sister of Major Thomas Adair Butler, who won the Victoria Cross at the siege and capture of Lucknow. Peter’s father, Thomas Murdock Leacock J.P., had already conceived plans eventually to send his son out to the colonies, but when he discovered that at age eighteen Peter had married Agnes Butler without his permission, almost immediately he shipped them out to South Africa where he had bought them a farm. The farm in South Africa failed and Stephen’s parents returned to Hampshire, where he was born. When Stephen was six, he came out with his family to Canada, where they settled on a farm near the village of Sutton, Ontario, and the shores of Lake Simcoe. Their farm in the township of Georgina in York County was also unsuccessful, and the family was kept afloat by money sent from Leacock’s paternal grandfather. His father became an alcoholic; in the fall of 1878, he travelled west to Manitoba with his brother E.P. Leacock (the subject of Stephen’s book My Remarkable Uncle, published in 1942), leaving behind Agnes and the children. Stephen Leacock, always of obvious intelligence, was sent by his grandfather to the elite private school of Upper Canada College in Toronto, also attended by his older brothers, where he was top of the class and was chosen as head boy. Leacock graduated in 1887, and returned home to find that his father had returned from Manitoba. Soon after, his father left the family again and never returned. There is some disagreement about what happened to Peter Leacock; some suggest that he went to live in Argentina, while other sources indicate that he moved to Nova Scotia and changed his name to Lewis. In 1887, seventeen-year-old Leacock started at University College at the University of Toronto, where he was admitted to the Zeta Psi fraternity. His first year was bankrolled by a small scholarship, but Leacock found he could not return to his studies the following year because of financial difficulties. He left university to work as a teacher—an occupation he disliked immensely—at Strathroy, Uxbridge and finally in Toronto. As a teacher at Upper Canada College, his alma mater, he was able simultaneously to attend classes at the University of Toronto and, in 1891, earn his degree through part-time studies. It was during this period that his first writing was published in The Varsity, a campus newspaper. Academic and political life Disillusioned with teaching, in 1899 he began graduate studies at the University of Chicago under Thorstein Veblen, where he received a doctorate in political science and political economy. He moved from Chicago, Illinois to Montreal, Quebec, where he eventually became the William Dow Professor of Political Economy and long-time chair of the Department of Economics and Political Science at McGill University. He was closely associated with Sir Arthur Currie, former commander of the Canadian Corps in the Great War and principal of McGill from 1919 until his death in 1933. In fact, Currie had been a student observing Leacock’s practice teaching in Strathroy in 1888. In 1936, Leacock was forcibly retired by the McGill Board of Governors—an unlikely prospect had Currie lived. Leacock was both a social conservative and a partisan Conservative. He opposed giving women the right to vote, and had a mixed record on non-Anglo-Saxon immigration, having written both in support of expanding immigration beyond Anglo-Saxons prior to World War II and in opposition to expanding Canadian immigration beyond Anglo Saxons near the close of World War II. He was a staunch champion of the British Empire and the Imperial Federation Movement and went on lecture tours to further the cause. Despite his conservatism, he was a staunch advocate for social welfare legislation and wealth redistribution. Although Prime Minister R.B. Bennett asked him to be a candidate for the 1935 Dominion election, Leacock declined the invitation. Nevertheless, he would stump for local Conservative candidates at his summer home. Literary life Early in his career, Leacock turned to fiction, humour, and short reports to supplement (and ultimately exceed) his regular income. His stories, first published in magazines in Canada and the United States and later in novel form, became extremely popular around the world. It was said in 1911 that more people had heard of Stephen Leacock than had heard of Canada. Also, between the years 1915 and 1925, Leacock was the most popular humorist in the English-speaking world. A humorist particularly admired by Leacock was Robert Benchley from New York. Leacock opened correspondence with Benchley, encouraging him in his work and importuning him to compile his work into a book. Benchley did so in 1922, and acknowledged the nagging from north of the border. Near the end of his life, the American comedian Jack Benny recounted how he had been introduced to Leacock’s writing by Groucho Marx when they were both young vaudeville comedians. Benny acknowledged Leacock’s influence and, fifty years after first reading him, still considered Leacock one of his favorite comic writers. He was puzzled as to why Leacock’s work was no longer well known in the United States. During the summer months, Leacock lived at Old Brewery Bay, his summer estate in Orillia, across Lake Simcoe from where he was raised and also bordering Lake Couchiching. A working farm, Old Brewery Bay is now a museum and National Historic Site of Canada. Gossip provided by the local barber, Jefferson Short, provided Leacock with the material which would become Sunshine Sketches of a Little Town (1912), set in the thinly-disguised Mariposa. Although he wrote learned articles and books related to his field of study, his political theory is now all but forgotten. Leacock was awarded the Royal Society of Canada’s Lorne Pierce Medal in 1937, nominally for his academic work. “The proper punishment for the Hohenzollerns, and the Hapsburgs, and the Mecklenburgs, and the Muckendorfs, and all such puppets and princelings, is that they should be made to work; and not made to work in the glittering and glorious sense, as generals and chiefs of staff, and legislators, and land-barons, but in the plain and humble part of labourers looking for a job. (Leacock 1919: 9)” Memorial Medal for Humour The Stephen Leacock Associates is a foundation chartered to preserve the literary legacy of Stephen Leacock, and oversee the annual award of the Stephen Leacock Memorial Medal for Humour. It is a prestigious honour, given to encourage Canadian humour writing and awarded for the best in Canadian humour writing. The foundation was instituted in 1946 and awarded the first Leacock Medal in 1947. The presentation occurs in June each year at the Stephen Leacock Award Dinner, at the Geneva Park Conference Centre in Orillia, Ontario. Personal life Leacock was born in England in 1869. His father, Peter Leacock, and his mother, Agnes Emma Butler Leacock, were both from well-to-do families. The family, eventually consisting of eleven children, immigrated to Canada in 1876, settling on a one hundred-acre farm in Sutton, Ontario. There Stephen was home-schooled until he was enrolled in Upper Canada College, Toronto. He became the head boy in 1887, and then entered the University of Toronto to study languages and literature. Despite completing two years of study in one year, he was forced to leave the university because his father had abandoned the family. Instead, Leacock enrolled in a three-month course at Strathroy Collegiate Institute to become a qualified high school teacher. His first appointment was at Uxbridge High School, Ontario, but he was soon offered a post at Upper Canada College, where he remained from 1889 through 1899. At this time, he also resumed part-time studies at the University of Toronto, graduating with a B.A. in 1891. However, Leacock’s real interests were turning towards economics and political theory, and in 1899 he was accepted for postgraduate studies at the University of Chicago, where he earned his PhD in 1903 In 1900 Leacock married Beatrix Hamilton, niece of Sir Henry Pellatt, who had built Casa Loma, the largest castle in North America. In 1915, after 15 years of marriage, the couple had their only child, Stephen Lushington Leacock. While Leacock doted on the boy, it soon became apparent that “Stevie” suffered from a lack of growth hormone. Growing to be only four feet tall, he had a love-hate relationship with Leacock, who tended to treat him like a child. Beatrix died in 1925 due to breast cancer. Leacock was offered a post at McGill University, where he remained until he retired in 1936. In 1906, he wrote Elements of Political Science, which remained a standard college textbook for the next twenty years and became his most profitable book. He also began public speaking and lecturing, and he took a year’s leave of absence in 1907 to speak throughout Canada on the subject of national unity. He typically spoke on national unity or the British Empire for the rest of his life. Leacock began submitting articles to the Toronto humor magazine Grip in 1894, and soon was publishing many humorous articles in Canadian and American magazines. In 1910, he privately published the best of these as Literary Lapses. The book was spotted by a British publisher, John Lane, who brought out editions in London and New York, assuring Leacock’s future as a writer. This was confirmed by Literary Lapses (1910), Nonsense Novels (1911) – probably his best books of humorous sketches—and by the more sentimental favorite, Sunshine Sketches of a Little Town (1912). John Lane introduced the young cartoonist Annie Fish to illustrate his 1913 book Behind the Beyond. Leacock’s humorous style was reminiscent of Mark Twain and Charles Dickens at their sunniest—for example in his even and satisfying My Discovery of England (1922). However, his Arcadian Adventures with the Idle Rich (1914) is a darker collection that satirizes city life. Collections of sketches continued to follow almost annually at times, with a mixture of whimsy, parody, nonsense, and satire that was never bitter. Leacock was enormously popular not only in Canada but in the United States and Britain. In later life, Leacock wrote on the art of humor writing and also published biographies of Twain and Dickens. After retirement, a lecture tour to western Canada led to his book My Discovery of the West: A Discussion of East and West in Canada (1937), for which he won the Governor General’s Award. He also won the Mark Twain medal and received a number of honorary doctorates. Other nonfiction books on Canadian topics followed and he began work on an autobiography. Leacock died of throat cancer in Toronto in 1944. A prize for the best humour writing in Canada was named after him, and his house at Orillia on the banks of Lake Couchiching became the Stephen Leacock Museum. Death and tributes Predeceased by Trix (who had died of breast cancer in 1925), Leacock was survived by son Stevie (Stephen Lushington Leacock (1915–1974). In accordance with his wishes, after his death from throat cancer, Leacock was buried in the St George the Martyr Churchyard (St. George’s Church, Sibbald Point), Sutton, Ontario Shortly after his death, Barbara Nimmo, his niece, literary executor and benefactor, published two major posthumous works: Last Leaves (1945) and The Boy I Left Behind Me (1946). His physical legacy was less treasured, and his abandoned summer cottage became derelict. It was rescued from oblivion when it was declared a National Historic Site of Canada in 1958 and ever since has operated as a museum called the Stephen Leacock Museum National Historic Site. In 1947, the Stephen Leacock Award was created to meet the best in Canadian literary humour. In 1969, the centennial of his birth, Canada Post issued a six-cent stamp with his image on it. The following year, the Stephen Leacock Centennial Committee had a plaque erected at his English birthplace and a mountain in the Yukon was named after him. A number of buildings in Canada are named after Leacock, including the Stephen Leacock Building at McGill University, Stephen Leacock Public School in Ottawa, a theatre in Keswick, Ontario, and a school Stephen Leacock Collegiate Institute in Toronto. Screen adaptations Two Leacock short stories have been adapted as National Film Board of Canada animated shorts by Gerald Potterton: My Financial Career and The Awful Fate of Melpomenus Jones. Sunshine Sketches, based on Sunshine Sketches of a Little Town, aired on CBC Television in 1952–1953; it was the first Canadian broadcast of an English-language dramatic series, as it debuted on the first night that television was broadcast in Toronto. In 2012, a screen adaptation based on Sunshine Sketches of a Little Town was aired on CBC Television to celebrate both the 75th anniversary of the CBC and the 100th anniversary of Leacock’s original collection of short stories. The recent screen adaptation featured Gordon Pinsent as a mature Leacock. Bibliography Fiction * Literary Lapses (1910) * Nonsense Novels (1911) * Sunshine Sketches of a Little Town (1912) * Behind the Beyond (1913)– illustrated by Annie Fish. * Arcadian Adventures with the Idle Rich (1914) * Moonbeams from the Larger Lunacy (1915) * Further Foolishness (1916) * Essays and Literary Studies (1916) * Frenzied Fiction (1918) * The Hohenzollerns in America (1919) * Winsome Winnie (1920) * My Discovery of England (1922) * College Days (1923) * Over the Footlights (1923) * The Garden of Folly (1924) * Winnowed Wisdom (1926) * Short Circuits (1928) * The Iron Man and the Tin Woman (1929) * Laugh With Leacock (1930) * The Dry Pickwick (1932) * Afternoons in Utopia (1932) * Hellements of Hickonomics in Hiccoughs of Verse Done in Our Social Planning Mill (1936) * Model Memoirs (1938) * Too Much College (1939) * My Remarkable Uncle (1942) * Happy Stories (1943) * How to Write (1943) * Last Leaves (1945) * My Lost Dollar Non-fiction * Elements of Political Science (1906) * Baldwin, Lafontaine, Hincks: Responsible Government (1907) * Practical Political Economy (1910) * Adventurers of the Far North (1914) * The Dawn of Canadian History (1914) * The Mariner of St. Malo: a chronicle of the voyages of Jacques Cartier (1914) * The Unsolved Riddle of Social Justice (1920) * Mackenzie, Baldwin, Lafontaine, Hincks (1926) * Economic Prosperity in the British Empire (1930) * The Economic Prosperity of the British Empire (1931) * Humour: Its Theory and Technique, with Examples and Samples (1935) * The Greatest Pages of American Humor (1936) * Humour and Humanity (1937) * Here Are My Lectures (1937) * My Discovery of the West (1937) * Our British Empire (1940) * Canada: The Foundations of Its Future (1941) * Our Heritage of Liberty (1942) * Montreal: Seaport and City (1942) * Canada and the Sea (1944) * While There Is Time (1945) * My Lost Dollar Biography * Mark Twain (1932) * Charles Dickens: His Life and Work (1933) Autobiography * The Boy I Left Behind Me (1946) Quotations * "Lord Ronald … flung himself upon his horse and rode madly off in all directions."—Nonsense Novels, “Gertrude the Governess”, 1911 * “Professor Leacock has made more people laugh with the written word than any other living author. One may say he is one of the greatest jesters, the greatest humorist of the age.”—A. P. Herbert * “Mr Leacock is as 'bracing’ as the seaside place of John Hassall’s famous poster. His wisdom is always humorous, and his humour is always wise.”—Sunday Times * “He is still inimitable. No one, anywhere in the world, can reduce a thing to ridicule with such few short strokes. He is the Grock of literature.”—Evening Standard * “I detest life-insurance agents: they always argue that I shall some day die, which is not so.” * “Hockey captures the essence of Canadian experience in the New World. In a land so inescapably and inhospitably cold, hockey is the chance of life, and an affirmation that despite the deathly chill of winter we are alive.” References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stephen_Leacock


Duncan Campbell Scott (August 2, 1862– December 19, 1947) was a Canadian bureaucrat, poet and prose writer. With Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, and Archibald Lampman, he is classed as one of Canada’s Confederation Poets. Scott was a Canadian lifetime civil servant who served as deputy superintendent of the Department of Indian Affairs from 1913 to 1932, and is better known today for advocating the assimilation of Canada’s First Nations peoples in that capacity. Life and legacy Scott was born in Ottawa, Ontario, the son of Rev. William Scott and Janet MacCallum. He was educated at Stanstead Wesleyan College. Early in life, he became an accomplished pianist. Scott wanted to be a doctor, but family finances were precarious, so in 1879 he joined the federal civil service. As the story goes, q:William Scott might not have money [but] he had connections in high places. Among his acquaintances was the prime minister, Sir John A. Macdonald, who agreed to meet with Duncan. As chance would have it, when Duncan arrived for his interview, the prime minister had a memo on his desk from the Indian Branch of the Department of the Interior asking for a temporary copying clerk. Making a quick decision while the serious young applicant waited in front of him, Macdonald wrote across the request: 'Approved. Employ Mr. Scott at $1.50.’ Scott "spent his entire career in the same branch of government, working his way up to the position of deputy superintendent of Indian Affairs in 1913, the highest non-elected position possible in his department. He remained in this post until his retirement in 1932.” Scott’s father also subsequently found work in Indian Affairs, and the entire family moved into a newly built house on 108 Lisgar St., where Duncan Campbell Scott would live for the rest of his life. In 1883 Scott met fellow civil servant, Archibald Lampman. It was the beginning of an instant friendship that would continue unbroken until Lampman’s death sixteen years later.... It was Scott who initiated wilderness camping trips, a recreation that became Lampman’s favourite escape from daily drudgery and family problems. In turn, Lampman’s dedication to the art of poetry would inspire Scott’s first experiments in verse. By the late 1880s Scott was publishing poetry in the prestigious American magazine, Scribner’s. In 1889 his poems “At the Cedars” and “Ottawa” were included in the pioneering anthology, Songs of the Great Dominion. Scott and Lampman "shared a love of poetry and the Canadian wilderness. During the 1890s the two made a number of canoe trips together in the area north of Ottawa.” In 1892 and 1893, Scott, Lampman, and William Wilfred Campbell wrote a literary column, “At the Mermaid Inn,” for the Toronto Globe. "Scott... came up with the title for it. His intention was to conjure up a vision of The Mermaid Inn Tavern in old London where Sir Walter Raleigh founded the famous club whose members included Ben Jonson, Beaumont and Fletcher, and other literary lights. In 1893 Scott published his first book of poetry, The Magic House and Other Poems. It would be followed by seven more volumes of verse: Labor and the Angel (1898), New World Lyrics and Ballads (1905), Via Borealis (1906), Lundy’s Lane and Other Poems (1916), Beauty and Life (1921), The Poems of Duncan Campbell Scott (1926) and The Green Cloister (1935). In 1894, Scott married Belle Botsford, a concert violinist, whom he had met at a recital in Ottawa. They had one child, Elizabeth, who died at 12. Before she was born, Scott asked his mother and sisters to leave his home (his father had died in 1891), causing a long-time rift in the family. In 1896 Scott published his first collection of stories, In the Village of Viger, "a collection of delicate sketches of French Canadian life. Two later collections, The Witching of Elspie (1923) and The Circle of Affection (1947), contained many fine short stories." Scott also wrote a novel, although it was not published until after his death (as The Untitled Novel, in 1979). After Lampman died in 1899, Scott helped publish a number of editions of Lampman’s poetry. Scott “was a prime mover in the establishment of the Ottawa Little Theatre and the Dominion Drama Festival.” In 1923 the Little Theatre performed his one-act play, Pierre; it was later published in Canadian Plays from Hart House Theatre (1926). His wife died in 1929. In 1931 he married poet Elise Aylen, more than 30 years his junior. After he retired the next year, "he and Elise spent much of the 1930s and 1940s travelling in Europe, Canada and the United States.” He died in December 1947 in Ottawa at the age of 85 and is buried in Ottawa’s Beechwood Cemetery. Indian Affairs Prior to taking up his position as head of the Department of Indian Affairs, in 1905 Scott was one of the Treaty Commissioners sent to negotiate Treaty No. 9 in Northern Ontario. Aside from his poetry, Scott made his mark in Canadian history as the head of the Department of Indian Affairs from 1913 to 1932. Even before Confederation, the Canadian government had adopted a policy of assimilation under the Gradual Civilization Act 1857. One biographer of Scott states that: The Canadian government’s Indian policy had already been set before Scott was in a position to influence it, but he never saw any reason to question its assumption that the 'red’ man ought to become just like the 'white’ man. Shortly after he became Deputy Superintendent, he wrote approvingly: ‘The happiest future for the Indian race is absorption into the general population, and this is the object and policy of our government.’... Assimilation, so the reasoning went, would solve the ‘Indian problem,’ and wrenching children away from their parents to 'civilize’ them in residential schools until they were eighteen was believed to be a sure way of achieving the government’s goal. Scott... would later pat himself on the back: ‘I was never unsympathetic to aboriginal ideals, but there was the law which I did not originate and which I never tried to amend in the direction of severity.’ while Scott himself wrote: I want to get rid of the Indian problem. I do not think as a matter of fact, that the country ought to continuously protect a class of people who are able to stand alone… Our objective is to continue until there is not a single Indian in Canada that has not been absorbed into the body politic and there is no Indian question, and no Indian Department, that is the whole object of this Bill. In 1920, under Scott’s direction, and with the concurrence of the major religions involved in native education, an amendment to the Indian Act made it mandatory for all native children between the ages of seven and fifteen to attend school. Attendance at a residential school was made compulsory. Although a reading of Bill 14 states that no particular kind of school was stipulated. Scott was in favour of residential schooling for aboriginal children, as he believed removing them from the influences of home and reserve would hasten the cultural and economic transformation of the whole aboriginal population. In cases where a residential school was the only kind available, residential enrollment did become mandatory, and aboriginal children were compelled to leave their homes, their families and their culture, with or without their parents’ consent. However, in 1901, 226 of the 290 Indian schools across Canada were day schools, and by 1961, the 377 day schools far outnumbered the 56 residential institutions. CBC has reported that "In all, about 150,000 aboriginal, Inuit and Métis children were removed from their communities and forced to attend the schools." The 150,000 enrollment figure is an estimate not disputed by Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development, but it is not clear what percentage were “removed from their communities and forced to attend the schools.” A percentage of the residential schools were in or close by the children’s communities. Moreover, while many aboriginal parents distrusted the residential schools or preferred to raise and educate their children in a traditional manner, other parents willingly enrolled their children, partly from a belief that the schooling of the “white man” would benefit them, and partly from a knowledge that schools would provide shelter, food and clothing which dire conditions on the reserve could not provide. Harsh criticism has been leveled at Scott and the residential school system, as children who attended some of the more poorly maintained or administered schools lived in terrible conditions; in some cases the mortality rate exceeded fifty percent due to the spread of infectious disease. This situation was made worse by the federal policy that tied funding to enrollment numbers, which resulted in some schools enrolling sick children in order to boost their numbers. Echoing Scott’s desire to absorb aboriginals into the wider Canadian population, many residential and day schools strongly discouraged students from speaking their native language, and harsh punishments were administered. Corporal punishment was sometimes justified by the belief that it was the only way to “save souls”, “civilize” the native children and, in the residential schools, punish runaways who might make the school responsible for injury or death while trying to return home. Many reports of physical, sexual and psychological abuse in the residential schools have surfaced over the years. Because any kind of scandal coming out of the residential schools would have caused Indian Affairs, the churches and the government of the day much embarrassment, incidents of abuse were often discounted or covered up. When Scott retired, his “policy of assimilating the Indians had been so much in keeping with the thinking of the time that he was widely praised for his capable administration.” At the time, Scott was able to point to evidence of success in increasing enrollment and attendance, as the number of First Nations children enrolled in any school rose from 11,303 in 1912 to 17,163 in 1932. Residential school enrollment during the same period rose from 3,904 to 8,213. Actual attendance figures from all schools had also risen sharply, going from 64% of enrollment in 1920 to 75% in 1930, and Scott attributed this rise partly to Bill 14's section on compulsory attendance but also to a more positive attitude among First Nations people toward education. However, despite the encouraging statistics, Scott’s efforts to bring about assimilation through residential schools could be judged a failure, as many former students retained their language, went on to maintain and preserve their tribe’s culture, and refused to accept full Canadian citizenship when it was offered. Moreover, over the long history of the residential system, only a minority of all enrolled students went beyond the elementary grades, and many former students found themselves lacking the skills that would enable them to find employment on or off the reserve. Honours and awards Scott was honoured for his writing during and after his lifetime. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada in 1899 and served as its president from 1921 to 1922. The Society awarded him the second-ever Lorne Pierce Medal in 1927 for his contributions to Canadian literature. In 1934 he was made a Companion of the Order of St. Michael and St. George. He also received honorary degrees from the University of Toronto (Doctor of Letters in 1922) and Queen’s University (Doctor of Laws in 1939). In 1948, the year after his death, he was designated a Person of National Historic Significance. Poetry Scott’s "literary reputation has never been in doubt. He has been well represented in virtually all major anthologies of Canadian poetry published since 1900.” In Poets of the Younger Generation (1901), Scottish literary critic William Archer wrote of Scott: He is above everything a poet of climate and atmosphere, employing with a nimble, graphic touch the clear, pure, transparent colours of a richly-furnished palette.... Though it must not be understood that his talent is merely descriptive. There is a philosophic and also a romantic strain in it... There is scarcely a poem of Mr. Scott’s from which one could not cull some memorable descriptive passage.... As a rule Mr. Scott’s workmanship is careful and highly finished. He is before everything a colourist. He paints in lines of a peculiar and vivid translucency. But he is also a metrist of no mean skill, and an imaginative thinker of no common capacity. The Government of Canada biography of him says that: Although the quality of Scott’s work is uneven, he is at his best when describing the Canadian wilderness and Indigenous peoples. Although they constitute a small portion of his total output, Scott’s widely recognized and valued 'Indian poems’ cemented his literary reputation. In these poems, the reader senses the conflict that Scott felt between his role as an administrator committed to an assimilation policy for Canada’s Native peoples and his feelings as a poet, saddened by the encroachment of European civilization on the Indian way of life. “There is not a really bad poem in the book,” literary critic Desmond Pacey said of Scott’s first book, The Magic House and Other Poems, “and there are a number of extremely good ones.” The 'extremely good ones’ include the strange, dream-like sonnets of “In the House of Dreams.” “Probably the best known poem from the collection is ‘At the Cedars,’ a grim narrative about the death of a young man and his sweetheart during a log-jam on the Ottawa River. It is crudely melodramatic,... but its style—stark understatement, irregular lines, and abrupt rhymes—makes it the most experimental poem in the book.” His next book, Labour and the Angel, “is a slighter volume than The Magic House in size and content. The lengthy title poem makes dreary reading.... Of greater interest is his growing willingness to experiment with stanza form, variations in line length, use of partial rhyme, and lack of rhyme.” Notable new poems included “The Cup” and the sonnet “The Onandaga Madonna.” But arguably “the most memorable poem in the new collection” was the fantasy, “The Piper of Arll.” One person who long remembered that poem was future British Poet Laureate John Masefield, who read “The Piper of Arll” as a teenager and years later wrote to Scott: I had never (till that time) cared very much for poetry, but your poem impressed me deeply, and set me on fire. Since then poetry has been the one deep influence in my life, and to my love of poetry I owe all my friends, and the position I now hold. New World Lyrics and Ballads (1905) revealed “a voice that is sounding ever more different from the other Confederation Poets... his dramatic power is increasingly apparent in his response to the wilderness and the lives of the people who lived there.” The poetry included “On the Way to the Mission” and the much-anthologized “The Forsaken,” two of Scott’s best-known “Indian poems.” Lundy’s Lane and Other Poems (1916) seemed “to have been cobbled together at the insistence of his publishers, who wanted a collection of his work that had not been published in any previous volume.”. The title poem was one that had won Scott, "in the Christmas Globe contest of 1908,... the prize of one hundred dollars, offered for the best poem on a Canadian historical theme.". Other notable poems in the volume include the pretty lyric “A Love Song,” the long meditation, “The Height of Land,” and the even longer “Lines Written in Memory of Edmund Morris.” Anthologist John Garvin called the last “so original, tender and beautiful that it is destined to live among the best in Canadian literature.” “In his old age, Scott would look back upon Beauty and Life (1921) as his favourite among his volumes of verse," E.K. Brown tells us, adding: “In it most of the poetic kinds he cared about are represented.” There is a great diversity, from the moving war elegy “To a Canadian Aviator Who Died For His Country in France,” to the strange, apocalyptic “A Vision.” The Green Cloister, published after Scott’s retirement, "is a travelogue of the sites he visited in Europe with Elise: Lake Como, Ravelllo, Kensington Gardens, East Gloucester, etc.—descriptive and contemplative poems by an observant tourist. Those with a Canadian setting include two Indian poems of near-melodrama—'A Scene at Lake Manitou’ and 'At Gull Lake, August 1810'—that are in stark contrast to the overall serenity of the volume." More typical is the title poem, “Chiostro Verde.” The Circle of Affection (1947) contains 26 poems Scott had written since Cloister, and several prose pieces, including his Royal Society address on “Poetry and Progress.” It includes “At Delos,” which brings to mind the poet’s approaching death: There is no grieving in the world As beauty fades throughout the years: The pilgrim with the weary heart Brings to the grave his tears. Reputation as an assimilationist In 2003, Scott’s Indian Affairs legacy came under attack from Neu and Therrien: [Scott] took a romantic interest in Native traditions, he was after all a poet of some repute (a member of the Royal Society of Canada), as well as being an accountant and a bureaucrat . He was three people rolled into one confusing and perverse soul. The poet romanticized the whole 'noble savage’ theme, the bureaucrat lamented our inability to become civilized, the accountant refused to provide funds for the so-called civilization process. In other words, he disdained all ‘living’ Natives but “extolled the freedom of the savages”. According to Encyclopædia Britannica, Scott is "best known at the end of the 20th century," not for his writing, but “for advocating the assimilation of Canada’s First Nations peoples.” As part of their Worst Canadian poll, a panel of experts commissioned by Canada’s National History Society named Scott one of the Worst Canadians in the August 2007 issue of The Beaver. In his 2013 Conversations with a Dead Man: The Legacy of Duncan Campbell Scott, fabulist Mark Abley explored the paradoxes surrounding Scott’s career. Abley did not attempt to defend Scott’s work as a bureaucrat, but he showed that Scott is more than simply a one-dimensional villain. Controversy over Arc Poetry prize Arc Poetry Magazine renamed the annual “Archibald Lampman Award” (given to a poet in the National Capital Region) to the Lampman-Scott Award in recognition of Scott’s enduring legacy in Canadian poetry, with the first award under the new name given out in 2007. The winner of the 2008 award, Shane Rhodes, turned over half of the $1,500 prize money to the Wabano Centre for Aboriginal Health, a First Nations health centre. “Taking that money wouldn’t have been right, with what I’m writing about,” Rhodes said. The poet was researching First Nations history and found Scott’s name repeatedly referenced. In the words of a CBC News report, Rhodes felt “Scott’s legacy as a civil servant overshadows his work as a pioneer of Canadian poetry”. The editor of Arc Poetry Magazine, Anita Lahey, responded with a statement that she thought Scott’s actions as head of Indian Affairs were important to remember, but did not eclipse his role in the history of Canadian literature. “I think it matters that we’re aware of it and that we think about and talk about these things,” she said. “I don’t think controversial or questionable activities in the life of any artist or writer is something that should necessarily discount the literary legacy that they leave behind.” More recently, the magazine has stated on its website that "For the years 2007 through 2009, the Archibald Lampman Award merged with the Duncan Campbell Scott Foundation to become the Lampman-Scott Award in honour of two great Confederation Poets. This partnership came to an end in 2010, and the prize returned to its former identity as the Archibald Lampman Award for Poetry.” Publications Poetry * The Magic House and Other Poems. London: Methuen and Co. 1893. - The Magic House and Other Poems at Google Books * Labor and the Angel. Boston: Copeland & Day. 1898. – Labor and the Angel at Google Books– Labor and the Angel - Scholar’s Choice Edition at Google Books * New World Lyrics and Ballads. Toronto: Morang & Co. – New World Lyrics and Ballads at Google Books– New World Lyrics and Ballads - Scholar’s Choice Edition at Google Books * Via Borealis. Toronto: W. Tyrell. 1906. * Lundy’s Lane and Other Poems. Toronto: McClelland, Stewart & Stewart. 1916. - Lundy’s Lane and Other Poems at Google Books * To the Canadian Mothers and Three Other Poems. Toronto: Mortimer. 1917. * “After a Night of Storm” (PDF). Dalhousie Review 1 (2). 1921. * Beauty and Life. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart. 1921. - Beauty and Life at Google Books * “Permanence” (PDF). Dalhousie Review 2 (4). 1923. * The Poems of Duncan Campbell Scott. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart. 1926. - The Poems of Duncan Campbell Scott at Google Books * “By the Sea” (PDF). Dalhousie Review 7 (1). 1927. * The Green Cloister: Later Poems. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart. 1935. - The Green Cloister: Later Poems at Google Books * Brown, E.K., ed. (1951). Selected Poems. Toronto: Ryerson. * Clever, Glenn, ed. (1974). Duncan Campbell Scott: Selected Poetry. Ottawa: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-9196-6252-0. * Souster, Raymond; Lochhead, Douglas, eds. (1985). Powassan’s Drum: Selected Poems of Duncan Campbell Scott. Ottawa: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-9196-6211-7. Fiction * In the Village of Viger. Boston: Copeland & Day. 1896. - In the Village of Viger at Google Books * The Witching of Elspie: A Book of Stories. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart. 1923. * The Circle of Affection and Other Pieces in Prose and Verse. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart. 1947. - mostly prose * Clever, Glenn, ed. (1987) [1972]. Selected Stories of Duncan Campbell Scott (revised 3rd ed.). Ottawa: University of Ottawa Press. ISBN 978-0-7766-0183-0. * Untitled Novel (posthumously published). Moonbeam, Ontario: Penumbra. 1979 [c. 1905]. ISBN 0-920806-04-X. * Ware, Tracy, ed. (2001). “The Uncollected Short Stories of Duncan Campbell Scott”. Duncan Campbell Scott. London, Ontario: Canadian Poetry Press. Non-fiction * John Graves Simcoe. Makers of Canada, volume VII. Toronto: Morang & Co. 1905. - John Graves Simcoe at Google Books * The Administration of Indian Affairs in Canada. Volume 3. Toronto: Canadian Institute of International Affairs. 1931. * Walter J. Phillips. Toronto: Ryerson. 1947. - Walter J. Phillips at Google Books * Bourinot, Arthur S., ed. (1960). More Letters of Duncan Campbell Scott. Ottawa: Bourinot. * Davies, Barrie, ed. (1979). At the Mermaid Inn: Wilfred Campbell, Archibald Lampman, Duncan Campbell Scott in the Globe 1892–93. Toronto: University of Toronto Press. ISBN 978-0-8020-6333-5. * Macdougall, Robert L., ed. (1983). The Poet and the Critic: A Literary Correspondence Between Duncan Campbell Scott and E.K. Brown. Ottawa: Carleton University Press. ISBN 978-0-8862-9013-9. Edited * Lampman, Archibald (1900). Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. The Poems of Archibald Lampman. Toronto: Morang & Co. * Lampman, Archibald (1925). Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. Lyrics of Earth: Sonnets and Ballads. Toronto: Musson. * Lampman, Archibald (1943). Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. At the Long Sault and Other New Poems. Toronto: Ryerson. * Lampman, Archibald (1947). Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. Selected Poems of Archibald Lampman. Toronto: Ryerson. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duncan_Campbell_Scott


Charles-Nérée Beauchemin (1850-1931) est un écrivain et médecin québécois. Il a écrit un magnifique poème intitulé Fleur d'Aurore: En voici un extrait: « Ensemble nous irons encore Cueillir dans les prés, au matin De ces bouquets couleur d'aurore Qui fleurent la rose et le thym... » Biographie Charles-Nérée Beauchemin naît le 20 février 1850 à Yamachiche, au Québec. Fils de Hyacinthe Beauchemin, un médecin, et d'Elzire Richer-Laflèche, il est lié, du côté de sa mère, à Monseigneur Laflèche, le 2e évêque de Trois-Rivières, à sir Lomer Gouin, ancien Premier Ministre de la province du Québec et à l'ancien gouverneur de l'État de Rhode Island, Aram Pothier. Il poursuit ses études au séminaire de Nicolet de 1863 à 1870 et à l'Université Laval de 1870 à 1874. Dans le premier cas, pour suivre des études classiques, dans le deuxième, pour suivre des études médicales. Après avoir reçu son diplôme, il s'établit à Yamachiche, où il passe le restant de sa vie. Là, il publie ses vers dans les journaux et les revues du temps et commence sa carrière en écriture. En 1878, il se marie à l'âge de 28 ans avec Anna Lacerte, fille d'un ancien député du comté de Saint-Maurice. Avec elle, il élève 5 garçons et 5 filles. Il est reconnu d'avoir eu des amitiés avec de grands poètes, tels Louis-Honoré Fréchette et Pamphile Lemay. Nérée Beauchemin publie son premier recueil, Les Floraisons matutinales, en 1897, avant son 47e anniversaire. Son confident, l'Abbé Albert Tessier, le persuade de publier ses poèmes inédits en un deuxième recueil. En 1928, Nérée Beauchemin publie Patrie intime. Il reçoit plusieurs diplômes. En 1888, il reçoit, de la part de la Société Royale du Canada, un diplôme d'honneur, et un diplôme de maîtrise en 1928 dans les jeux florimontains. Au 11 novembre 1928, il reçoit le Grand Prix d'apostolat laïque par la poésie et un doctorat dans les lettres de Laval. Il accepte, le 13 septembre 1930, la médaille de l'Académie française. Il meurt à Yamachiche le 29 juin 1931 à 81 ans. Le 22 octobre 1950, la Société Royale et l'Académie canadienne-française se font représenter aux cérémonies d'hommage de Yamachiche, où les villageois célèbrent le 100e anniversaire du poète. La même année, avec une étude-préface de Clément Marchand, Choix de poésies de Nérée Beauchemin se fait publier posthumément. Au 4 janvier 1952, Yamachiche rend un dernier hommage au poète en se donnant une rue Nérée Beauchemin. Trois-Rivières accomplit le même hommage en mémoire de Beauchemin. Aujourd'hui, il est considéré comme un des premiers écrivains du terroir. Les références Wikipedia – https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nérée_Beauchemin


Frederick George Scott (7 April 1861– 19 January 1944) was a Canadian poet and author, known as the Poet of the Laurentians. He is sometimes associated with Canada’s Confederation Poets, a group that included Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, Archibald Lampman, and Duncan Campbell Scott. Scott published 13 books of Christian and patriotic poetry. Scott was a British imperialist who wrote many hymns to the British Empire—eulogizing his country’s roles in the Boer Wars and World War I. Many of his poems use the natural world symbolically to convey deeper spiritual meaning. Frederick George Scott was the father of poet F. R. Scott.


Marjorie Lowry Christie Pickthall (14 September 1883, Gunnersbury, London– 19 April 1922, Vancouver), was a Canadian writer who was born in England but lived in Canada from the time she was seven. She was once “thought to be the best Canadian poet of her generation.” According to her father, she had planned her career before she was six; she would be a writer and illustrator of books. Her parents encouraged her artistic talents with lessons in drawing and music; an accomplished violinist, she continued studying violin until she was twenty.


Lieutenant Colonel John McCrae, MD (November 30, 1872– January 28, 1918) was a Canadian poet, physician, author, artist and soldier during World War I, and a surgeon during the Second Battle of Ypres, in Belgium. He is best known for writing the famous war memorial poem “In Flanders Fields”. McCrae died of pneumonia near the end of the war.


Alphonse Beauregard (1881-1924) est un poète québécois. Biographie Né à La Patrie (Compton en Québec) le 5 janvier 1881, Alphonse Beauregard doit abandonner ses études à la mort de son père. Il pratique alors divers métiers, tout en publiant des poèmes dès 1906 dans quelques journaux et revues (parfois sous pseudonyme de A. Chasseur). Il prend une part active à la rédaction du Terroir et devient secrétaire de l'école littéraire de Montréal, tout en travaillant comme commis au port de Montréal. À peine élu président de l'école, il meurt asphyxié au gaz le 15 janvier 1924. Son poème « Impuissance » est paradoxalement un des plus puissants de cette époque. Ses œuvres * Les forces, 1912, édité par Arbour & Dupont à Montréal * Les alternances : poèmes, 1921, édité par Dupont et Roger Maillet à Montréal * La brume:poésie * Bonheur lucide Les références Wikipedia – https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/


William Wilfred Campbell (15 June 1860– 1 January 1918) was a Canadian poet. He is often classed as one of the country’s Confederation Poets, a group that included fellow Canadians Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, Archibald Lampman, and Duncan Campbell Scott; he was a colleague of Lampman and Scott. By the end of the 19th century, he was considered the “unofficial poet laureate of Canada.” Although not as well known as the other Confederation poets today, Campbell was a “versatile, interesting writer” who was influenced by Robert Burns, the English Romantics, Edgar Allan Poe, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Thomas Carlyle, and Alfred Tennyson. Inspired by these writers, Campbell expressed his own religious idealism in traditional forms and genres.


Theodore Goodridge Roberts (July 7, 1877– February 24, 1953) was a Canadian novelist and poet. He was the author of thirty-four novels and over one hundred published stories and poems. He was the brother of poet Charles G.D. Roberts, and the father of painter Goodridge Roberts. Life He was born George Edwards Theodore Goodridge Roberts in Fredericton, to Emma Wetmore Bliss and Anglican Rev. George Goodridge Roberts. The poet Charles G.D. Roberts, and the writers William Carman Roberts and Jane Roberts MacDonald, were his siblings. He published his first poem in 1899, when he was eleven, in the New York Independent (where his cousin Bliss Carman was working), and his first prose piece (a comparison of the Battle of Waterloo and the Battle of Gettysburg) in the Century two years later. Roberts attended Fredericton Collegiate School, though (since school records were lost in a fire) the exact years are unknown. He later went to University of New Brunswick (UNB), but left without graduating. He published poetry in UNB’s University Magazine. In 1897 he moved to New York City, living with his brothers Charles and William and working at The Independent. In 1898 the magazine sent him to Cuba, as a special correspondent, to cover the Spanish–American War. While on the island he contracted malaria—he was sent back to New York and consulted specialists, who sent him back to Fredericton “to die.” An unnamed surgeon saved Roberts’s life, and he was nursed back to heath by Frances Seymour Allen (whom he would subsequently marry). The next year he travelled to Newfoundland, where he helped to found and edit The Newfoundland Magazine. He published his first book of poetry (Northand Lyrics, an anthology edited by Charles G.D. Roberts and featuring his three siblings) in 1899, and his first novel, The House of Isstens, in 1900. In 1901 Roberts sailed on a barkentine to Brazil. In 1902 he returned to Fredericton and briefly edited a second magazine, The Kit-Bag. Roberts married Frances Seymour Allen in November 1903, and they had a two-year honeymoon in Barbados where their first child was born. They would have four children: William Goodridge, Dorothy Mary Gostwick, Theodora Frances Bliss and Loveday (who died as an infant). Roberts averaged three novels a year from 1908 until 1914. At that time his “many novels of adventure and romance” already enoyed a “wide popularity in English-speaking lands.” A former militiaman, Roberts re-enlisted in 1914 when World War I broke out, serving as a lieutenant in the 12th Canadian Infantry Battalion, commanded by Lt.-Col. Harry Fulton McLeod of Fredericton—Roberts’ entire family followed him to England. When the 12th Battalion was assigned to a reserve and training roll in early 1915, Roberts was transferred to a position perhaps better fitted to his combination of military knowledge and literary skill. "In the summer of 1915, he was transferred to the Canadian War Records Office at the request of Max Aitken, Lord Beaverbrook. Roberts wrote official reports and battlefield accounts and published three works in collaboration with others." He was promoted captain early in 1916. When Roberts was in Europe he left his manuscripts and papers, including work not yet published, with a Dr. Wainwright in Saint John, who stored them in his basement. They were destroyed in the spring of 1919 when the Saint John River flooded. In 1929 Roberts wrote a weekly column for the Saint John Telegraph-Journal, “Under the Sun.” From April through September 1930 he edited another small magazine, Acadie. In 1932 he undertook his last major sea cruise, sailing through the Panama Canal to Vancouver and back. The same year he did a cross-Canada reading tour, which “culminated with festivities in Vancouver.” Roberts moved to Toronto in 1935, and in 1937 briefly edited another magazine, Spotlight. In 1939 he relocated to Aylmer, Quebec, where he briefly founded another magazine, Swizzles. He returned to New Brunswick in 1941, and in 1945 moved to Digby, Nova Scotia, where he would die eight years later. He is buried beside Charles G.D. Roberts and Bliss Carman in Fredericton’s Forest Hill Cemetery. Writing The Dictionary of Literary Biography (DLB) says that T.G. Roberts’s “poetry and fiction, staggering in sheer quantity and variety, show at their best Roberts’s most enduring gifts: in his poetry a love of nature well served by a keen eye for local color and detail, a good ear for clean, clear rhythm and rhyme, and a forceful, uncluttered narrative line; and in fiction a talent for presenting his abiding perception of universal struggles between good and evil either in mythic tales of adventure or in regional stories animated by local settings, customs, and dialects.” Of the poems in his 1926 collection, The Lost Shipmate, The Encyclopedia of Literature commented: "Had this volume appeared forty years earlier it might have won for Theodore a reputation equal to that of his brother Charles or of Bliss Carman. Poems such as ‘The sandbar’ and ‘Magic’ are unmatched in Canadian poetry for a facility and clarity of image suggestive of high-realist painting. However, much of what Roberts wrote has been forgotten with time, or has not stood the tests of time and changing fashion. The Merriest Knight The writing that Roberts is most likely to be recognized for today is The Merriest Knight, his collection of Arthurian tales. This looks like the one book by Roberts currently in print - ironically, considering that it was never published as a book during Roberts’s lifetime. Roberts began to write Arthurian fiction in the 1920s; most of these stories, though, were published in the late 1940s and early 1950s in the fiction magazine Blue Book. Roberts planned to publish them as a collection, but died in 1953 before he could do so. In 2001 Mike Ashley, editor of the Mammoth publishing group, brought them out under his Green Knight imprint. A review for SFSite called the collection’s writing “polished,” “erudite,” and “eminently readable,” but “somewhat tame”: “literature for the afternoon tea and crumpets crowd– in a word 'polite’ Arthurian fiction.” Still, it concluded, “if you’re looking for something a bit more upbeat, some Arthuriana-lite, The Merriest Knight is just the book for you.” Recognition The University of New Brunswick awarded Roberts a Doctorate of literature in 1930. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada in 1934. Publications Fiction * The House of Isstens. Boston: L.C. Page, 1900. * Hemming the Adventurer. Boston: L.C. Page, 1904. * Brothers in Peril: A Story of Old Newfoundland, 1905. Boston: L.C. Page & Company, 1905. * Red Feathers: a story of remarkable adventures when the world was young. Boston: L.C. Page, 1907. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart. ISBN 978-0-7710-9227-5 * Captain Love. Boston: L.C. Page & Company, 1908. * Flying Plover: His Stories, Told Him by Squat-by-the-Fire. Boston: L.C. Page, 1909. * A Cavalier of Virginia: a romance. Chicago: M.A. Donohue, 1910. * Comrades of the Trails. Boston: L.C. Page & Company, 1910. * Love on a Smokey River. 1911. * A Captain of Raleigh’s: a romance. Boston: L.C. Page & Company, 1911. * A Soldier of Valley Forge. with Robert Neilson Stephens. Boston: L.C. Page, 1911. * Blessington’s Folly. London: John Long, 1912. * Rayton: a backwoods mystery. Boston: L.C. Page, 1912. * The Harbor Master. Chicago: M.A. Donohue, 1913. * Two Shall Be Born. New York: Cassell, 1913. * The Wasp. Toronto: Bell & Cockburn, 1914. * The Toll of the Tides. 1914. * In the High Woods. London: John. Long, 1916. * Forest Fugitives. Toronto: McClelland, Goodchild & Stewart, 1917. * The Islands of Adventure. London; Toronto: Hodder and Stoughton, 1918. * Jess of the River. London: John Long, 1918. * The Exiled Lover. London: John Long, 1919. * Honest Fool. New York: F.A. Munsey, 1925. * The Master of the Moosehorn and Other Backwoods Stories. London; Toronto: Hodder and Stoughton, 1919. * Moonshine. London: Hodder and Stoughton, [1920?]. * The Lure of Piper’s Glen. Garden City, NY: Doubleday, Page, 1921. * The Fighting Starkleys. George Varian illus. Boston: Page, 1922. * Musket House. 1922. * Tom Akerley: his adventures in the tall timber and at Gaspard’s clearing on the Indian River. Boston: L.C. Page, 1923. * Green Timber Thoroughbreds. New York: Garden City, 1924. * The Stranger from Up-Along. Garden City, NJ: Doubleday, Page & co., 1924. * The Red Pirogue: a tale of adventure in the Canadian wilds. Boston: L.C. Page, 1924. * The Oxford Wizard. Garden City, NY: Garden City Pub., 1924. * The Lost Shipmate. Toronto: Ryerson, 1926. * The Golden Highlanders. Boston: L.C. Page, 1929. * The Merriest Knight: The Collected Arthurian Tales of Theodore Goodridge Roberts. Mike Ashley ed. Green Knight, 2001. ISBN 978-1-928999-18-8 Non-fiction * Patrols and Trench Raids. 1916. * Battalion Histories. 1918. * Thirty Canadian V.Cs 23rd April 1915 to 30th March 1918, with Robin Richards and Stuart Martin. London: Skeffington, 1918. * Loyalists: a compilation of histories, biographies and genealogies of United empire loyalists and their descendants. Toronto: T. Goodridge Roberts, 1937. Poetry * Northland Lyrics, William Carman Roberts, Theodore Roberts & Elizabeth Roberts Macdonald; selected and arranged with a prologue by Charles G.D. Roberts and an epilogue by Bliss Carman. Boston: Small, Maynard & Co., 1899. ISBN 0-665-12501-1 * Seven Poems. private, 1925. chapbook. * The Lost Shipmate. Toronto: Ryerson Chapbook, 1926. * The Leather Bottle. Toronto: Ryerson, 1934. * That Far River: Selected Poems of Theodore Goodridge Roberts. Martin Ware, ed. London, ON: Canadian Poetry Press, 1998. * Except where noted, bibliographical information courtesy St. Thomas University. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theodore_Goodridge_Roberts


Sir Charles George Douglas Roberts (January 10, 1860– November 26, 1943) was a Canadian poet and prose writer who is known as the Father of Canadian Poetry. He was “almost the first Canadian author to obtain worldwide reputation and influence; he was also a tireless promoter and encourager of Canadian literature. He published numerous works on Canadian exploration and natural history, verse, travel books, and fiction.” “At his death he was regarded as Canada’s leading man of letters.” Besides his own body of work, Roberts is also called the “Father of Canadian Poetry” because he served as an inspiration and a source of assistance for other Canadian poets of his time.

Agnes Ethelwyn Wetherald was born of English-Quaker parents at Rockwood, Ontario, April 26th, 1857. Her father was the late Rev. William Wetherald, who founded the Rockwood Academy about the middle of the last century, and was its principal for some years. He was a lover of good English, spoken and written, and his talented daughter has owed much to his careful teaching. He was the teacher whom the late James J. Hill, the railway magnate, had held in such grateful remembrance. Additional education was received by Miss Wetherald at the Friends' Boarding School, Union Springs, N.Y., and at Pickering College. Miss Wetherald began the writing of poetry later in life than most poets and her first book of verse, The House of the Trees and Other Poems, did not appear until 1895. This book at once gave her high rank among women poets. Prior to this, she had collaborated with G. Mercer Adam on writing and publishing a novel, An Algonquin Maiden, and had conducted the Woman's Department in The Globe, Toronto, under the nom de plume, 'Bel Thistlewaite.' In 1902, appeared her second volume of verse, Tangled in Stars, and, in 1904, her third volume, The Radiant Road. In the autumn of 1907, a collection of Miss Wetherald's best poems was issued, entitled, The Last Robin: Lyrics and Sonnets. It was warmly welcomed generally, by reviewers and lovers of poetry. The many exquisite gems therein so appealed to Earl Grey, the then Governor-General of Canada, that he wrote a personal letter of appreciation to the author, and purchased twenty-five copies of the first edition for distribution among his friends. For years Miss Wetherald has resided on the homestead farm, near the village of Fenwick, in Pelham Township, Weland county, Ontario, and there in the midst of a large orchard and other rural charms, has dreamed, and visioned, and sung, pouring out her soul in rare, sweet songs, with the naturalness of a bird. And like a bird she has a nest in a large willow tree, cunningly contrived by a nature-loving brother, where her muse broods contentedly, intertwining her spirit with every aspect of the beautiful environment.


Arthur Stringer (February 26, 1874– September 13, 1950) was a Canadian novelist, screenwriter, and poet who later moved to the United States. He published 45 works of fiction and 15 other books, in addition to writing numerous filmscripts and articles. Stringer was born in Chatham, Ontario. “He was a high spirited boy who spent his childhood days fishing, swimming, raiding orchards and manning a pirate ship.” He attended University College, University of Toronto from 1892 to 1894 and later studied at Oxford University. His first book of poetry, Watchers of Twilight and Other Poems, was published in 1894.


George Frederick Cameron (24 September 1854– 17 September 1885) was a Canadian poet, lawyer, and journalist, best known for the libretto for the operetta Leo, the Royal Cadet. He moved to Boston in April 1869. He graduated from the Boston University School of Law in 1877. He worked for the law firm Dean, Butler and Abbot of Boston from 1877 to 1882. He contributed poetry to Boston periodicals, including the Courier and the Transcript. In fall 1882 he enrolled in Queen’s College in Kingston, Ontario where he won a poetry prize in 1883 for “Adelphi.” He is sometimes considered one of the Confederation Poets.


Charles Sangster (July 16, 1822– December 9, 1893) was a Canadian poet whose 1856 volume, The St. Lawrence and the Saguenay, “was received with unanimous acclaim as the best and most important book of poetry produced in Canada until that time.” He was “the first poet who made appreciative use of Canadian subjects in his poetical work.” The Dictionary of Canadian Biography calls him “the best of the pre-confederation poets.” Life Sangster was born at the Navy Yard on Point Frederick (now the site of Royal Military College of Canada), near Kingston, Ontario, the son of Ann Ross and James Sangster. A twin sister died in infancy. His father, a “joiner” or shipbuilder who worked for the British Navy around the Great Lakes, died at Penetanguishene just before Charles turned 2. His mother raised Charles and his 4 siblings on her own. Sangster was an indifferent student, finding “the school curriculum irrelevant and his masters stern and uninspiring.” At 15 years old, he left school to help provide for the family. He took a job in the naval lab making cartridges at Fort Henry and two years later was transferred to the Ordnance office at the fort. About this time (1839) Sangster wrote his first serious poem, a 700-line narrative in rhyming couplets called “The Rebel.” The poem “contains an extensive vocabulary and rich and imaginative historical and geographical allusions,... beyond what might be expected of a boy... who had so little formal education.... the content and form suggest considerable previous writing.” During the 12 years he worked at the Ordinance office Sangster began doing part-time work for a Kingston newspaper, the British Whig. He also continued writing poetry and submitting it, anonymously or pseudonymously, to the local papers. Writing career and success In 1849 Sangster quit his job at Fort Henry and moved to Amherstburg, Ontario, where he became editor of the Amherstburg Courier. When James Reeves, owner of the Courier, died the same year, Sangster returned to Kingston, to work as a proofreader and bookkeeper for the British Whig. Sangster first gained national attention as a poet in 1850, when his poetry began appearing in Canada’s Literary Garland magazine. Soon his work appeared in other magazines, such as Anglo-American Magazine. In 1853 Sangster took a steamship excursion down the St. Lawrence River and up the Saguenay River in Quebec, which he wrote about for the Whig in a series of travel letters called “Etchings by the Way”—material he would also use in his long poem, “The St. Lawrence and the Saguenay”. Sangster published his first book of poetry, The St Lawrence and the Saguenay, and Other Poems, in 1856. The book was widely praised by reviewers and readers. Susanna Moodie wrote to Sangster; "If a native of Canada, [one] may well be proud of her Bard, who has sung in such lofty strains the natural beauties of his native land." The National Magazine of London echoed the same sentiment: “Well may the Canadians be proud of such contributions to their infant literature.... In some sort, and according to his degree, Mr. Sangster may be regarded as the Wordsworth of Canada.” Charles Sangster "married 21-year-old Mary Kilborn of Kingston on Sept. 16, 1856, and the newlyweds moved into a brick house at 144 Barrie Street across from the grassy park. (An historical plaque directly across the street honours the Sangster home.)" Mary was to die of pneumonia just 16 months later. In 1859, Sangster wrote the poem “Brock”, commissioned for the inauguration of the monument to General Isaac Brock at Queenston Heights. Sangster’s second book of poetry, Hesperus and Other Poems and Lyrics, appeared in 1860, published in Kingston and Montreal. “A rousing success, Hesperus... received even more approval than his first book.” “Hesperus was well received, and many critics considered it superior to The St. Lawrence and the Saguenay, as did Sangster himself.” The same year, Sangster remarried, to Henrietta Charlotte Mary Meagher, who was only 17 years of age (to his 38). In 1864, Sangster became a reporter for the Kingston Daily News, and 16 of his poems appeared in the first-ever anthology of Canadian poetry, Selections from Canadian Poets. The same year, the Sangsters celebrated the birth of their first child, Charlotte Mary. Post office and retirement By 1867, Sangster “was in a poor financial situation and suffered increasingly from ill health, depression, and a nervous disorder that would cause him deep mental pain the rest of his life.” To help him out his neighbor, the new Postmaster-General Alexander Campbell arranged a job for Sangster with Canada’s new Post Office Department. Accordingly, in 1868, at 46, Sangster “accepted a position in the Post-Office Department at Ottawa, where his poetic energy and ambition succumbed, apparently, to the incessant drudgery and to the hampering cares of ill-paid employment.”, “With his appointment... Sangster’s life became characterized by overwork, ill health and scant literary output.” He remained with the Post Office until his retirement in 1886. Sangster was also kept busy by a growing family. Sadly, Charlotte died in 1868, shortly after the move to Ottawa. The same year, though, Mrs. Sangster gave birth to a second daughter, Florence. Two years later, in 1870, their third daughter, Gertrude was born, followed in 1879 by a son, Roderick. Sangster published 16 poems in magazines between 1868 and 1878, most of which he had written before moving to Ottawa. He wrote virtually nothing for the 18 years he worked at the Post Office. As he later wrote: "When I went down to Ottawa... I took a pile of M.S. of a third volume with me, as I thought 'ready for the press’, but in all the 18 years I remained there I did little more than correct.... When they get a man into the Civil Service, their first duty is to crush him flat, and if he is a fool of a Poet, or dares to think of any nonsense of that kind, draw him through a Knot or a gimlet hole a few times, pile with agony of toil, toil, toil until his nerves are flattened out, all the rebound knocked out of him, and then– superannuate him... and tell him he should be thankful.” Sangster had a nervous breakdown in 1875, and developed a chronic nervous system condition during the 1880s. To make matters worse, Henrietta died sometime between 1883 and 1886, leaving him to raise his new family alone. After another breakdown in March 1886, he took a six-month leave of absence, and also resigned from the Royal Society of Canada (which had elected him in 1882). Finally, that September he retired and moved back to Kingston. For the first years of retirement, Sangster did little but convalesce. In July 1888, he received a letter from W.D. Lighthall, inquiring about new poems for an upcoming anthology (most likely Lighthall’s 1889 Songs of the Great Dominion. Sangster replied the next day, and the two men struck up a friendship by mail. Revitalized, Sangster began revising his poetry. He doubled the size of “The Saint Lawrence and the Saguenay” to over 200 stanzas, and sent the manuscript to his cousin Amos Sangster to illustrate. When Amos died, the manuscript and the new poem was lost. However, 40 of the new stanzas survived thanks to being published in various magazines. Charles Sangster also cut many of the “other” poems in the first volume, and made over 2,000 changes to the ones he kept. Hesperus got off easier, but Sangster still made more than 200 revisions to the work. As well, Sangster prepared two more volumes for publication, mostly from poems he’d written before moving to Ottawa: Norland Echoes & Other Strains, and The Angel Guest & Other Poems. By the summer of 1871, all four manuscripts were complete, and Sangster sent them off to Lighthall (who had become his literary executor). However, before any of them could be published, Sangster died. None of them were published until the 1970s. Charles Sangster died in Kingston in 1893, and is buried in the city’s Cataraqui Cemetery. Writing The Canadian Encyclopedia says that “Sangster’s poetry distinguishes him as a lover and keen observer of the natural world. He displays overwhelming passion in some poems and equally extreme melancholy in others. Whatever his mood he is consistently and intensely serious and deeply religious.” Sangster’s inspiration was drawn from three themes he was passionate about: love, nature and religion. He wrote many poems about his experiences and was commended for his ability to express the beauty of Canada’s landscapes. Sangster was often called the “father of Canadian poetry” because of this. Many of the love poems from his first book were directed towards his first wife; the nature poems were of his travels. For a man with limited educational training, Charles Sangster had a vast vocabulary and an extraordinary knowledge of history, classics, mythology and authors. His poems include an extensive knowledge of classic, historic, and mythological works, as well as British and American authors, including Shakespeare, Milton, Burns, Wordsworth, P.J. Bailey, and Longfellow. Recognition Sangster was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada in 1892. Publications * The St. Lawrence and the Saguenay, and Other Poems. Kingston, ON: J. Creighton & J. Duff, 1856. New York: Miller, Orton & Mulligan, 1856. * Hesperus, and Other Poems and Lyrics. Kingston: J. Creighton, 1860. Montreal: J. Lovell, 1860. London, UK: Trubner, 1860. * Our Norland. Toronto: Copp Clark, [1890]. * The St Lawrence and the Saguenay and other poems; Hesperus and other poems and lyrics, intro. Gordon Johnston (Toronto: University of Toronto Press and Buffalo, N.Y., 1972. ISBN 0-8020-1935-8 * Norland echoes and other strains and lyrics,. Frank M. Tierney ed. Ottawa: Tecumseh, 1976. ISBN 0-919662-59-5 * The angel guest and other poems and lyrics. Frank M. Tierney ed. Ottawa: Tecumseh, 1977. ISBN 0-919662-63-3 * Hesperus and other poems and lyrics(rev. ed.). Frank M. Tierney ed. Ottawa: Tecumseh, 1979. ISBN 0-919662-72-2 * St. Lawrence and the Saguenay and other poems (rev. ed.). Frank M. Tierney ed. Ottawa: Tecumseh, 1984. ISBN 0-919662-95-1, ISBN 0-919662-96-X * Except where noted, bibliographic information courtesy Dictionary of Canadian Biography. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Sangster


William Harris Lloyd Roberts (31 October 1884– 28 June 1966) was a Canadian writer, poet, and playwright. He was born in Fredericton, New Brunswick, the son of noted Canadian poet Charles George Douglas Roberts and Mary Isabel Fenety. After an education by private tutors, he attended King’s Collegiate School then, in 1905, Fredericton High School. In 1903 he performed clerical work at McClure’s magazine. From 1904 until 1907 he was an assistant editor at the Outing magazine, based in New York City. He wrote short stories and poetry for various magazines, plus performing part-time newspaper work starting in 1911. On January 1, 1914, he was married to Helen Hope Farquhar Bolmain. The couple had a daughter, Patricia Bliss, before Helen died. In 1912, he became editor of immigration literature for the Canadian Department of Interior in Ottawa. Two years later, he served as a correspondent for the Timer and Grazing branch of the Interior Department in Ottawa. On August 15, 1914, he married his second wife, Lila White; the couple divorced shortly thereafter. After 1920 he retired from work in order to devote all of his time to writing fiction, drama, poetry, and special articles. From 1925 until 1939 he was a correspondent for the Christian Science Monitor, then he performed public relations for the Royal Canadian Mounted Police up to 1945. His third marriage in 1943 was to Julia Bristow, and they would have two daughters. Bibliography * England Over Seas (1914) * Come Quietly, Britain (1915) * Mother Doneby (1916) * The Book of Roberts (1923) * Along the Ottawa (1927) * I Sing of Life (1937) References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Harris_Lloyd_Roberts


Susan Frances Harrison née Riley (February 24, 1859– May 5, 1935) (a.k.a. Seranus) was a Canadian poet, novelist, music critic and music composer who lived and worked in Ottawa and Toronto. Life Susie Frances Riley was born in Toronto of Irish-Canadian ancestry, the daughter of John Byron Riley. She studied music with Frederic Boscovitz, at a private school for girls in Toronto, and later in Montreal. She reportedly began publishing poetry, in the Canadian Illustrated News, at 16 under the pseudonym “Medusa.” After completing her education, she worked as a pianist and singer. In 1880 she married organist John W. F. Harrison, of Bristol, England, who was the organist of St. George’s Church in Montreal. The couple had a son and a daughter. The Harrisons lived in Ottawa in 1883, when Susie Harrison composed the song “Address of Welcome to Lord Lansdowne” to celebrate the first public appearance of the new Governor General, the Marquess of Lansdowne. In 1887 the Harrisons moved to Toronto, where John Harrison became organist and choirmaster of St. Simon the Apostle, and Susan Harrison began a literary career under the pseudonym “Seranus” (a misreading of her signature, “S. Frances”), soon publishing articles in “many of the leading journals and periodicals.” She wrote a number of songs published in the United States and England under the name Seranus, and published other songs in England under the name, Gilbert King. She was the music critic of The Week from December 1886 to June 1887 under her pen-name of Seranus. She wrote the “Historical sketch on Canadian music” for the 1898 Canada: An Encyclopedia of the Country. Susan Harrison was considered an authority on folk music, and often lectured on the subject. She used traditional Irish melodies in her String Quartet on Ancient Irish Airs, and French-Canadian music in her 1887 Trois Esquisses canadiennes (Three Canadian Sketches), ‘Dialogue,’ ‘Nocturne,’ and 'Chant du voyageur’. She also incorporated French-Canadian melodies in her three-act opera, Pipandor (with libretto by F.A. Dixon of Ottawa). Her String Quartet on Ancient Irish Airs, is likely the first string quartet composed in Canada by a woman. In 1896 and 1897 she presented a series of well-received lectures in Toronto on "The Music of French Canada. For 20 years Harrison was the principal of the Rosedale branch of the Toronto Conservatory of Music. During the 1900s she contributed to and edited the Conservatory’s publication Conservatory Monthly, and contributed to its successor Conservatory Quarterly Review. She wrote the article on “Canada” for the 1909 Imperial History and Encyclopedia of Music. In addition, she wrote at least six books of poetry, and three novels. Writing Poetry Harrison’s musical training is reflected in her poetry: “she was adept in her handling of the rhythmic complexities of poetic forms such as the sonnet and the villanelle. Like other Canadian poets of the late nineteenth century, her prevailing themes include nature, love, and patriotism. Her landscape poetry, richly influenced by the works of Charles G.D. Roberts and Archibald Lampman, paints the Canadian wilderness as beguilingly beautiful yet at the same time mysterious and distant.” Harrison was a master of the villanelle. The villanelle was a French verse form that had been introduced to English readers by Edmund Gosse in his 1877 essay, “A Plea for Certain Exotic Forms of Verse”. Novels Her two novels “articulate a fascination with a heavily mythologized Quebec culture that Harrison shared with many English-speaking Canadians of her time... characterized by a gothic emphasis on horror, madness, aristocratic seigneurial manor houses, and a decadent Catholicism.” “Harrison writes elegiacally of a regime whose romantic qualities are largely the creation of an Upper Canadian quest for a distinctive historical identity.” Recognition Harrison experienced a decline in reputation in her lifetime. In 1916 anthologist John Garvin called her “one of our greater poets whose work has not yet had the recognition in Canada it merits.”. "By 1926, Garvin describes her merely as 'one of our distinctive poets’.” The Dictionary of Literary Biography wrote of Susan Frances Harrison, in 1990, that “Harrison’s unpublished work has not been preserved, her published work is out of print and difficult to obtain, and her once-substantial position in the literary life of her country is now all but forgotten.” Publications Selected songs * Song of Welcome. * Pipandor. opera * ‘Trois Esquisses canadiennes: ’Dialogue,' ‘Nocturne,’ 'Chant du voyageur’. 1887. * Quartet on Ancient Irish Airs. Poetry * Four Ballads and a Play. Toronto: Author, 1890. * Pine, Rose and Fleur De Lis. Toronto: Hart, 1891. * In Northern Skies and Other Poems. Toronto: Author, 1912. * Songs of Love and Labor. Toronto: Author, 1925. * Later Poems and New Villanelles. Toronto: Ryerson, 1928. * Penelope and Other Poems. Toronto: Author, 1934. * Bibliographical information on poems from Wanda Campbell, Hidden Rooms. Prose * Crowded Out and Other Sketches. Ottawa: Evening Journal, 1886. * The Forest of Bourg-Marie, novel. Toronto: G.N. Morang, 1898. * Ringfield, novel. London: Hodder & Stoughton, 1914. Edited * Canadian Birthday Book. Toronto: Robinson, 1887. Poetry anthology. Articles * “Historical sketch of music in Canada,” Canada: An Encyclopedia of the Country, vol 4, J.C. Hopkins ed., Toronto, 1898. * “Canada,” The Imperial History and Encyclopedia of Music, vol 3: History of Foreign Music, W.L. Hubbard ed., New York ca 1909. Discography * Harrison’s piano music has been recorded and issued on media, including: * Keillor, Elaine. By a Canadian Lady Piano Music 1841-1997 Carleton Sound * Keillor, Elaine. Piano Music by Torontonians (1984) References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Susie_Frances_Harrison


Charles Mair (September 21, 1838– July 7, 1927) was a Canadian poet and journalist. He was a fervent Canadian nationalist noted for his participation in the Canada First movement and his opposition to Louis Riel during the two Riel Rebellions in western Canada. Life Mair was born at Lanark, Upper Canada, to Margaret Holmes and James Mair. He attended Queen’s University but did not graduate. On leaving college, he became a journalist. In Ottawa in 1868, Mair was introduced by civil servant and writer Henry Morgan to young lawyers George Denison, William Foster, and Robert Haliburton. “Together they organized the overtly nationalistic Canada First movement, which began as a small social group.” Mair “represented the Montreal Gazette during the first Riel Rebellion, and was imprisoned and narrowly escaped being shot by the rebels.” Mair was a Freemason Mair "was an Officer of the Governor-General’s Body Guard during the second Riel rebellion in 1885, and was later employed in the Canadian civil service in the West." He died in Victoria, British Columbia. Writing Mair published the first book of poetry in post-Confederation Canada, 1868's Dreamland and Other Poems. “Negligible as verse,” says The Canadian Encyclopedia, "the volume gained interest when Mair escaped after being captured by Louis Riel during the Red River disturbances of 1869-70.” The Dictionary of Canadian Biography (DCB) states that Dreamland “demonstrates a conventional colonial approach to poetry. Such poems as 'August’ succeed in their attention to natural detail: descriptions of the blueflies, the milkmaids, and the 'ribby-lean’ cattle in parched fields anticipate the mature nature poetry of Archibald Lampman. But too often he wrote not of the timberlands he knew but of a dreamland weakly modelled upon the romantic flights of Keats.” However, the book was praised by “the established poet Charles Sangster, who referred to Canada’s sophisticated literary tradition as one that was habitually overlooked in the popular press.” Writing later in the Ottawa Journal, William Wilfred Campbell saw Dreamland as a precursor to the nature poetry later popularized in Canada by the Confederation Poets: “The thirty-three poems constitute the first attempt to deal with Canadian nature, in the manner of Keats and the other classic poets, and many of them in theme and treatment are similar to the verse of Lampman and Roberts.... And there are strong evidences in Mair’s work that he influenced these poets to a great extent.” Mair published Tecumseh, a historical drama mainly in blank verse dealing with the War of 1812, in 1886. Canadian critic Alan Filewood wrote of the political and philosophical ideas expressed by Mair in the poem: Mair’s projection of Canadian nationhood is embodied in the character of Lefroy, a Byronesque poet who flees civilization to seek solace in nature’s genius. He learns– tragically– from the British General Brock that natural law finds its outward form in the monarchic principle, and from the Indian chieftain Tecumseh that nature must be defended against the perversion of American materialism. The dying Tecumseh legitimizes the proto-(Anglo) Canadians as the natural guardians of the land, and Canadian manhood finds mature expression in a race of armed poets.(...) Mair looked to the day when the dominions would assume the responsibilities of adulthood: Then shall a whole family of young giants stand 'Erect, unbound, at Britain’s side-' her imperial offspring oversea, the upholders in the far future of her glorious tradition, or, should exhaustion ever come, the props and supports of her declining years. The DCB calls Tecumseh "a major contribution to our 19th-century literary heritage, wherein the War of 1812 is the central event of Canadian history. Among the many literary treatments of this war, including works by Sangster, John Richardson, and Sarah Anne Curzon... Tecumseh stands as the most accomplished." The Canadian Encyclopedia says that the poem’s “blank verse is pedestrian and untheatrical”, but it also tells us that “Tecumseh was important in the development of Canadian drama. It presents a vision of Canada as a co-operative enterprise in contrast with the self-seeking individualism of the United States.” Recognition Mair was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada in 1889. In 1937 he was designated a Person of National Historic Significance. Canadian folksinger Gordon Lightfoot adapted a line from Tecumseh, “There was a time on this fair continent,” for the first line in his 1967 historical ballad, “The Canadian Railroad Trilogy” ("There was a time in this fair land when the railroad did not run"). Publications * Dreamland and Other Poems. London: S. Low, 1868. Montreal: Dawson, 1868, * Tecumseh. Toronto: Hunter, Rose & Co., 1886. London: Chapman & Hall, 1886. * Through the Mackenzie Basin: A Narrative of the Athabasca and Peace River Treaty Expedition of 1899 . London: Simpkin, Marshall, Hamilton, Kent & Co., 1903. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Mair


Florence Randall Livesay, daughter of Stephen and Mary Louisa Randal, was born at Compton, P. Q., and educated at Compton Ladies' College, now King's Hall. She taught for one year in a private school in New York, and subsequently for seven years was a member of the staff of the Evening Journal, Ottawa,–editor of the Woman's Page. In 1902, the Hon. Joseph Chamberlain requested Canada to send some teachers to the Boer Concentration Camps and Miss Randal, offering her services, was one of the forty chosen. She remained for one year and then returned to Canada, locating at Winnipeg. She joined the staff of the Winnipeg Telegram, and three years later that of the Manitoba Free Press. For several years she edited the Children's Department of the latter, but now writes as a 'free lance.' In 1908, she married Mr. J. Fred. B. Livesay of Winnipeg, Manager and Secretary of the Western Associated Press, Limited, and is now the mother of two girls. Of recent years, Mrs. Livesay has contributed poems, short stories and articles to Canadian and American magazines and journals, and a volume of her verse, entitled Songs of Ukraina is now being published by J. M. Dent & Sons. Mrs. Livesay's folk songs translated from the Ruthenian are unusual and notable, but her poetical gift is quite as discernible in her other poems. She has the imagination and the practiced touch of the artist., daughter of Stephen and Mary Louisa Randal, was born at Compton, P. Q., and educated at Compton Ladies' College, now King's Hall. She taught for one year in a private school in New York, and subsequently for seven years was a member of the staff of the Evening Journal, Ottawa,–editor of the Woman's Page. In 1902, the Hon. Joseph Chamberlain requested Canada to send some teachers to the Boer Concentration Camps and Miss Randal, offering her services, was one of the forty chosen. She remained for one year and then returned to Canada, locating at Winnipeg. She joined the staff of the Winnipeg Telegram, and three years later that of the Manitoba Free Press. For several years she edited the Children's Department of the latter, but now writes as a 'free lance.' In 1908, she married Mr. J. Fred. B. Livesay of Winnipeg, Manager and Secretary of the Western Associated Press, Limited, and is now the mother of two girls. Of recent years, Mrs. Livesay has contributed poems, short stories and articles to Canadian and American magazines and journals, and a volume of her verse, entitled Songs of Ukraina is now being published by J. M. Dent & Sons. Mrs. Livesay's folk songs translated from the Ruthenian are unusual and notable, but her poetical gift is quite as discernible in her other poems. She has the imagination and the practiced touch of the artist.


Edward William Thomson was born in Toronto township, county of Peel, Ontario, February 12th, 1849. His father was William Thomson, grandson of Archibald Thomson, the first settler in Scarboro. His grandfather Edward William Thomson, was present at the taking of Detroit, and served with distinction under Brock at Queenston Heights; and was afterwards well known in Upper Canada as Col. E. W. Thomson of the Legislative Council, and as the one successful opponent of William Lyon Mackenzie in an election for the Legislature. The mother of the present E. W. Thomson was Margaret Hamilton Foley, sister of the Hon. M. H. Foley, twice Postmaster-General of the united Canadas. The future poet was educated at the Brantford Grammar School, and at the Trinity College Grammar School at Weston; but when about fourteen years of age, he was sent to an uncle and aunt in Philadelphia and given a position in a wholesale mercantile house as 'office junior.' Finding this employment very uncongenial, he enlisted in the Union army, in October, 1864, as a trooper in the 3rd Pennsylvania Cavalry. This corps was engaged twice at Hatcher's Run, and was with Grant when he took Petersburgh. Discharged in August, 1865, he returned to the parental home at Chippewa, Ontario. In June, 1866, when the Fenians raided Upper Canada, young Thomson promptly enlisted in the Queen's Own, and was in action at the Ridgeway fight. The following year he entered the profession of Civil Engineering, and in 1872 was registered a Provincial Land Surveyor. He practised his profession until December, 1878, when at the invitation of the Hon. George Brown, he joined the staff of The Globe, Toronto, as an editorial writer. Four years later the Manitoba boom attracted him, and he practised surveying for two or three years in Winnipeg. In 1885, he rejoined The Globe staff, but retired again in 1891, because of his opposition to the Liberal policy of Unrestricted Reciprocity. Shortly afterwards he was invited to join the staff of the Youth's Companion. He accepted and remained for eleven years. Since 1903, he has lived in Ottawa, employed as a newspaper correspondent and engaged in literary work.The Many-Mansioned House and Other Poems was issued in 1909. His poems, like his short stories, are lucid, vital, original. References http://digital.library.upenn.edu/women/garvin/poets/thomson.html


Agnes Ethelwyn Wetherald was born of English-Quaker parents at Rockwood, Ontario, April 26th, 1857. Her father was the late Rev. William Wetherald, who founded the Rockwood Academy about the middle of the last century, and was its principal for some years. He was a lover of good English, spoken and written, and his talented daughter has owed much to his careful teaching. He was the teacher whom the late James J. Hill, the railway magnate, had held in such grateful remembrance. Additional education was received by Miss Wetherald at the Friends' Boarding School, Union Springs, N.Y., and at Pickering College. Miss Wetherald began the writing of poetry later in life than most poets and her first book of verse, The House of the Trees and Other Poems, did not appear until 1895. This book at once gave her high rank among women poets. Prior to this, she had collaborated with G. Mercer Adam on writing and publishing a novel, An Algonquin Maiden, and had conducted the Woman's Department in The Globe, Toronto, under the nom de plume, 'Bel Thistlewaite.' In 1902, appeared her second volume of verse, Tangled in Stars, and, in 1904, her third volume, The Radiant Road. In the autumn of 1907, a collection of Miss Wetherald's best poems was issued, entitled, The Last Robin: Lyrics and Sonnets. It was warmly welcomed generally, by reviewers and lovers of poetry. The many exquisite gems therein so appealed to Earl Grey, the then Governor-General of Canada, that he wrote a personal letter of appreciation to the author, and purchased twenty-five copies of the first edition for distribution among his friends. For years Miss Wetherald has resided on the homestead farm, near the village of Fenwick, in Pelham Township, Weland county, Ontario, and there in the midst of a large orchard and other rural charms, has dreamed, and visioned, and sung, pouring out her soul in rare, sweet songs, with the naturalness of a bird. And like a bird she has a nest in a large willow tree, cunningly contrived by a nature-loving brother, where her muse broods contentedly, intertwining her spirit with every aspect of the beautiful environment.


In a very real sense Miss Laura Elizabeth McCully is a Toronto writer, as, with the exception of one academic year in the United States and a few months in Ottawa, she has lived all her life in this city. She is a grand niece of the late Hon. John McCully, of Truro, Nova Scotia, one of the Fathers of Confederation; and is the daughter of Samuel Edward McCully, M.D., and Helen (Fitzgibbon) McCully. Her father is of Manx descent, and her mother is a descendant of the late James McBride of Halton county, Ontario, magistrate, who was one of the pioneers of this province, and who heroically cleared off forest and left to his heirs, one thousand acres of valuable farm lands. Miss McCully's poetry is enriched by classical illustrations, and expressed in forceful and melodious language. Her imagination relates us to the universe and to humanity. Wordsworth found new lessons in the fields and woods, and taught them; Lanier made trees, flowers and clouds our intimate friends; when we read Miss McCully's nature poems we are not conscious of the moralizing of the poet, we are in the glens ourselves looking at the afterglow, with the purity, the glory, the growth spirit and the transforming beauty of nature flowing into our lives. In a few flaming lines her stories reveal the love, the despair, and the ultimately triumphant faith of humanity. With tender pathos she unveils the evils of social and industrial conditions, and in clear tones arouses each soul, and makes it conscious of the splendour of the better conditions ahead, and thrills it with the determination to achieve for justice, freedom, and truth. – JAMES L. HUGHES, LL. D.


